Zimbabwe
Countries and Regions of the World Collection 
Zimbabwe is a land-locked nation on twelve-and-a-half million people in southern Africa, situated between South Africa and Zambia.
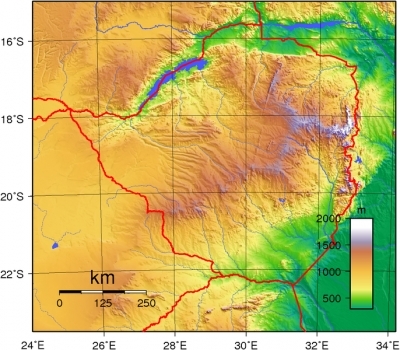
It is mostly high plateau with higher central plateau (high veld); with mountains in east.
The Zambezi River forms a natural riverine boundary with Zambia which includes the noted Victoria Falls. In full flood (February-April) the massive Victoria Falls on the river forms the world's largest curtain of falling water.
Zimbabwe's major environmental issues include:
- deforestation;
- soil erosion;
- land degradation;
- air pollution and water pollution
- Zimbabwe's black rhinoceros herd, once the largest concentration of the species in the world, has been significantly reduced by poaching, largely for the export market to China.
- poor mining practises have led to toxic waste and heavy metal pollution.
It is susceptible to recurring droughts; and, uncommonly, floods and severe storms.
Contents
Geography
Location: Southern Africa, between South Africa and Zambia
Geographic Coordinates: 20 00 S, 30 00 E
Area: 390,580 km2 (386,670 km2 land and 3,910 km2 water)
Land Boundaries: 3066 kilometres. Border countries: Botswana 813 km, Mozambique 1231 km, South Africa 225 km, Zambia 797 km
Natural Hazards: recurring droughts; floods and severe storms are uncommon
Terrain: Mostly high plateau with higher central plateau (high veld); mountains in east. Its lowest point is the junction of the Runde and Save rivers (162 metres) and its highest point is Inyangani (2592 metres).
Climate: Tropical; moderated by altitude; rainy season (November to March)
Ecology and Biodiversity
- Zambezian and Mopane woodlands
- Southern Miombo woodlands
- Eastern Zimbabwe montane forest-grassland mosaic
- Southern Africa bushveld
- Zambezian Baikiaea woodlands
See also
- Regional biodiversity hotspot (Eastern Afromontane)
- Mana Pools National Park
- Victoria Falls National Park
People and Society
Population: 12,619,600 (July 2012 est.)
Ethnic Groups: African 98% (Shona 82%, Ndebele 14%, other 2%), mixed and Asian 1%, white less than 1%
Age Structure:
0-14 years: 41.9% (male 2,555,916/female 2,504,947)
15-64 years: 54.3% (male 3,063,580/female 3,500,366)
65 years and over: 3.8% (male 193,380/female 266,115) (2011 est.)
Population Growth Rate: 4.357% (2011 est.) - The second highest growth rate in the world after Qatar
Birth Rate: 32.19 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
Death Rate: 12.38 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
Net Migration Rate: 23.77 migrant(s)/1,000 population. Note: there is an increasing flow of Zimbabweans into South Africa and Botswana in search of better economic opportunities (2011 est.)
Life Expectancy at Birth: 51.82 years
male: 51.95 years
female: 51.68 years (2011 est.)
Total Fertility Rate: 3.61 children born/woman (2011 est.)
Languages: English (official), Shona, Sindebele (the language of the Ndebele, sometimes called Ndebele), numerous but minor tribal dialects
Literacy: 90.7% (2003 est.)
Urbanization: 38% of total population (2010) growing at an annual rate of change of 3.4% (2010-15 est.)
History
The United Kingdom annexed Southern Rhodesia from the [British] South Africa Company in 1923.
A 1961 constitution was formulated. In 1965 the government unilaterally declared its independence, but the UK did not recognize the act and demanded more complete voting rights for the black African majority in the country (then called Rhodesia).

UN sanctions and a guerrilla uprising finally led to free elections in 1979 and independence (as Zimbabwe) in 1980. Robert Mugabe, the nation's first prime minister, has been the country's only ruler (as president since 1987) and has dominated the country's political system since independence. His chaotic land redistribution campaign, which began in 2000, caused an exodus of white farmers, crippled the economy, and ushered in widespread shortages of basic commodities. Ignoring international condemnation, Mugabe rigged the 2002 presidential election to ensure his reelection.
The ruling ZANU-PF party used fraud and intimidation to win a two-thirds majority in the March 2005 parliamentary election, allowing it to amend the constitution at will and recreate the senate, which had been abolished in the late 1980s.
In April 2005, Harare embarked on Operation Restore Order, ostensibly an urban rationalization program, which resulted in the destruction of the homes or businesses of 700,000 mostly poor supporters of the opposition.
Mugabe in June 2007 instituted price controls on all basic commodities causing panic buying and leaving store shelves empty for months.
General elections held in March 2008 contained irregularities but still amounted to a censure of the ZANU-PF-led government with the opposition winning a majority of seats in parliament. MDC opposition leader Morgan Tsvangirai won the most votes in the presidential polls, but not enough to win outright. In the lead up to a run-off election in late June 2008, considerable violence enacted against opposition party members led to the withdrawal of Tsvangirai from the ballot. Extensive evidence of violence and intimidation resulted in international condemnation of the process. Difficult negotiations over a power-sharing government, in which Mugabe remained president and Tsvangirai became prime minister, were finally settled in February 2009, although the leaders failed to agree upon many key outstanding governmental issues. Mugabe publicly called for early elections in 2011 - two years before his term ends - but no election was held.
Government
Government Type: Parliamentary Democracy
Capital: Harare - 1.606 million (2009)
Administrative Divisions: 8 provinces and 2 cities* with provincial status; Bulawayo*, Harare*, Manicaland, Mashonaland Central, Mashonaland East, Mashonaland West, Masvingo, Matabeleland North, Matabeleland South, Midlands
Independence Date: 18 April 1980 (from UK)
Legal System: mixture of Roman-Dutch and English common law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage: 18 years of age; universal
International Environmental Agreements
Zimbabwe is party to international agreements on: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, and Ozone Layer Protection.
Water
Total Renewable Water Resources: 20 cubic kilometres (1987)
Freshwater Withdrawal: Total: 4.21 cu km/yr (14% domestic, 7% industrial, 79% agricultural).
Per capita Freshwater Withdrawal: 324 cu m/yr (2002)
Access to improved Drink Waters Sources: 82% of population
Access to Improved Sanitation Facilities: 44% of population
Agriculture
Agricultural Products: corn, cotton, tobacco, wheat, coffee, sugarcane, peanuts; sheep, goats, pigs
Irrigated Land: 1740 square kilometres (2003)
Resources
Natural Resources: wildlife, coal, chromium ore, asbestos, gold, nickel, copper, iron ore, vanadium, lithium, tin, platinum group metals.
Land Use:
arable land: 8.24%
permanent crops: 0.33%
other: 91.43% (2005)
Energy
| Energy in Zimbabwe | |||||
| Production | Consumption | Exports | Imports | Reserves | |
| Electricity | 7.723 billion kWh (2008 est.) |
12.47 billion kWh (2008 est.) |
54 million kWh (2008 est.) |
5.268 billion kWh (2008 est.) |
|
| Oil | 0 bbl/day (2010 est.) |
11,000 bbl/day (2010 est.) |
0 bbl/day (2009 est.) |
13,140 bbl/day (2009 est.) |
0 bbl (1 January 2011 est.) |
| Natural Gas | 0 cu m (2009 est.) |
0 cu m (2009 est.) |
0 cu m (2009 est.) |
0 cu m (2009 est.) |
0 cu m (1 January 2011 est.) |
| Source: CIA Factbook | |||||
Conflict
International Disputes: Botswana built electric fences and South Africa has placed military along the border to stem the flow of thousands of Zimbabweans fleeing to find work and escape political persecution; Namibia has supported, and in 2004 Zimbabwe dropped objections to, plans between Botswana and Zambia to build a bridge over the Zambezi River, thereby de facto recognizing a short, but not clearly delimited, Botswana-Zambia boundary in the river
Refugees and Internally Displaced Persons: refugees (country of origin): 2,500 (Democratic Republic of Congo) - IDPs: 569,685 (Mugabe-led political violence, human rights violations, land reform, and economic collapse) (2007)
Economy
Zimbabwe's economy is growing at a brisk pace despite continuing political uncertainty. Following a decade of contraction, Zimbabwe's economy recorded real growth of 5.9% in 2010.
But the government of Zimbabwe still faces a number of difficult economic problems, including a large external debt burden and insufficient formal employment.
Zimbabwe's 1998-2002 involvement in the war in the Democratic Republic of the Congo drained hundreds of millions of dollars from the economy.
The government's land reform program, characterized by chaos and violence, has badly damaged the commercial farming sector, the traditional source of exports and foreign exchange and the provider of 400,000 jobs, turning Zimbabwe into a net importer of food products. The EU and the US provide food aid on humanitarian grounds, though on a smaller scale than before.
Until early 2009, the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe routinely printed money to fund the budget deficit, causing hyperinflation.
The power-sharing government formed in February 2009 has led to some economic improvements, including the cessation of hyperinflation by eliminating the use of the Zimbabwe dollar and removing price controls.
The economy is registering its first growth in a decade, but will be reliant on further political improvement for greater growth.
GDP (Purchasing Power Parity): $5.916 billion (2011 est.)
GDP (Official Exchange Rate): $9.2 billion. Note: in 2009, the Zimbabwean dollar was taken out of circulation, making Zimbabwe's GDP at the official exchange rate a highly inaccurate statistic (2010 est.)
GDP- per capita (PPP): $500 (2011 est.)
GDP- composition by sector:
agriculture: 20.4%
industry: 24.6%
services: 54.9% (2011 est.)
Population Below Poverty Line: 68% (2004)
Industries: mining (coal, gold, platinum, copper, nickel, tin, clay, numerous metallic and nonmetallic ores), steel; wood products, cement, chemicals, fertilizer, clothing and footwear, foodstuffs, beverages
Exports: platinum, cotton, tobacco, gold, ferroalloys, textiles/clothing
Export Partners: Democratic Republic of the Congo 14.8%, South Africa 13.4%, Botswana 13.2%, China 12.7%, Netherlands 5.9%, Italy 4.6% (2010)
Imports: machinery and transport equipment, other manufactures, chemicals, fuels
Import Partners: South Africa 58%, China 8.7% (2010)
Currency: Zimbabwean dollar (ZWD)
Ports and Terminals: Binga, Kariba