Ha Long Bay, Vietnam
| Topics: |
Contents
- 1 IntroductionThe Ha Long Bay (106°58'-107°22'E, 20°45'-20°56'N) is a World Heritage Site (Ha Long Bay, Vietnam) in Vietnam.
- 2 Geographical location
- 3 Date and history of establishment
- 4 Area
- 5 Land tenure
- 6 Altitude
- 7 Physical features
- 8 Vegetation
- 9 Fauna
- 10 Cultural heritage
- 11 Local human population
- 12 Visitors and visitor facilities
- 13 Conservation value
- 14 Conservation management
- 15 IUCN Management Category
- 16 Further Reading
IntroductionThe Ha Long Bay (106°58'-107°22'E, 20°45'-20°56'N) is a World Heritage Site (Ha Long Bay, Vietnam) in Vietnam.
Geographical location
The Bay consists of a group of offshore islands, some 164 kilometers (km) south-east of Hanoi, in Tonkin Gulf. 106°58'-107°22'E, 20°45'-20°56'N
Date and history of establishment
Ha Long Bay was established as a historical and cultural relict and national scenic spot under Decision No. 313/VH VP on 28 April 1962, which was issued by the Minister of Culture. The bay was inscribed on the World Heritage List in 1994.
Area
 Ha Long Bay, Vietnam. (Source: Hanoi University of Technology (MICA Center))
Ha Long Bay, Vietnam. (Source: Hanoi University of Technology (MICA Center)) The entire bay is 150,000 hectares (ha).
Land tenure
Ha Long Bay is owned by the Government.
Altitude
The Bay ranges from sea level to 100-200 meters (m) high.
Physical features
Ha Long is a large bay with a multitude of limestone rocks emerging from the Hon Gai Sea, schistic islands from the Cam Pha Sea and a limited number of earth islands formed from decayed lateritic mountains. In total, there are 1,600 islands and islets, of which 1,000 have been named. Larger islands, rising to 100-200 m, are found in the south, with smaller islets of only 5-10 m height interspersed. To the east of the Bay medium size islands feature almost vertical slopes. Numerous caves and grottoes are found, with stalactites and stalagmites. The earth islands are inhabited.
Vegetation
There is a diverse flora throughout Ha Long, and primary tropical forest is found, mostly on the islands of Ba Mun and Cat Ba.
Fauna
Results from preliminary surveys indicate the presence of about 1,000 fish species. Mammals, reptiles and birds are found on the islands, especially the earth type.
Cultural heritage
Numerous archaeological sites have been found and at Giap Khau (Hon Gai) there is evidence to suggest occupation by the Hoa Binh Culture, some 10,000 years ago present. Archaeological sites at Tuan Chau, Ngoc Vung, Cai Dam, Dong Naim and Cat have revealed so many artifacts that they have been grouped under the term 'Ha Long Culture', typical of the northeastern coast of Viet Nam in the Neolithic Age. During prehistoric times, Ha Long was a significant port, located on the trade routes between China, Japan, and other countries in South East Asia.
Local human population
An unspecified population makes its living in and around Ha Long, which is a major center for fishing, agriculture and maritime transport. Steps have been taken to open new ports, factories and housing on the shore in line with a long-term economic development program.
Visitors and visitor facilities
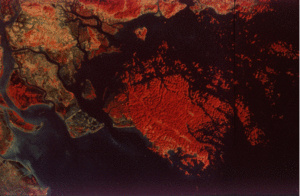 Satellite image of Ha Long Bay. (Source: Charles Sturt University)
Satellite image of Ha Long Bay. (Source: Charles Sturt University) Ha Long is extremely popular with both Vietnamese and international tourists. During 1990-1991, some one million visitors came to the Bay.
Conservation value
The principal conservation values appear to be scenic, landscape values; geological interest; biological diversity, especially in marine species; and archaeological remains.
Conservation management
The Ministry of Culture, Information and Sports is responsible for the overall management of Ha Long, although the People's Committee of Quang Ninh Province has the immediate responsibility for the administration and management of territory within its jurisdiction. Despite development in the region, it appears that Ha Long itself will be protected as a major tourist and cultural center.
Management constraints
There are two potential threats to the site. First, a new port is to be developed in the Bay that could route larger transport ships through the site. Second, a Singapore company has received a license to provide a large floating hotel in the site which will have further impacts on the already heavy tourist pressures on the Bay. The license for the floating hotel was withdrawn in 1997.
Staff
No information.
Budget
The national government provides a budget to the provincial People's Committee; more specific data are not available.
IUCN Management Category
- Unassigned
- Natural World Heritage Site - Criterion iii
Further Reading
- Anon. (1992). Nomination form of Ha Long - Vietnam. Minister of Culture, Information and Sports. 6 pp. Unpublished.
- Anon. (1995). Articles in the Viet Nam Economic News and Viet Nam News (19 October).
| Disclaimer: This article is taken wholly from, or contains information that was originally published by, the United Nations Environment Programme-World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC). Topic editors and authors for the Encyclopedia of Earth may have edited its content or added new information. The use of information from the United Nations Environment Programme-World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC) should not be construed as support for or endorsement by that organization for any new information added by EoE personnel, or for any editing of the original content. |