Indonesia
Indonesia is a nation of 248 million people in southeast Asia composed of 17,508 islands (of which 6,000 are inhabited) which straddle the equator between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. Countries and Regions of the World Collection 
The largest islands are Sumatra, Java, Borneo (called Kalimantan in Indonesia, which has sovereignty over about two-thirds of the island), Sulawesi, and New Guinea (eastern half). Other notable islands include Timor (eastern half), the Maluku Islands, and the Lesser Sunda Islands which include Bali.
Indonesia is the 4th most populous nation in the world (after China, India, and the United States).
Its major environmental issues include:
- deforestation;
- water pollution from industrial wastes, sewage;
- air pollution in urban areas; and,
- smoke and haze from forest fires.
It is susceptible to occasional floods; severe droughts; tsunamis; earthquakes; volcanoes; and, forest fires.
Natural disasters have devastated many parts of Indonesia over the past few years. On December 26, 2004, a 9.1 to 9.3 magnitude earthquake took place in the Indian Ocean, and the resulting tsunami killed over 130,000 people in Aceh and left more than 500,000 homeless. On March 26, 2005, an 8.7 magnitude earthquake struck between Aceh and northern Sumatra, killing 905 people and displacing tens of thousands. After much media attention on the seismic activity on Mt. Merapi in April and May 2006, a 6.2 magnitude earthquake occurred 30 miles to the southwest. It killed more than 5,000 people and left an estimated 200,000 people homeless in the Yogyakarta region. An earthquake of 7.4 struck Tasikmalaya, West Java, on September 2, 2009, killing approximately 100 people. On September 30, 2009, a 7.6 magnitude earthquake struck Western Sumatra. No official statistics were released on deaths and injuries; however, press reports indicated more than 1,100 fatalities.
The Dutch began to colonize Indonesia in the early 17th century; Japan occupied the islands from 1942 to 1945.
Indonesia declared its independence after Japan's surrender, but it required four years of intermittent negotiations, recurring hostilities, and UN mediation before the Netherlands agreed to transfer sovereignty in 1949.
Free and fair legislative elections took place in 1999 after decades of repressive rule. Indonesia is now the world's third most populous democracy, the world's largest archipelagic state, and home to the world's largest Muslim population.
Current issues include: alleviating poverty, improving education, preventing terrorism, consolidating democracy after four decades of authoritarianism, implementing economic and financial reforms, stemming corruption, holding the military and police accountable for human rights violations, addressing climate change, and controlling infectious diseases, particularly those of global and regional importance.
In 2005, Indonesia reached a historic peace agreement with armed separatists in Aceh, which led to democratic elections in Aceh in December 2006. Indonesia continues to face low intensity armed resistance by the separatist Free Papua Movement.
Contents
Geography
Location: Southeastern Asia, archipelago between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. The archipelago includes 17,508 islands (6,000 inhabited); straddles equator; and is strategic location astride or along major sea lanes from Indian Ocean to Pacific Ocean
Geographic Coordinates: 5 00 S, 120 00 E
Area: 1,904,569 km2(1,811,569 km2 land and 93,000 km2 water)
arable land: 11.03%
permanent crops: 7.04%
other: 81.93% (2005)
Land Boundaries: Total: 2,830 km. Border countries: Timor-Leste (East Timor) 228 km, Malaysia 1,782 km, and Papua New Guinea 820 km
Note: Indonesia has a stated foreign policy objective of establishing stable fixed land and maritime boundaries with all of its neighbors; some sections of border along Timor-Leste's Oecussi exclave and maritime boundaries with Timor-Leste remain unresolved; many refugees from Timor-Leste who left in 2003 still reside in Indonesia and refuse repatriation; a 1997 treaty between Indonesia and Australia settled some parts of their maritime boundary but outstanding issues remain; ICJ's award of Sipadan and Ligitan islands to Malaysia in 2002 left the sovereignty of Unarang rock and the maritime boundary in the Ambalat oil block in the Celebes Sea in dispute; the ICJ decision has prompted Indonesia to assert claims to and to establish a presence on its smaller outer islands; Indonesia and Singapore continue to work on finalization of their 1973 maritime boundary agreement by defining unresolved areas north of Indonesia's Batam Island; Indonesian secessionists, squatters, and illegal migrants create repatriation problems for Papua New Guinea; maritime delimitation talks continue with Palau; Indonesian groups challenge Australia's claim to Ashmore Reef; Australia has closed parts of the Ashmore and Cartier Reserve to Indonesian traditional fishing and placed restrictions on certain catches
Coastline: 54,716 km
Maritime Claims (measured from claimed archipelagic straight baselines): territorial sea: 12 nautical miles. Exclusive economic zone: 200 nautical miles.
Natural Hazards: Occasional floods; severe droughts; tsunamis; earthquakes; volcanoes; forest fires
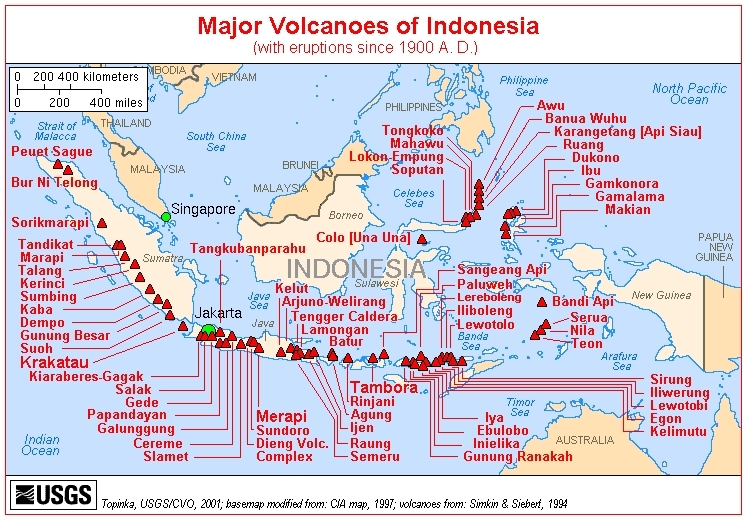
Volcanism: Indonesia contains the most volcanoes of any country in the world - some 76 are historically active; significant volcanic activity occurs on Java, western Sumatra, the Sunda Islands, Halmahera Island, Sulawesi Island, Sangihe Island, and in the Banda Sea; Merapi (elev. 2,968 m, 9,737 ft), Indonesia's most active volcano and in eruption since 2010, has been deemed a "Decade Volcano" by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to its explosive history and close proximity to human populations; other notable historically active volcanoes include Agung, Awu, Karangetang, Krakatau (Krakatoa), Makian, Raung, and Tambora
Terrain: Mostly coastal lowlands; larger islands have interior mountains. The highest point is Puncak Jaya 5,030 m
Climate: Tropical; hot, humid; more moderate in highlands
Ecology and Biodiversity
See Biological diversity in Sundaland and Biological diversity in Wallacea as well as the following ecoregions:
- Sunda Shelf mangroves
- Sumatran tropical pine forests
- Sumatran montane rain forests
- Sumatran lowland rain forests
- Sumatran peat swamp forests
- Sumatran freshwater swamp forests
- Peninsular Malaysian rain forests
- Sundaland heath forests
- Mentawai Islands rain forests
- Western Java rain forests
- Western Java montane rain forests
- Eastern Java-Bali rain forests
- Eastern Java-Bali montane rain forests
- Lesser Sundas deciduous forests
- Sumba deciduous forests
- Timor and Wetar deciduous forests
- Southwest Borneo freshwater swamp forests
- Borneo peat swamp forests
- Borneo montane rain forests
- Borneo lowland rain forests
- Sulawesi lowland rain forests
- Sulawesi montane rain forests
- Buru rain forests
- Halmahera rain forests
- Seram rain forests
- Banda Sea Islands moist deciduous forests
- Vogelkop-Aru lowland rain forests
- Vogelkop montane rain forests
- New Guinea mangroves
- Biak-Numfoor rain forests
- Yapen rain forests
- Northern New Guinea lowland rain and freshwater swamp forests
- Northern New Guinea montane rain forests
- Central Range montane rain forests
- Central Range sub-alpine grasslands
- Southern New Guinea freshwater swamp forests
- Trans Fly savanna and grasslands
See also: Indonesian Sea large marine ecosystem
Protected areas: See Komodo National Park, Lorentz National Park, Tropical Rainforest Heritage of Sumatra and Ujung Kulon National Park and Krakatau Nature Reserve
People and Society
Indonesia's approximately 248 million people make it the world's fourth-most populous nation. The island of Java, roughly the size of New York State, is the most populous island in the world (136.6 million, 2010 est.) and one of the most densely populated areas in the world. Indonesia includes numerous related but distinct cultural and linguistic groups, many of which are ethnically Malay. Since independence, Bahasa Indonesia (the national language, a form of Malay) has spread throughout the archipelago and has become the language of most written communication, education, government, business, and media. Local languages are still important in many areas, however. English is the most widely spoken foreign language. Education is compulsory for children through grade 9. In primary school, more than 94% of eligible children are enrolled whereas 57% of eligible children are enrolled in secondary school.
Constitutional guarantees of religious freedom apply to the six religions recognized by the state, namely Islam (86.1%), Protestantism (5.7%), Catholicism (3%), Hinduism (1.8%), Buddhism (about 1%), and Confucianism (less than 1%). On the resort island of Bali, over 90% of the population practices Hinduism. In some remote areas, animism is still practiced.
| The thick brown plume of ash, steam, and volcanic gas rising from Anak Krakatau in this true-color image is a common sight at the volcano. Responsible for one of the largest and most destructive eruptions in Indonesia's history (1883), Krakatau still erupts frequently. For this reason, the volcano is one of 100 that NASA automatically monitors by satellite. Photo courtesy of NASA. |
| Southeast of the island of Timor (center), a phytoplankton bloom is coloring the waters of the Timor Sea, which separates Timor from northwestern Australia. To the north of Timor is Flores, which is home to numerous active volcanoes. (The red dots are due to fire, not volcanic activity.) The eastern half of Timor, as well as an exclave to the west and a few offshore islands, constitute the country of Timor-Leste. The western portion of Timor and the remaining islands (including Flores) belong to Indonesia. Image courtesy of NASA. |
| Kuta Beach, Bali. |
| View from the cliffs at Pura Luhur Uluwatu, Bali. |
| The Sea Temple of Pura Luhur at Uluwatu in south Bali dates back to the 11th century. |
| The monkeys at Pura Luhur Uluwatu on Bali are notorious pickpockets. |
| Jakarta. Source: Kevin Aurell/Wikimedia Commons |
Population: 248,216,193 (July 2012 est.) (4th largest after China, India, and the United States)
Ethnic groups: Javanese 40.6%, Sundanese 15%, Madurese 3.3%, Minangkabau 2.7%, Betawi 2.4%, Bugis 2.4%, Banten 2%, Banjar 1.7%, other or unspecified 29.9% (2000 census)
Age Structure:
0-14 years: 27.3% (male 34,165,213/female 32,978,841)
15-64 years: 66.5% (male 82,104,636/female 81,263,055)
65 years and over: 6.1% (male 6,654,695/female 8,446,603) (2011 est.)
Population Growth Rate: 1.04% (2012 est.)
Birthrate: 17.76 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
Death Rate: 6.28 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
Net Migration Rate: -1.08 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
Urbanization: 44% of total population (2010) growing at 1.7% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
Life Expectancy at Birth: 71.62 years
male: 69.07 years
female: 74.29 years (2012 est.)
Total Fertility Rate: 2.23 children born/woman (2012 est.)
Languages: Bahasa Indonesia (official, modified form of Malay), English, Dutch, local dialects (the most widely spoken of which is Javanese)
Literacy: 90.4% (male: 94%; female: 86.8%) (2004 est.)
History
By the time of the Renaissance, the islands of Java and Sumatra had already enjoyed a 1,000-year heritage of advanced civilization spanning two major empires. During the 7th-14th centuries, the Buddhist kingdom of Srivijaya flourished on Sumatra. At its peak, the Srivijaya Empire reached as far as West Java and the Malay Peninsula. Also by the 14th century, the Hindu Kingdom of Majapahit had risen in eastern Java. Gadjah Mada, the empire's chief minister from 1331 to 1364, succeeded in gaining allegiance from most of what is now modern Indonesia and much of the Malay archipelago as well. Legacies from Gadjah Mada's time include a codification of law and an epic poem. Islam arrived in Indonesia sometime during the 12th century and supplanted Hinduism by the end of the 16th century in Java and Sumatra. Bali, however, remains overwhelmingly Hindu. In the eastern archipelago, both Christian and Islamic proselytizing took place in the 16th and 17th centuries, and, currently, there are large communities of both religions on these islands.
Beginning in 1602, the Dutch slowly established themselves as rulers of Indonesia, exploiting the weakness of the small kingdoms that had replaced that of Majapahit. The only exception was East Timor, which remained under Portugal's control until 1975. During 300 years of rule, the Dutch developed the Netherlands East Indies into one of the world's richest colonial possessions, extracting natural resources through co-opted local elites but doing little to modernize Indonesia.
During the first decade of the 20th century, an Indonesian independence movement began and expanded rapidly, particularly between the two World Wars. Its leaders came from a small group of young professionals and students, some of whom had been educated in the Netherlands. Many, including Indonesia's first president, Soekarno (1945-67), were imprisoned for political activities.
During World War II, Japan invaded Indonesia (in early 1942), outclassing a combined American, British, Dutch, and Australian military command. Sizeable U.S. naval forces and smaller air and ground forces sent to defend Indonesia were defeated, with heavy losses in ships and large numbers of Americans killed or captured. The Japanese treated captured Allied troops and interned Western civilians with extreme cruelty. Because of local animosity toward Dutch colonial rule, there was no anti-Japanese guerilla movement as in the Philippines and Malaysia, and most Indonesians initially welcomed the Japanese as liberators. But increasingly harsh Japanese rule strengthened the prewar independence movement, and on August 17, 1945, 3 days after Japan’s surrender to the Allies, a small group of Indonesians, led by Soekarno and Mohammad Hatta, proclaimed independence and established the Republic of Indonesia. They set up a provisional government and adopted a constitution to govern the republic until elections could be held and a new constitution written. Fighting soon broke out between Indonesian independence groups and Allied forces--mainly British, Indian, and Australian forces--sent to accept the Japanese surrender. Dutch efforts later to reestablish complete control met resistance. Following the Philippines' independence in 1946, the U.S. was unwilling to see the Netherlands use post-war Marshall Plan support to indirectly fund the suppression of Indonesia’s independence. Negotiations and on-and-off fighting in Indonesia continued until 1949. The stalemate, combined with reduced international support and a devastated economy in the Netherlands, led to the Dutch decision to withdraw from Indonesia. Colonial rule and its violent end left a legacy in Indonesia of mistrusting foreign motives, especially those of large powers. In 1950, Indonesia became the 60th member of the United Nations.
Shortly after hostilities with the Dutch ended in 1949, Indonesia adopted a new constitution, providing for a parliamentary system of government in which the executive was chosen by and accountable to parliament. Parliament was divided among many political parties before and after the country's first nationwide election in 1955, and stable governmental coalitions were difficult to achieve. The role of Islam in Indonesia was debated. Soekarno defended a secular state based on Pancasila, five principles of the state philosophy--monotheism, humanitarianism, national unity, representative democracy by consensus, and social justice--codified in the 1945 constitution, while some Muslim groups preferred either an Islamic state or a constitution that included a preambular provision requiring adherents of Islam to be subject to Islamic law. At the time of independence, the Dutch retained control over the western half of New Guinea (known as Irian Jaya in the Soekarno and Suharto eras and as Papua since 2000) and permitted steps toward self-government and independence.
Negotiations with the Dutch on the incorporation of Irian Jaya into Indonesia failed, and armed clashes broke out between Indonesian and Dutch troops in 1961. In August 1962, the two sides reached an agreement, and Indonesia assumed administrative responsibility for Irian Jaya on May 1, 1963. The Indonesian Government conducted an "Act of Free Choice" in Irian Jaya under UN supervision in 1969 in which 1,025 Papuan representatives of local councils agreed by consensus to remain a part of Indonesia. A subsequent UN General Assembly resolution confirmed the transfer of sovereignty to Indonesia. Opposition to Indonesian administration of Papua gave rise to small-scale guerrilla activity in the years following Jakarta's assumption of control. In the more open atmosphere since 1998, there have been more explicit expressions within Papua calling for independence from Indonesia.
Unsuccessful rebellions on Sumatra, Sulawesi, West Java, and other islands beginning in 1958, plus a failure by the constituent assembly to develop a new constitution, weakened the parliamentary system. Consequently, in 1959, when President Soekarno unilaterally revived the provisional 1945 constitution that provided for broad presidential powers, he met little resistance. From 1959 to 1965, President Soekarno imposed an authoritarian regime under the label of "Guided Democracy."
Soekarno favored a foreign policy of nonalignment, a stance supported by other prominent leaders of former colonies who rejected formal alliances with either the West or Soviet bloc. Under Soekarno's auspices, these leaders gathered in Bandung, West Java, in 1955 to lay the groundwork for what became known as the Non-Aligned Movement. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, President Soekarno moved closer to Asian communist states and toward the Indonesian Communist Party (PKI) in domestic affairs. The PKI represented the largest communist party outside the Soviet Union and China.
By 1965, the PKI controlled many of the mass civic and cultural organizations that Soekarno had established to mobilize support for his regime and, with Soekarno's acquiescence, embarked on a campaign to establish a "Fifth Column" by arming its supporters. Army leaders resisted this campaign. Under circumstances that have never been fully explained, on October 1, 1965, PKI sympathizers within the military, including elements from Soekarno's palace guard, occupied key locations in Jakarta and kidnapped and murdered six senior generals. Major General Suharto, the commander of the Army Strategic Reserve, rallied army troops opposed to the PKI to reestablish control over the city. Violence swept throughout Indonesia in the aftermath of the October 1 events, and unsettled conditions persisted through 1966. Right-wing groups killed tens of thousands of alleged communists in rural areas. Estimates of the number of deaths range between 160,000 and 500,000. The violence was especially brutal in Java and Bali. During this period, PKI members by the tens of thousands turned in their membership cards. The emotions and fears of instability created by this crisis persisted for many years as the communist party remains banned from Indonesia.
Throughout the 1965-66 period, President Soekarno vainly attempted to restore his political stature and shift the country back to its pre-October 1965 position. Although he remained President, in March 1966, Soekarno transferred key political and military powers to General Suharto, who by that time had become head of the armed forces. In March 1967, the Provisional People's Consultative Assembly (MPRS) named General Suharto acting President. Soekarno ceased to be a political force and lived under virtual house arrest until his death in 1970.
President Suharto proclaimed a "New Order" in Indonesian politics and dramatically shifted foreign and domestic policies away from the course set in Soekarno's final years. The New Order established economic rehabilitation and development as its primary goals and pursued its policies through an administrative structure dominated by the military but with advice from Western-educated economic experts. In 1968, the People's Consultative Assembly (MPR) formally selected Suharto to a full 5-year term as President, and he was reelected to successive 5-year terms in 1973, 1978, 1983, 1988, 1993, and 1998. In mid-1997, Indonesia suffered from the Asian financial and economic crisis, accompanied by the worst drought in 50 years and falling prices for commodity exports. As the exchange rate changed from a fixed to a managed float to fully floating, the rupiah (IDR or Rp) depreciated in value, inflation increased significantly, and capital flight accelerated. Demonstrators, initially led by students, called for Suharto's resignation. Amid widespread civil unrest, Suharto resigned on May 21, 1998, 3 months after the MPR had selected him for a seventh term. Suharto's hand-picked Vice President, B.J. Habibie, became Indonesia's third President. President Habibie reestablished International Monetary Fund (IMF) and donor community support for an economic stabilization program. He released several prominent political and labor prisoners, initiated investigations into the unrest, and lifted controls on the press, political parties, and labor unions.
In January 1999, Habibie and the Indonesian Government agreed to a process, with UN involvement, under which the people of East Timor would be allowed to choose between autonomy and independence through a direct ballot held on August 30, 1999. Some 98% of registered voters cast their ballots, and 78.5% of the voters chose independence over continued integration with Indonesia. Many people were killed by Indonesian military forces and military-backed militias in a wave of violence and destruction after the announcement of the pro-independence vote.
Indonesia's first elections in the post-Suharto period were held for the national, provincial, and sub-provincial parliaments on June 7, 1999. Forty-eight political parties participated in the elections. For the national parliament, Partai Demokrasi Indonesia Perjuangan (PDI-P, Indonesian Democratic Party of Struggle, led by Megawati Sukarnoputri) won 34% of the vote; Golkar ("Functional Groups" party) 22%; Partai Kebangkitan Bangsa (PKB, National Awakening Party, linked to the moderate Islamic organization Nadhlatul Ulama headed by former President Abdurrahman Wahid) 13%; and the conservative Islamic Partai Persatuan Pembangunan (PPP, United Development Party, led by Hamzah Haz) 11%. The MPR selected Abdurrahman Wahid as Indonesia's fourth President in November 1999 and replaced him with Megawati Sukarnoputri in July 2001.
The constitution, as amended in the post-Suharto era, now provides for the direct election by popular vote of the president and vice president. Under the 2004 amendment, only parties or coalitions of parties that gained at least 3% of the House of Representatives (DPR) seats or 5% of the vote in national legislative elections were eligible to nominate a presidential and vice presidential ticket.
The 2004 legislative elections took place on April 5 and were considered to be generally free and fair. Twenty-four parties took part in the elections. Big parties lost ground, while small parties gained larger shares of the vote. However, the two Suharto-era nationalist parties, PDI-P and Golkar, remained in the lead. PDI-P (opposition party during the Suharto era) lost its plurality in the House of Representatives, dropping from 33% to 18.5% of the total vote (and from 33% to 20% of the seats). The Golkar Party (Suharto’s political party) declined slightly from 1999 levels, going from 22% to 21% of the national vote (from 26% to 23% of DPR seats). The third- and fourth-largest parties (by vote share) were two Islamic-oriented parties, the United Development Party (PPP) (8% of the votes, 10.5% of the seats) and National Awakening Party (PKB) (10.5% of the vote, 9.45% of the seats). Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono’s nationalist Democratic Party (PD) won 7.45% of the national vote and 10% of the DPR seats, making it the fourth-largest party in the DPR. Seven of the 24 parties won no DPR seats; six won 1-2 seats, and the other six won between 2%-6% of the national vote (between 5-52 DPR seats).
The first direct presidential election was held on July 5, 2004, contested by five tickets. As no candidate won at least 50% of the vote, a runoff election was held on September 20, 2004, between the top two candidates, President Megawati Sukarnoputri and retired General Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono. In this final round, Yudhoyono won 60.6% of the vote. Approximately 76.6% of the eligible voters participated, a total of roughly 117 million people, making Indonesia's presidential election the largest single-day election in the world. The Carter Center, which sent a delegation of election observers, issued a statement congratulating "the people and leaders of Indonesia for the successful conduct of the presidential election and the peaceful atmosphere that has prevailed throughout the ongoing democratic transition."
In 2009, national legislative elections were held on April 9 and presidential elections were held in July. They were peaceful and considered free and fair. New electoral rules required that a party win 2.5% of the national vote in order to enter parliament. A total of thirty-eight national and six local (Aceh only) parties contested the 2009 legislative elections. At least 171 million voters registered to vote in these elections. Voter turnout was estimated to be 71% of the electorate. Nine parties won parliamentary seats in the House of Representatives (DPR). The top three winners were secular nationalist parties: President Yudhoyono’s Partai Demokrat, with 20.85% of the vote; Vice President Jusuf Kalla’s Golkar Party, 14.45%; and former president Megawati’s opposition PDI-P party, with 14.03%. The next four largest parties were all Islamic-oriented parties: PKS, PAN (6%), PPP (5.3%), and PKB (4.9%). Only PKS maintained its 2004 vote share (7.88%); the other three declined in popularity. The smallest two parties in Parliament, Gerindra and Hanura, with 4.46 and 3.77% of the vote respectively, were headed by retired Suharto-era army generals Prabowo Subianto and Wiranto (one name only). The 2009 DPR members took their seats October 1.
Also in 2009, the threshold was revised so that only parties or coalitions of parties that gained at least 20% of the House of Representatives (DPR) seats or 25% of the vote in the 2009 national legislative elections would be eligible to nominate a presidential and vice presidential ticket. Partai Demokrat, Golkar, and PDI-P parties, the top winners in the legislative elections, nominated presidential candidates. To win in one round, a presidential candidate was required to receive more than 50% of the vote and more than 20% of the vote in 17 of Indonesia’s 33 provinces. If no candidate did so, the top two candidates would have competed in a second round in September 2009.
Three tickets competed in the presidential elections. Incumbent President Yudhoyono and his running mate, non-partisan former Central Bank Chair and Economics Minister Boediono, won the election with such a significant plurality--60.6%--that it obviated the need for a second round of elections. Main challenger and former president and opposition leader Megawati Sukarnoputri and running mate Prabowo Subianto trailed with 28%. Meanwhile, Vice President Jusuf Kalla and running mate Wiranto came in last at 12.7%. Indonesia’s Consultative Assembly (MPR) inaugurated President Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono for his second term as president on October 20, 2009.
Government
Government Type: Republic
Indonesia is a republic based on the 1945 constitution providing for a separation of executive, legislative, and judicial power. Substantial restructuring has occurred since President Suharto's resignation in 1998 and the short, transitional Habibie administration in 1998 and 1999. The Habibie government established political reform legislation that formally set up new rules for the electoral system, the House of Representatives (DPR), the People's Consultative Assembly (MPR), and political parties without changing the 1945 Indonesian constitution. After these reforms, the constitution now limits the president to two terms in office.
Indonesia adopted a bicameral legislative system following the establishment of the DPD (Regional Representatives Council), which was first elected in 2004. The DPD is composed of four representatives from each of Indonesia’s 33 provinces. Although it can make proposals and submit opinions on legislative matters concerning the regions, it does not have the power to create legislation. The MPR consists of both the DPD and the DPR. The MPR has the power to inaugurate and to impeach the president (upon the recommendation of the DPR). The current Speaker of the MPR is Taufik Kiemas (from the opposition PDI-P Party) and the Speaker of the DPR is Marzuki Alie (from the ruling Democrat Party). These speakers and four deputy speakers for the DPR and MPR took up their positions on October 5, 2009. The largest party in the DPR, now President Yudhoyono’s Partai Demokrat, filled the influential DPR speaker position.
The president, elected for a 5-year term, is the top government and political figure. The president and the vice president were elected by popular vote for the first time on September 20, 2004. Previously, the MPR selected Indonesia's president. In 1999, the MPR selected Abdurrahman Wahid, also known as Gus Dur, as the fourth President. The MPR removed Gus Dur in July 2001, immediately appointing then-Vice President Megawati Sukarnoputri as the fifth President. In 2004, Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono was directly elected to succeed Megawati. He was re-elected in 2009.
The president, assisted by an appointed cabinet, has the authority to conduct the administration of the government.
Capital: Jakarta - 9.121 million (2009)
Other major cities: Surabaya 2.509 million; Bandung 2.412 million; Medan 2.131 million; Semarang 1.296 million (2009)
Administration: Indonesia has 30 provinces, 2 special regions (Aceh and Yogyakarta), and 1 special capital city district (Jakarta Raya). The provinces are: Bali, Banten, Bengkulu, Gorontalo, Jambi, Jawa Barat, Jawa Tengah, Timur, Kalimantan Barat, Kalimantan Selatan, Kalimantan Tengah, Kalimantan Timur, Kepulauan Bangka Belitung, Kepulauan Riau, Lampung, Maluku, Maluku Utara, Nusa Tenggara Barat, Nusa Tenggara Timur, Papua, Papua Barat, Riau, Sulawesi Barat, Sulawesi Selatan, Sulawesi Tengah, Sulawesi Tenggara, Sulawesi Utara, Sumatera Barat, Sumatera Selatan, and Sumatera Utara.
Following the implementation of decentralization beginning on 1 January 2001, the 465 regencies and municipalities have become the key administrative units responsible for providing most government services.
Independence Date: 17 August 1945 (declared); 27 December 1949 (recognized by the Netherlands)
Legal System: Based on Roman-Dutch law, substantially modified by indigenous concepts and by new criminal procedures and election codes; has not accepted compulsory International Court of Justice jurisdiction
International Environmental Agreements
Indonesia is party to international agreements on: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands. It has signed, but not ratified an international agreement on Marine Life Conservation.
Environment
President Yudhoyono's administration has significantly increased Indonesia's global profile on environmental issues, and U.S.-Indonesia cooperation on the environment has grown substantially. Indonesia is particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, which include rising sea levels and erosion of coastal areas, increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, species extinction, and the spread of vector-borne diseases. At the same time, Indonesia faces challenges in addressing the causes of climate change. Indonesia has the world's second-largest tropical forest and the fastest deforestation rate, making it the third-largest contributor of greenhouse gas emissions, behind China and the U.S. President Yudhoyono pledged at the 2009 G-20 in Pittsburgh to reduce Indonesia’s greenhouse gas emissions by up to 41% below business as usual by 2020, in addition to eliminating fossil fuel subsidies. Indonesia continues expanding its constructive engagement in Southeast Asia, within the G-20 and Major Economies Forum, and in other international bodies to encourage other developing countries to adopt and implement ambitious steps to reduce the impacts of global climate change. In June 2010, President Barack Obama pledged to support U.S.-Indonesia shared goals on climate change through a Science, Oceans, Land Use, Society and Innovation (SOLUSI) partnership and through the establishment of a climate change center. The United States is providing $6.9 million in support – with matching funds from Norway – for the new Indonesia Climate Change Center (ICCC), which will focus on mapping and monitoring of carbon-rich peat lands and tropical forests with expertise from the U.S. Forest Service, bringing the best available science and analysis to policy leaders on key strategies and decisions to mitigate and adapt to climate change.
In 2004, President Yudhoyono initiated a multi-agency drive against illegal logging that has significantly decreased illegal logging through stronger enforcement activities. The Department of Justice-sponsored Environmental Crimes Task Force supports this enforcement effort. The State Department and the U.S. Trade Representative negotiated with the Indonesian Ministries of Trade and Forestry the U.S. Government's first Memorandum of Understanding on Combating Illegal Logging and Associated Trade. Presidents George W. Bush and Yudhoyono announced the MOU during President Bush's November 2006 visit to Indonesia. Implementation of the MOU includes collaboration on sustainable forest management, improved law enforcement, and improved markets for legally harvested timber products. This effort will strengthen the enabling conditions for avoiding deforestation, specifically addressing the trade issues that are involved. The U.S. Government also contributed to the start of the Heart of Borneo conservation initiative to conserve a high-biodiversity, transboundary area that includes parts of Indonesia, Malaysia, and Brunei. The three countries launched the Heart of Borneo initiative in February 2007. In 2009, the Governments of Indonesia and the U.S. concluded a Tropical Forest Conservation Act (TFCA1) agreement, and in 2012 are expected to finalize a new TFCA2 agreement. The agreements reduce Indonesia's debt payments to the U.S. over the next 10 years; these funds will be redirected toward tropical forest conservation in Indonesia.
Through the recently signed Millennium Challenge Corporation (MCC) Compact for Indonesia, the Government of Indonesia will implement a Green Prosperity Project totaling $332.5 million to support environmentally sustainable economic growth through enhancing management of forests, peat lands, and other natural resources and deployment of renewable energy.
In June 2011, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and Indonesia’s Ministry of Environment signed an MOU, expanding environmental cooperation and formalizing cooperation on the “Breathe Easy, Jakarta” initiative to improve air quality and protect public health.
Indonesia has the world’s greatest repository of marine biological resources and is one of the most important fisheries. It lies at the epicenter of the Coral Triangle, covering just 3 percent of the globe but containing more than half the world’s reefs and three-quarters of all known coral species. Fisheries generate some 20 percent of Indonesia’s GDP, and over 60 percent of the nation’s protein comes from the sea. The number of coastal fishers in Indonesia has increased by over 40 percent in the last 10 years.
President Yudhoyono called for a Coral Triangle Initiative (CTI) in August 2007. The Coral Triangle Initiative is a regional plan of action to enhance coral conservation, promote sustainable fisheries, and ensure food security in the face of climate change. In December 2007, the U.S. Government announced its support for the six CTI nations (Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Timor-Leste, Papua New Guinea, and Solomon Islands), and to date the United States is the largest bilateral donor to the CTI. Indonesia hosted the first-ever World Oceans Conference in Manado, North Sulawesi, May 11-15, 2009. The World Oceans Conference was also the venue for the Coral Triangle Initiative Summit, at which leaders from the six CTI nations launched the CTI Regional Plan of Action.
U.S. support to Indonesia’s globally important marine resources includes USAID’s five year $35 million Marine Resources Program, partnerships on ocean research and exploration, and maritime law enforcement capacity-building.
From June to August 2010, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) research vessel Okeanos Explorer and the Indonesian Baruna Jaya research fleet made a pioneering joint mission to the "Coral Triangle" in the Indo-Pacific region. NOAA works actively with Indonesian marine scientists on research and capacity-building efforts, including developing tsunami early detection systems, deploying ocean instruments that allow scientists to predict long-term climate change, exploring uncharted deepwater habitats, and anticipating and monitoring outbreaks of harmful toxins affecting our food sources. The United States and Indonesia are also working with private sector partners to develop sustainable alternative business models to improve food security and increase incomes in economically disadvantaged coastal communities.
Water
See Water profile of Indonesia
Total Renewable Water Resources: 2,838 cu km (1999)
Freshwater Withdrawal: Total: 82.78 cu km/yr (8% domestic, 1% industrial, 91% agricultural).
Per capita Freshwater Withdrawal:: 372 cu m/yr (2000)
Access to improved sources of drinking water: 80% of population
Access to improved sanitation facilities: 52% of population
Agriculture
Agriculture accounts for 43% of total employment and 15% of the GDP.
Agricultural products: Rice, cassava (tapioca), peanuts, rubber, cocoa, coffee, palm oil, copra; poultry, beef, pork, eggs.
Irrigated Land: 45,000 sq km (2003)
Resources
Indonesia has a wide range of mineral deposits and production, including bauxite, silver, and tin, copper, nickel, gold, and coal. Although the coal sector was open to foreign investment in the 1990s through coal contracts of work, new investment was closed again after 2000. A new mining law, passed in December 2008, opened coal to foreign investment again, although it eliminated the difference between foreign and domestic ownership structures. Total coal production reached 255 million metric tons in 2010, including exports of 198 million tons. Two U.S. firms operate two copper/gold mines in Indonesia, with a Canadian and a U.K. firm holding significant investments in nickel and gold, respectively. Although coal production has increased dramatically over the past 10 years, the number of new metals mines has declined. This decline does not reflect Indonesia's mineral prospects, which are high; rather, the decline reflects earlier uncertainty over mining laws and regulations, low competitiveness in the tax and royalty system, and investor concerns over divestment policies and the sanctity of contracts.
In early 2010, the Government of Indonesia also formally decided to become a candidate country of the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative (EITI), which will increase accountability and transparency in energy revenue transactions between the government and oil, gas, and mining firms.
Natural Resources: Petroleum, tin, natural gas, nickel, timber, bauxite, copper, fertile soils, coal, gold, silver
Energy
Indonesia left the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) in 2008, as it had been a net petroleum importer since 2004. Crude and condensate output averaged 944,000 barrels per day (bpd) in 2010, down slightly from 948,000 in 2009. In 2010, the oil and gas sector is estimated to have contributed $23.3 billion to government revenues, or 20.9% of the total. U.S. companies have invested heavily in the petroleum sector. Indonesia ranked third in world liquefied natural gas (LNG) exports production in 2010. Indonesia's oil, oil products, and gasturned positive in 2009 with a $29.4 million surplus, but have been negative since with a 2010 oil and gas trade deficit of $627 million and a deficit of$602 million deficit Jan-Nov 2011.
See Energy profile of Indonesia
| Production | Consumption | Exports | Imports | Reserves | |
| Electricity | 129 billion kWh (2008 est.) |
119.3 billion kWh (2007 est.) |
0 kWh (2009 est.) |
0 kWh (2009 est.) |
|
| Oil | 1.023 million bbl/day (2009 est.) |
1.115 million bbl/day (2009 est.) |
322,000 bbl/day (2009 est.) |
456,700 bbl/day (2009 est.) |
4.05 billion bbl (1 January 2010 est.) |
| Natural Gas | 85.7 billion cu m (2009 est.) |
45.2 billion cu m (2008) |
33.5 billion cu m (2008 est.) |
0 cu m (2008 est.) |
3.001 trillion cu m (1 January 2010 est.) |
Economy
Indonesia, a vast polyglot nation, has weathered the global financial crisis relatively smoothly because of its heavy reliance on domestic consumption as the driver of economic growth.
Increasing investment by both local and foreign investors is also supporting solid growth.
Indonesia has a market-based economy in which the government plays a significant role. There are 141 state-owned enterprises, and the government administers prices on several basic goods, including fuel, rice, and electricity.
In the mid-1980s, the government began eliminating regulatory obstacles to economic activity. The steps were aimed primarily at the external and financial sectors and were designed to stimulate employment and growth in the non-oil export sector. Annual real gross domestic product (GDP) growth averaged nearly 7% from 1987-97 and most analysts recognized Indonesia as a newly industrializing economy and emerging major market.
The Asian financial crisis of 1997 altered the region's economic landscape. With the depreciation of the Thai currency, the foreign investment community quickly reevaluated its investments in Asia. Foreign investors dumped assets and investments in Asia, leaving Indonesia the most affected in the region. In 1998, Indonesia experienced a negative GDP growth of 13.1% and unemployment rose to 15%-20%.
In the aftermath of the 1997-98 financial crisis, the government took custody of a significant portion of private sector assets via debt restructuring, but subsequently sold most of these assets, averaging a 29% return.
Indonesia has since recovered, albeit more slowly than some of its neighbors, by recapitalizing its banking sector, improving oversight of capital markets, and taking steps to stimulate growth and investment, particularly in infrastructure. GDP growth steadily rose in the following decade, achieving real growth of 6.3% in 2007 and 6.1% growth in 2008. Although the economy slowed to 4.6% growth in 2009 from the 6%-plus growth rate recorded in 2007 and 2008, by 2010 growth returned to a 6% rate and remained there in 2011.
During the recession, Indonesia outperformed most of its regional neighbors. The country experienced high inflation in early 2010, mainly due to food shortages, but agencies across the government acted quickly to ensure sufficiant food stocks.
The government made economic advances under the first administration of President Yudhoyono, introducing significant reforms in the financial sector, including tax and customs reforms, the use of Treasury bills, and capital market development and supervision, and in December 2011, Fitch Ratings Agency upgraded the country's credit rating to investment grade for the first time since 1997.
Indonesia's debt-to-GDP ratio in recent years has declined steadily because of increasingly robust GDP growth and sound fiscal stewardship. Indonesia still struggles with poverty and unemployment, inadequate infrastructure, corruption, a complex regulatory environment, and unequal resource distribution among regions.
In 2011 the government faces the ongoing challenge of improving Indonesia's insufficient infrastructure to remove impediments to economic growth, while addressing climate change mitigation and adaptation needs, particularly with regard to conserving Indonesia's forests and peatlands.
Indonesia’s improving growth prospects and sound macroeconomic policy have many analysts suggesting that it will become the newest member of the “BRIC” grouping of leading emerging markets. In December 2011, Fitch Ratings upgraded Indonesia’s sovereign debt rating to investment grade. A similar upgrade to investment grade is expected from Standard and Poor’s and Moody’s.
GDP: (Purchasing Power Parity): $1.121 trillion (2011 est.)
GDP: (Official Exchange Rate): $834.3 billion (2011 est.)
GDP- per capita (PPP): $4,700 (2011 est.)
GDP- composition by sector:
agriculture: 14.9%
industry: 46%
services: 39.1% (2011 est.)
Industries: Petroleum and natural gas, textiles, apparel, footwear, mining, cement, chemical fertilizers, plywood, rubber, food, and tourism.
Currency: Indonesian rupiah (IDR)
Economic Policy: After he took office on October 20, 2004, President Yudhoyono moved quickly to implement a "pro-growth, pro-poor, pro-employment" economic program, which he has continued in his second term. The State Ministry of National Development Planning (BAPPENAS) released a Medium-Term Development Plan for 2010-2014 focused on development of a “prosperous, democratic and just” Indonesia. The Medium-Term Development Plan targets average economic growth of 6.3%-6.8% for the period, reaching 7% or above by 2014, unemployment of 5%-6% by the end of 2014, and a poverty rate of 8%-10% by the end of 2014.
President Yudhoyono’s economic team in his second administration is led by Coordinating Minister for Economic Affairs Hatta Rajasa. Sri Mulyani Indrawati continued as Finance Minister until May 2010, when she resigned to take a senior position at the World Bank. She was succeeded by Agus Martowardojo, a well-respected banker who had led Indonesia’s largest state-owned bank. In July 2010, Indonesia’s DPR Commission XI approved the appointment of Darmin Nasution as Governor of Bank Indonesia, following a 14-month vacancy of the position after former Governor Boediono stepped down to become Yudhoyono’s running mate. In May 2010, President Yudhoyono established a National Economic Committee to provide strategic recommendations to accelerate national economic development and a National Innovation Committee to provide input and recommendations to increase national productivity, create a culture of innovation, and speed up economic growth.
In May 2011, President Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono launched the Master Plan for the Acceleration and Expansion of Indonesia’s Economic Development (MP3EI), to increase infrastructure and investment spending and to provide a roadmap for Indonesia to move up the value-chain and increase the level of innovation. The plan outlines Rp 4,000 trillion ($ 468.5 billion) in potential infrastructure projects in multiple sectors including hydroelectric and solar power, palm oil, new roads including toll motorways, mining , expansion of broadband internet, and nickel, cobalt and aluminum factories.
Indonesia's overall macroeconomic picture is stable. By 2004, real GDP per capita returned to pre-financial crisis levels and income levels are rising. In 2010, domestic consumption continued to account for the largest portion of GDP, at 56.7%, followed by investment at 32.2%, government consumption at 9.1%, and net exports at 1.6%. Domestic consumption has been the main growth driver from the expenditure side during the last half century while government consumption has hovered between 5-10% of GDP for most of that time.
In 2010, Indonesia has seen an increase in manufacturing output and exports, with relatively cheap labor and a complementary large and growing domestic market. Exports of natural resources, such as oil and gas, coal and crude palm oil (CPO) have made up around 50% of Indonesia’s exports and have been key drivers of growth. With the share of total exports to fast-growing emerging markets increasing and demand for commodities likely sustainable, export growth is likely to remain buoyant. In contrast, imports may grow even faster with infrastructure development andstrong domestic demand growth. ,. Net exports will likely continue to diminish and, with higher net income outflows (the counterpart to large portfolio inflows), it is expected the current account will eventually shift into deficit in the medium term.
Following a significant run-up in global energy prices in 2007-2008, the Indonesian Government raised fuel prices by an average of 29% on May 24, 2008 in an effort to reduce its fuel subsidy burden. Energy subsidies had been allocated Rp 223 trillion ($23 billion) in 2008, or 5.6% of GDP. The fuel price hikes, along with rising food prices, led consumer price inflation to a peak of 12.1% in September 2008. To help its citizens cope with higher fuel and food prices, the Indonesian Government implemented a direct cash compensation package for low-income families through February 2009 and an extra range of benefits including an expanded subsidized rice program and additional subsidies aimed at increasing food production. Citing high opportunity costs and poor targeting, the government has continued to signal its intent to reform subsidies. They plan to prohibit private cars from consuming subsidized fuels in Java and Bali beginning April 1, 2012. By 2015, the policy is expected to be implemented nationwide.
Banking Sector: Indonesia has 120 commercial banks (October 2011), of which 10 are majority foreign-owned and 28 are foreign joint venture banks while the number of bank branches has continuously increased from 6,397 in 2000 to 14,510 in 2011. The top 10 banks control about 62.4% of assets in the sector. Four state-owned banks (Bank Mandiri, BNI, BRI, BTN) control about 34.8% of assets (September 2011). The Indonesian central bank, Bank Indonesia (BI), announced plans in January 2005 to strengthen the banking sector by encouraging consolidation and improving prudential banking and supervision. BI hoped to encourage small banks with less than Rp 100 billion (about U.S. $11 million) in capital to either raise more capital or merge with healthier "anchor banks" before end-2010, announcing the criteria for anchor banks in July 2005. In October 2006, BI announced a single presence policy to further prompt consolidation. The policy stipulated that a single party could own a controlling interest in only one banking organization; exceptions would be granted in controlling two banks that do business under different principles, such as commercial and sharia, or one of which is a joint venture bank. Controlling interest is defined as 25% or more of total outstanding shares or having direct or indirect control of the institution.
BI has started to move toward Basel II standards in 2011, which focus on advancing other aspects of the Indonesian Banking Architecture (IBA) and has improved operations of its credit bureau to centralize data on borrowers. The IBA is a joint effort between BI, the Capital Market and Financial Institution Supervisory Board (BAPEPAM-LK), and the Ministry of Finance that was launched in 2004. A cornerstone program of the IBA is the structural reinforcement of the national banking system, aimed at building stronger capitalization for commercial banks to underpin its expansion and accelerate the required consolidation process among Indonesia’s 120+ banks. Another important banking sector reform was the decision to eliminate the blanket guarantee on bank third-party liabilities. BI and the Indonesian Government completed the process of replacing the blanket guarantee with a deposit insurance scheme run by the independent Indonesian Deposit Insurance Agency (also known by its Indonesian acronym, LPS) in March 2007. The removal of the blanket guarantee did not produce significant deposit outflows from or among Indonesian banks. Sharia banking has grown in Indonesia in recent years, but represented only 3.7% of the banking sector, about $14.4 billion in assets as of October 2011.
In October 2011, Indonesia has a new regulator to oversee a growing financial industry. The new regulator, Financial Services Supervisory Authority (OJK), will take over the supervision of banks, brokerages and insurance firms from the central bank (BI) and the capital market watchdog BAPEPAM-LK. By early 2013, OJK will have the power to supervise capital markets and non-banking institutions, while the oversight of commercial banks will start from 2014.
Exports and Trade: Indonesia's exports were $158 billion in 2010, a rise of 35% from $116.5 billion in 2009. The largest export commodities for 2010 were oil and gas (17.8%), minerals (14.9%), textile and footwear (8.9%), crude palm oil (8.54%), electrical appliances (8.2%), and rubber products (4.7%). The top destinations for exports for 2010 were Japan (16.3%), China (11.6%), the U.S. (11.1%), Singapore (8.5%), and Korea (8.3%). Meanwhile, total imports in 2010 were $136 billion, up from $96.83 billion in 2009. Indonesia is currently our 28th-largest goods trading partner with $23.4 billion in total (two-way) goods trade during 2010. The U.S. trade deficit with Indonesia totaled $9.5 billion in 2010 ($6.9 billion in exports versus $16.5 billion in imports).
Investment: President Yudhoyono and his economic ministers have stated repeatedly their intention to improve the climate for private sector investment to raise the level of GDP growth and reduce unemployment. However, in addition to general corruption and legal uncertainty, businesses have cited a number of specific factors that have reduced the competitiveness of Indonesia's investment climate, including: corrupt and inefficient customs services; non-transparent and arbitrary tax administration; inflexible labor markets that have reduced Indonesia's advantage in labor-intensive manufacturing; increasing infrastructure bottlenecks; and uncompetitive investment laws and regulations. In each of the past three years, the Government of Indonesia has announced a series of economic policy packages aimed at stimulating investment and infrastructure improvements and implementing regulatory reform. A new investment law was enacted in 2007, which contains provisions to restrict the share of foreign ownership in a range of industries. The 2010 iteration of the negative investment list includes long-awaited legal clarifications alongside limited liberalization. The clarifications include a continuous review of closed sectors for increased market access. The decree confirms that investment restrictions do not apply retroactively unless the new provisions are more beneficial to the investor. The changes also clarify that capital investments in publicly listed companies through the stock exchange are not subject to Indonesia's negative list unless an investor is buying a controlling interest.
In 2010, the Overseas Private Investment Corporation (OPIC) updated its 1967 investment support agreement between the United States and Indonesia by adding OPIC products such as direct loans, coinsurance, and reinsurance to the means of OPIC support which U.S. companies may use to invest in Indonesia. Over its 39-year history OPIC had committed more than $2.1 billion in financing and political risk insurance to 111 projects in Indonesia. Currently, OPIC is providing more than $75 million in support to seven projects in Indonesia in the energy, manufacturing, and services sectors and is also now supporting several new renewable resources/clean tech investment funds that are privately-managed and can look to invest in commercially-attractive projects in Indonesia.
On September 2, 2008, the DPR passed long-awaited tax reform legislation. The legislation reduced corporate and personal income tax rates as of January 1, 2009. Corporate income tax rates fell from 30% to 28% in 2009 and to 25% in 2010, with additional reductions for small and medium enterprises and publicly listed companies. The legislation raises the taxable income threshold for individuals, cuts the maximum personal income tax from 35% to 30%, and provides lower marginal personal income tax rates across four income categories. Taxes on dividends also fell from a maximum of 20% to a maximum of 10%. Long-planned labor reforms have been delayed.
The passage of a new copyright law in July 2002 and accompanying optical disc regulations in 2004 greatly strengthened Indonesia's intellectual property rights (IPR) regime. Despite the government's significantly expanded efforts to improve enforcement, IPR piracy remains a major concern to U.S. intellectual property holders and foreign investors, particularly in the high-technology sector. In March 2006, President Yudhoyono issued a decree establishing a National Task Force for IPR Violation Prevention. The IPR Task Force was intended to formulate national policy to prevent IPR violations and determine additional resources needed for prevention, as well as to help educate the public through various activities and improve bilateral, regional, and multilateral cooperation to prevent IPR violations. It has yet to fully realize these aims. In 2007, Indonesia was removed from the U.S. Trade Representative's "Priority Watch" list and placed on the "Watch" list. However, Indonesia was raised back to the Priority Watch List in 2009 due to an overall deterioration of the climate for IPR protection and enforcement and some concerns over market access barriers for IP products. There have not been signs of improvement in recent years. Amendments to the copyright and patent laws are scheduled to be discussed by Parliament in 2012.