Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas)
| Topics: |
Countries and Regions of the World Collection  The Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas) is an island group with two main islands (East and West Falkland) in the South Atlantic Ocean, east of southern Argentina. The islands are a territory of the United Kingdom, but claimed by Argentina. The islands have a population of just over 3,100 people, most of whom live in the capital, Stanley.
The Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas) is an island group with two main islands (East and West Falkland) in the South Atlantic Ocean, east of southern Argentina. The islands are a territory of the United Kingdom, but claimed by Argentina. The islands have a population of just over 3,100 people, most of whom live in the capital, Stanley.
The green land offers rich pastureland, and domestic sheep graze much of the land of the two main islands. The population of sheep here has been estimated at over a half-million animals. The ocean offers a bounty as well, as the Malvinas (Falkland) Current sweeps north of the Islands and along the east coast of South America. As a branch of the Circumpolar Current, the waters are cold and nutrient-rich. Along with wool and sheep, a rich fishery provides economic income to the population.
Surround by the consistently cool waters of the Atlantic Ocean, the climate of the Falklands is very much influenced by the ocean, giving it a narrow annual temperature range. The average maximum temperature in January is 13°C (55°F) and in July it is 4°C (39°F). The annual rainfall is about 22 inches, but snow, which is rare, can occur at almost any time of the year. Winds tend to be constant and heavy gales often blow across the lands.
Its major environmental issues include overfishing by unlicensed vessels is a problem. Reindeer were introduced to the islands in 2001 for commercial reasons; this is the only commercial reindeer herd in the world unaffected by the 1986 Chornobyl disaster.
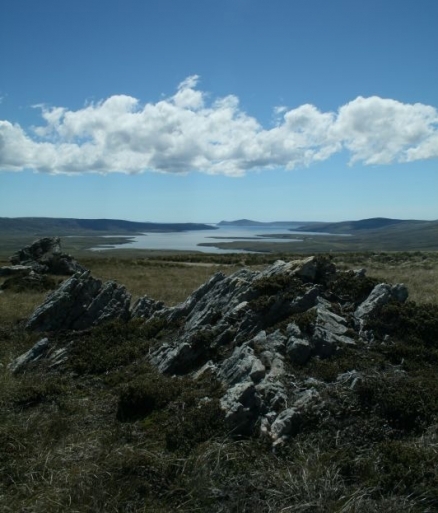
Deeply indented coast provides good natural harbors. The climate supports only a short growing season. Strong winds persist throughout the year over the islands.
Although first sighted by an English navigator in 1592, the first landing (English) did not occur until almost a century later in 1690, and the first settlement (French) was not established until 1764. The colony was turned over to Spain two years later and the islands have since been the subject of a territorial dispute, first between Britain and Spain, then between Britain and Argentina.
The UK asserted its claim to the islands by establishing a naval garrison there in 1833. Argentina invaded the islands on 2 April 1982. The British responded with an expeditionary force that landed seven weeks later and after fierce fighting forced an Argentine surrender on 14 June 1982.
Argentina, which claims the islands in its constitution, agreed in 1995 to no longer seek settlement by force; the UK continues to reject Argentine requests for sovereignty talks.
Contents
Geography
Location: Southern South America, islands in the South Atlantic Ocean, east of southern Argentina
Geographic Coordinates: 51 45 S, 59 00 W
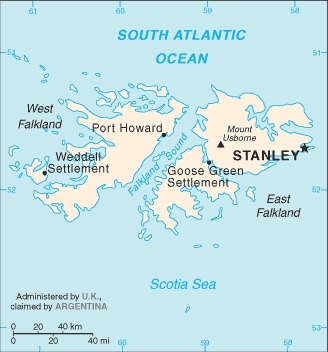
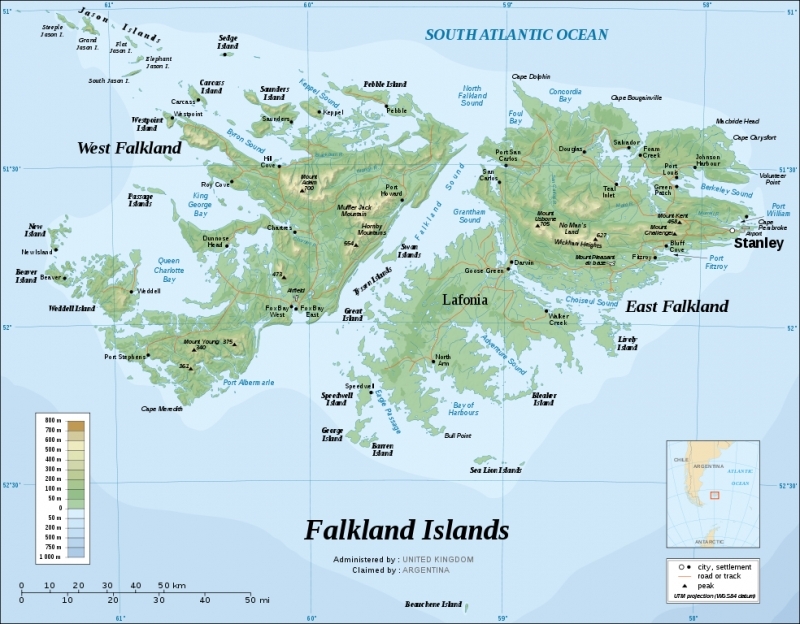
Area: 12,173 sq km (4,700 square miles) Note: includes the two main islands of East and West Falkland and about 200 small islands. Most of the land is found on the two main islands, West Falkland and East Falkland.
Coastline: 1,288 km (800 miles)
Maritime Claims:
territorial sea: 12 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm
exclusive fishing zone: 200 nm
Natural Hazards: strong winds persist throughout the year
Terrain: rocky, hilly, mountainous with some boggy, undulating plains. The highest point is Mount Usborne (705 m)
Climate: cold marine; strong westerly winds, cloudy, humid; rain occurs on more than half of days in year; average annual rainfall is 24 inches in Stanley; occasional snow all year, except in January and February, but typically does not accumulate
Topography of the Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas). Sourse; Wikipedia.
Ecology and Biodiversity
The islands are included within the Patagonian steppe ecoregion. This ecoregion extends roughly from the mid-Andean Precordillera southward, ending just north of the Straights of Magellan near the Rio Gallegos. This steppe is bordered on the west by the cold temperate forest slopes of the Andes, and on the east by the Pacific Ocean. It extends north-west as shrubland steppe and to the north as thorn thicket, gradually making the transition to Argentine Monte. This area is a cold desert scrub steppe, with very high wind velocities throughout the year as well as year around frosts likely. This ecoregion has high levels of endemism in both plants and animals.
The Falkland Islands Government notes:
There are five different species of breeding Penguin in the Falkland Islands (Rockhopper, Magellanic, Gentoo, King and Macaroni). These are perhaps the most striking species of bird life in the Islands. The Islands are the most important world site for the endangered Rockhopper Penguin and are also home to 80% of the world's breeding population of Black-Browed Albatross, although most of the major colonies are remote and inaccessible. Several rare and threatened species of Petrel nest on offshore islands.
The Elephant Seal, Sea Lion and Fur Seal all breed on the Islands. Whilst Elephant Seals and Sea Lions are widespread and accessible, the only really accessible place to observe the Fur Seal is on New Island. Very rarely, seals found breeding in Antarctic waters occur on Falkland Island shorelines, most notably Leopard seals as well as Ross Seals. The largest Elephant Seal breeding site is found on Sea Lion Island, where there are over 500 individuals.
Porpoise and dolphin are often seen from the shoreline. Sightings and strandings of whales are now regularly reported as numbers continue to grow. Orcas, Sei Whales and Sperm Whales are the most abundant.
In places where there are fresh water ponds, especially near the coast, the Upland Goose and the Ruddy-Headed or "Brent" Goose have contributed to the formation of fine green grass by their continued cropping. Silver Teal, Chiloe Wigeon, White-tufted Grebe and other species frequent such areas too.
There are over 250 species of plant in the Falkland Islands, of which 164 are recorded as native (including the Islands' national flower, the Pale Maiden) and 13 endemic to the Islands.
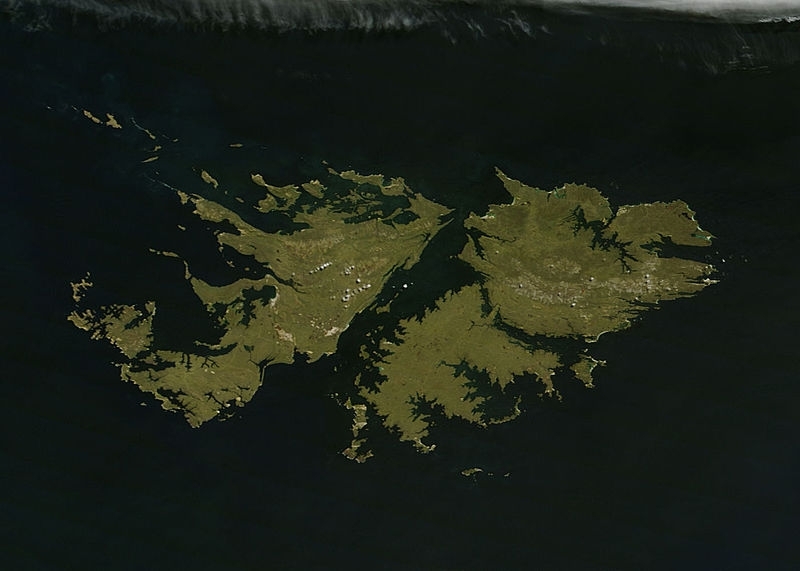
The green lands Falkland Islands sparkle in the southern Atlantic Ocean about 250 nautical miles (460 miles) off the coast of southern Argentina. Also known as Islas Malvinas, the archipelago consists of over 775 islands and is a self-governing British Overseas Territory. On January 23, 2011 the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Terra Satellite captured this true-color image as it passed over the region. Source: NASA - Jeff Schmaltz MODIS Land Rapid Response Team, NASA GSFC
Government
Dependency Status: overseas territory of the UK; also claimed by Argentina
Capital: Stanley (population: 2,000 est. 2009)
Legal System: English common law and local statutes
People and Society
Population: 3,140 (July 2008 est.)
Population Growth Rate: 0.011% (2009 est.)
Urbanization: 74% of total population (2010) growing at an annual rate of growth of 0.9% (2010-15 est.)
Resources
Natural Resources: fish, squid, wildlife, calcified seaweed, sphagnum moss
Land Use:
arable land: 0%
permanent crops: 0%
other: 100% (99% permanent pastures, 1% other) (2005)
Economy
The economy was formerly based on agriculture, mainly sheep farming, but today fishing contributes the bulk of economic activity.
In 1987, the government began selling fishing licenses to foreign trawlers operating within the Falkland Islands' exclusive fishing zone. These license fees total more than $40 million per year, which help support the island's health, education, and welfare system. Squid accounts for 75% of the fish taken.
Dairy farming supports domestic consumption; crops furnish winter fodder.
Foreign exchange earnings come from shipments of high-grade wool to the UK and the sale of postage stamps and coins. The islands are now self-financing except for defense.
The British Geological Survey announced a 200-mile oil exploration zone around the islands in 1993, and early seismic surveys suggest substantial reserves capable of producing 500,000 barrels per day; to date, no exploitable site has been identified.
An agreement between Argentina and the UK in 1995 seeks to defuse licensing and sovereignty conflicts that would dampen foreign interest in exploiting potential oil reserves.
Political tensions between the UK and Argentina rose in early 2010 after a UK company began oil drilling activities in the waters around the Falkland Islands but abated somewhat when the drilling operation failed to discover commercially exploitable oil reserves.
Tourism, especially eco-tourism, is increasing rapidly, with about 30,000 visitors in 2001.
Another large source of income is interest paid on money the government has in the bank.
The British military presence also provides a sizeable economic boost.
GDP: (Purchasing Power Parity): $105.1 million (2002 est.)
GDP: (Official Exchange Rate): $105.1 million (2002 est.)
GDP- per capita (PPP): $35,400 (2002 est.)
GDP- composition by sector:
agriculture: 95%
industry: NA%
services: NA% (1996)
Agricultural products: fodder and vegetable crops; sheep, dairy products; fish, squid
Industries: fish and wool processing; tourism
Currency: Falkland pounds (FKP)