U.S. (United States)
Contents
United States
Countries and Regions of the World Collection  The United States of America (also USA, the United States, the U.S. and sometime simply America) is a nation of 313 million people in North America, bordering both the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Pacific Ocean, between Canada and Mexico.
The United States of America (also USA, the United States, the U.S. and sometime simply America) is a nation of 313 million people in North America, bordering both the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Pacific Ocean, between Canada and Mexico.
By area, the United States is the third largest country in the world (after Russia and Canada); about half the size of Russia; about three-tenths the size of Africa; about half the size of South America (or slightly larger than Brazil); slightly larger than China; more than twice the size of the European Union.
The United States is also the third nmost populous country in the world (after China and India)
Its major environmental issues include:
- Air pollution resulting in acid rain in both the USA and Canada;
- Until 2007, the US was the largest single emitter of carbon dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels; since then China has been the largest emitter;
- Water pollution from runoff of herbicides, pesticides and fertilizers;
- Limited natural freshwater resources in much of the western part of the country require careful management; and,
- Desertification
Britain's American colonies broke with the mother country in 1776 and were recognized as the new nation of the United States of America following the Treaty of Paris in 1783.
During the 19th and 20th centuries, 37 new states were added to the original 13 as the nation expanded across the North American continent and acquired a number of overseas possessions.
The two most traumatic experiences in the nation's history were the Civil War (1861-65), in which a northern Union of states defeated a secessionist Confederacy of 11 southern slave states, and the Great Depression of the 1930s, an economic downturn during which about a quarter of the labor force lost its jobs.
Buoyed by victories in World Wars I and II and the end of the Cold War in 1991, the US remains the world's most powerful nation state.
Since the end of World War II, the economy has achieved relatively steady growth, low unemployment and inflation, and rapid advances in technology.
Geography
Location: North America, bordering both the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Pacific Ocean, between Canada and Mexico
Geographic Coordinates: 38 00 N, 97 00 W
Area: 9,826,675 sq km (land: 9,161,966 sq km; water: 664,709 sq km) Note: includes only the 50 states and District of Columbia
Land Boundaries: 12,034 km (Canada 8,893 km which includes 2,477 km with Alaska, Mexico 3,141 km) Note: US Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay, Cuba is leased by the US and is part of Cuba; the base boundary is 28 km. Much of the boundary between the United States and Mexico is defined by the Rio Grande River
Coastline: 19,924 km
Maritime Claims:
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: not specified
Natural Hazards: tsunamis; volcanoes; earthquake activity around Pacific Basin; hurricanes along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coasts; tornadoes in the Midwest and Southeast; mud slides in California; forest fires in the west; flooding; permafrost in northern Alaska, a major impediment to development
See: Earthquakes in the United States - Risk, Detection, Warning, and Research
Volcanism: the United States experiences volcanic activity in the Hawaiian Islands, Western Alaska, the Pacific Northwest, and in the Northern Mariana Islands; both Mauna Loa (elev. 4,170 m) in Hawaii and Mount Rainier (elev. 4,392 m) in Washington have been deemed "Decade Volcanoes" by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to their explosive history and close proximity to human populations.
Pavlof (elev. 2,519 m) is the most active volcano in Alaska's Aleutian Arc and poses a significant threat to air travel since the area constitutes a major flight path between North America and East Asia.
St. Helens (elev. 2,549 m, famous for the devastating 1980 eruption, remains active today.
Numerous other historically active volcanoes exist, mostly concentrated in the Aleutian arc and Hawaii. They include: in Alaska: Aniakchak, Augustine, Chiginagak, Fourpeaked, Iliamna, Katmai, Kupreanof, Martin, Novarupta, Redoubt, Spurr, Wrangell; in Hawaii: Trident, Ugashik-Peulik, Ukinrek Maars, Veniaminof; in the Northern Mariana Islands: Anatahan; and in the Pacific Northwest: Mount Baker, and Mount Hood. See: Hawaii Volcanoes National Park
Terrain: vast central plain, mountains in west, hills and low mountains in east; rugged mountains and broad river valleys in Alaska; rugged, volcanic topography in Hawaii. The highest point is Mount McKinley (6,194 m) and the lowest point Death Valley (-86 m).Note: the peak of Mauna Kea (4,207 m above sea level) on the island of Hawaii rises about 10,200 m above the Pacific Ocean floor; by this measurement, it is the world's tallest mountain - higher than Mount Everest, which is recognized as the tallest mountain above sea level.
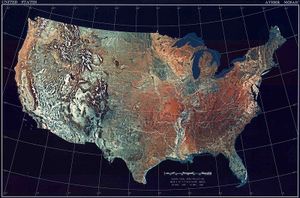
Climate: mostly temperate, but tropical in Hawaii and Florida, arctic in Alaska, semiarid in the great plains west of the Mississippi River, and arid in the Great Basin of the southwest; low winter temperatures in the northwest are ameliorated occasionally in January and February by warm chinook winds from the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains.
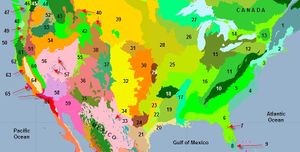
Ecology and Biodiversity
|
|
|
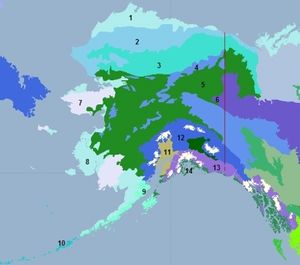
In Alaska:
|
|
|
In Hawaii: See also:
|
See National Parks:
- Olympic National Park
- Great Smoky Mountains National Park
- Yosemite National Park
- Grand Canyon National Park
- Carlsbad Caverns National Park
- Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve
- Big Bend National Park
- Everglades National Park
- Hawaii Volcanoes National Park
- Redwood National Park
- Yellowstone National Park
- Arctic National Wildlife Refuge
People and Society
Population: 313,847,465 (July 2012 est.)

Ethnic Groups: white 79.96%, black 12.85%, Asian 4.43%, Amerindian and Alaska native 0.97%, native Hawaiian and other Pacific islander 0.18%, two or more races 1.61% (July 2007 estimate)
Note: a separate listing for Hispanic is not included because the US Census Bureau considers Hispanic to mean persons of Spanish/Hispanic/Latino origin including those of Mexican, Cuban, Puerto Rican, Dominican Republic, Spanish, and Central or South American origin living in the US who may be of any race or ethnic group (white, black, Asian, etc.); about 15.1% of the total US population is Hispanic.
Age Structure:
0-14 years: 20.1% (male 32,107,900/female 30,781,823)
15-64 years: 66.8% (male 104,411,352/female 104,808,064)
65 years and over: 13.1% (male 17,745,363/female 23,377,542) (2011 est.)
Population Growth Rate: 0.899% (2012 est.)
Birthrate: 13.68 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
Death Rate: 8.39 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
Net Migration Rate: 3.62 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
Life Expectancy at Birth: 78.49 years
male: 76.05 years
female: 81.05 years (2012 est.)
Total Fertility Rate: 2.06 children born/woman (2012 est.)
Languages: English 82.1%, Spanish 10.7%, other Indo-European 3.8%, Asian and Pacific island 2.7%, other 0.7% (2000 census). Note: Hawaiian is an official language in the state of Hawaii.
Literacy (age 15 and over can read and write): 99% (2003 est.)
Urbanization: 82% of total population (2010) growing at an annual rate of change of 1.2% (2010-15 est.)
Government
Government Type: Constitution-based federal republic; strong democratic tradition
Capital: Washington - 4.421 million (2009)
Other Major Cities: New York-Newark 19.3 million; Los Angeles-Long Beach-Santa Ana 12.675 million; Chicago 9.134 million; Miami 5.699 million (2009)

Administrative divisions: 50 states and 1 district*; Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, District of Columbia*, Florida, Georgia, Hawaii, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Carolina, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Vermont, Virginia, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin, Wyoming.
Dependent Areas: American Samoa, Baker Island, Guam, Howland Island, Jarvis Island, Johnston Atoll, Kingman Reef, Midway Islands, Navassa Island, Northern Marianna Islands, Palmyra Atoll, Puerto Rico, United States Virgin Islands, Wake Island
Independence Date: 4 July 1776 (declared); 3 September 1783 (recognized by Great Britain)
Legal System: common law system based on English common law at the federal level; state legal systems based on common law except Louisiana, which is based on Napoleonic civil code; judicial review of legislative acts. The United States withdrew acceptance of compulsory International Court of Justics (ICJ) jurisdiction in 2005;and withdrew acceptance of International Criminal Court (ICCt) jurisdiction in 2002.
International Environmental Agreements
The United States is party to international agreements on: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, and Whaling.
It has signed, but not ratified international agreements on: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Biodiversity, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, and Hazardous Wastes.
See: Kyoto Protocol and the United States
Water
Total Renewable Water Resources: 3069 cubic kilometers (1985)
Major Rivers: Mississippi River, Columbia River, Yukon River, Colorado River, Arkansas River, Snake River.
Freshwater Withdrawal: 477 cu km/yr (13% domestic, 46% industrial, 41% agricultural)
Per Capita Freshwater Withdrawal: 1,600 cu m/yr (2000)
Agriculture
Agricultural products: wheat, corn, other grains, fruits, vegetables, cotton; beef, pork, poultry, dairy products; fish; forest products
Irrigated Land: 230,000 sq km (2008)
Resources
Natural Resources: coal, copper, lead, molybdenum, phosphates, rare earth elements, uranium, bauxite, gold, iron, mercury, nickel, potash, silver, tungsten, zinc, petroleum, natural gas, timber. Note: the US has the world's largest coal reserves with 491 billion short tons accounting for 27% of the world's total.
Land Use:
arable land: 18.01%
permanent crops: 0.21%
other: 81.78% (2005)
Economy
The US has the largest and most technologically powerful economy in the world, with a per capita GDP of $48,100.
In this market-oriented economy, private individuals and business firms make most of the decisions, and the federal and state governments buy needed goods and services predominantly in the private marketplace. USA business firms enjoy greater flexibility than their counterparts in Western Europe and Japan in decisions to expand capital plant, to lay off surplus workers, and to develop new products. At the same time, they face higher barriers to enter their rivals' home markets than foreign firms face entering USA markets.
USA firms are at or near the forefront in technological advances, especially in computers and in medical, aerospace, and military equipment; their advantage has narrowed since the end of World War II.
The onrush of technology largely explains the gradual development of a "two-tier labor market" in which those at the bottom lack the education and the professional/technical skills of those at the top and, more and more, fail to get comparable pay raises, health insurance coverage, and other benefits.
Since 1975, practically all the gains in household income have gone to the top 20% of households.
Since 1996, dividends and capital gains have grown faster than wages or any other category of after-tax income.
Imported oil accounts for nearly 55% of US consumption. Oil prices doubled between 2001 and 2006, the year home prices peaked; higher gasoline prices ate into consumers' budgets and many individuals fell behind in their mortgage payments. Oil prices increased another 50% between 2006 and 2008. In 2008, soaring oil prices threatened inflation and caused a deterioration in the US merchandise trade deficit, which peaked at $840 billion.
In 2009, with the global recession deepening, oil prices dropped 40% and the US trade deficit shrank, as US domestic demand declined, but in 2011 the trade deficit ramped back up to $803 billion, as oil prices climbed once more. The global economic downturn, the sub-prime mortgage crisis, investment bank failures, falling home prices, and tight credit pushed the United States into a recession by mid-2008. GDP contracted until the third quarter of 2009, making this the deepest and longest downturn since the Great Depression.
To help stabilize financial markets, in October 2008 the US Congress established a $700 billion Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP). The government used some of these funds to purchase equity in US banks and industrial corporations, much of which had been returned to the government by early 2011. In January 2009 the US Congress passed and President Barack Obama signed a bill providing an additional $787 billion fiscal stimulus to be used over 10 years - two-thirds on additional spending and one-third on tax cuts - to create jobs and to help the economy recover.
In 2010 and 2011, the federal budget deficit reached nearly 9% of GDP; total government revenues from taxes and other sources are lower, as a percentage of GDP, than that of most other developed countries.
The wars in Iraq and Afghanistan required major shifts in national resources from civilian to military purposes and contributed to the growth of the US budget deficit and public debt - through 2011, the direct costs of the wars totaled nearly $900 billion, according to US government figures.
In March 2010, President Obama signed a health insurance reform bill into law that will extend coverage to an additional 32 million American citizens by 2016, through private health insurance for the general population and Medicaid for the impoverished.
In July 2010, the president signed the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, a bill designed to promote financial stability by protecting consumers from financial abuses, ending taxpayer bailouts of financial firms, dealing with troubled banks that are "too big to fail," and improving accountability and transparency in the financial system - in particular, by requiring certain financial derivatives to be traded in markets that are subject to government regulation and oversight.
Long-term problems include inadequate investment in deteriorating infrastructure, rapidly rising medical and pension costs of an aging population, sizable current account and budget deficits - including significant budget shortages for state governments - energy shortages, and stagnation of wages in lower-income families.
GDP: (Purchasing Power Parity): $15.04 trillion (2011 est.)
Note: In 2011, the combined GDP of the twenty-seven Nations that form the European Union was slightly higher at $15.39 trillion
GDP: (Official Exchange Rate): $15.06 trillion (2011 est.)
GDP- per capita (PPP): $48,100 (2011 est.)
Note that this is the 11th largest GDP per capita behind Liechtenstein, Qatar, Luxembourg, Bermuda (UK), Singapore, Jersey (UK), Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas), Norway, Brunei, and United Arab Emirates.
GDP- composition by sector:
agriculture: 1.2%
industry: 22.1%
services: 76.7% (2011 est.)
Industries: highly diversified, world leading, high-technology innovator, second largest industrial output in world; petroleum, steel, motor vehicles, aerospace, telecommunications, chemicals, electronics, food processing, consumer goods, lumber, mining
Currency: US dollar
International Disputes:
- the US has intensified domestic security measures and is collaborating closely with its neighbors, Canada and Mexico, to monitor and control legal and illegal personnel, transport, and commodities across the international borders;
- abundant rainfall in recent years along much of the Mexico-US border region has ameliorated periodically strained water-sharing arrangements;
- 1990 Maritime Boundary Agreement in the Bering Sea still awaits Russian Duma ratification;
- Canada and the USA dispute how to divide the Beaufort Sea and the status of the Northwest Passage but continue to work cooperatively to survey the Arctic continental shelf;
- The Bahamas and USA have not been able to agree on a maritime boundary;
- US Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay is leased from Cuba and only mutual agreement or US abandonment of the area can terminate the lease;
- Haiti claims US-administered Navassa Island;
- USA has made no territorial claim in Antarctica (but has reserved the right to do so) and does not recognize the claims of any other states;
- Marshall Islands claims Wake Island;
- Tokelau included American Samoa's Swains Island among the islands listed in its 2006 draft constitution