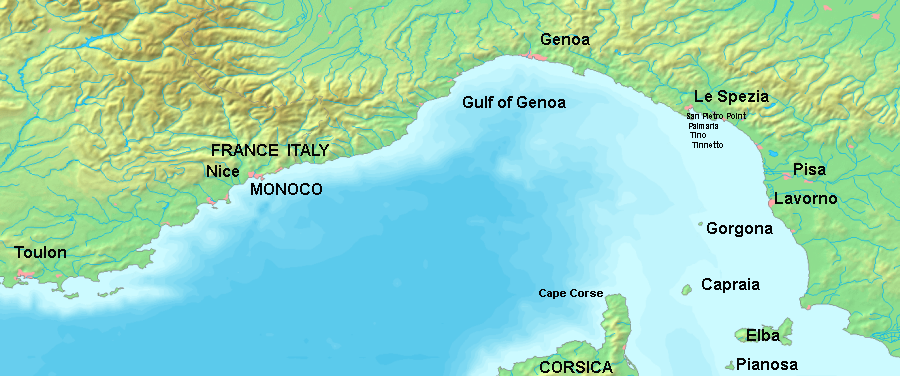
Ligurian Sea
Seas of the World  The Ligurian Sea is part of the Mediterranean Sea located north of the island of Corsica and south of the Italian mainland. The northern part of the sea is the Gulf of Genoa.
The Ligurian Sea is part of the Mediterranean Sea located north of the island of Corsica and south of the Italian mainland. The northern part of the sea is the Gulf of Genoa.
The Balearic Sea lies to the west and the Tyrrhenian Sea to the southeast.
Contents
Geography
There are no broadly accepted boundaries for the Ligurian Sea.
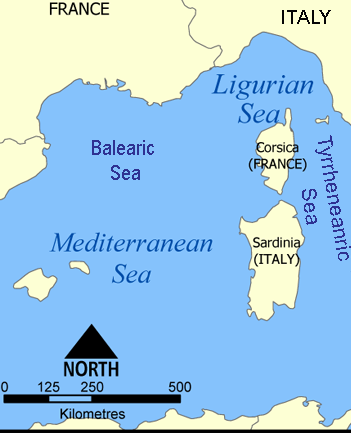 Regional setting of the Ligurean Sea. Source: Norman Einstein
Regional setting of the Ligurean Sea. Source: Norman Einstein
The International Hydrographic Organization (1953) set forth precise limits as follows:
- Southwest - a line joining Cape Corse (Cape Grosso), the northern point of Corsica to the Frontier between France and Italy
- Southeast - a line joining Cape Corse with Tinetto Island and thence through Tino and Palmaria Islands to San Pietro Point on the coast of Italy
- North - the Ligurian coast of Italy
Others extend the western boundary to the Balearic Sea beyond the French-Italian border along the French Côte d'Azur; and the extend the southeast boundary to the Tyrrhenian Sea to the southeast as the Tuscan Archipelago (Gorgona, Capraia, Elba, Pianosa, Montecristo, Giglio, and Giannutri).
The area near to Italian mainland is known as the Gulf of Genoa. The Italian city port of Genoa lies near the center of the Ligurian coast.
The Ligurian Sea has its greatest depth northwest of Corsica where the sea bottom extends more than 2850 meters (9300 feet) below the surface.
Pelagos Sanctuary for Mediterranean Marine Mammals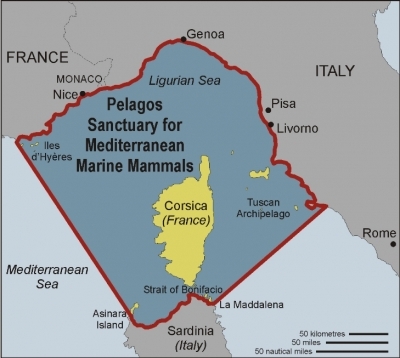
The entire Ligurian Sea is included in the Pelagos Sanctuary for Mediterranean Marine Mammals which was originally called originally called the Ligurian Sea Sanctuary. The Pelagos Sanctuary is a Marine Protected Area recognized by the three nations with coastlines on it - France, Italy and Monoco. It came into existance in 2003. 47 per cent of the sanctuary lies in the national waters of these three countries, while 53 per cent lies in international waters.
The Cetacean species found in the sanctuary include:
- Fin whale
- Sperm whale
- Striped dolphin
- Common bottlenose dolphin
- Saddle-backed dolphin (Short-beaked common dolphin)
- Risso's dolphin
- Long-finned pilot whale
- Cuvier's beaked whale
and those with an occasional presence include:
- Northern Minke whale (Common Minke whale)
- Humpback whale
- Killer whale
- False killer whale
- Rough-toothed dolphin
In addition, there are species of tuna, swordfish, sunfish, sharks and giant devil rays within the sanctuary.
Further Reading
- Seas of the world on the Encyclopedia of Earth
- See Fairbridge [1966] and Astraldi et al. [1990].
- "Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition". International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. Retrieved 7 February 2010.
- Sverdrup, H. U., Johnson, M.W., and Fleming, R.H. 1942, The Oceans Their Physics, Chemistry, and General Biology, New York: Prentice-Hall
- Hoyt, E. 2005. Marine Protected Areas for Whales, Dolphins and Porpoises: A worldwide handbook for cetacean habitat conservation. Earthscan, London,
- Cetacean Habitat, Case study: Pelagos Sanctuary for Mediterranean Marine Mammals