Fraser River, Canada
General Description
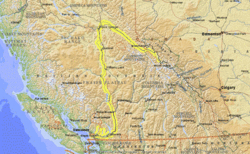
The Fraser River is the longest river in British Columbia, traveling almost 1400 kilometers (km) and sustained by a drainage area covering 220 000 sq. km. Its source is near Mt. Robson on the western slope of the Rocky Mountains in central British Columbia. The Fraser flows southwest, draining into the Pacific Ocean just south of Vancouver. It discharges 112 cubic kilometers of water per year, dumping 20 million tons of sediment into the Pacific (a sediment load of 0.179 kg per cubic meter).
River Course

The upper section of the river flows northwest in the Rocky Mountain trench, falling 1400 m over the first 150 km, then turns south through the Cariboo Mountains where it is joined by the Nechako River. The middle section flows south across the interior plains with the Quesnel and Thompson tributaries joining from the east, and the West Road and Chilcotin rivers from the west. It then enters the Fraser canyon, which is 115 km long, cutting across the Coast Ranges amid spectacular scenery via Hell's Gate. In its lower reaches, the Fraser is a meandering, braided stream bordered by rich farmland in a large floodplain covering over 2000 sq. km. At the mouth the river has formed a delta, dividing into two main channels on either side of Lulu Island.

The Fraser is believed to have flowed in its present course for four million years, although the glacial period caused considerable alterations in its flow patterns. Its modern drainage basin was only established about 8900 years before present (ybp) after the withdrawal of the Cordilleran Ice Sheet.
Human Impact

The [[river]s], [[stream]s] and estuary of the Fraser River Basin are among the most productive in the world and are home to an abundance of fish and wildlife. Eighty percent of British Columbia's economic production stems from the Fraser. Urban growth, industrial development and expanding demand for natural resources are causing environmental stress. The Fraser has been called a "resource in need of rescue" as its lower reaches have been extensively modified. Overfishing, damming for hydroelectric power, pollution (Water pollution) from pulp mills, mines and farms, runoff due to deforestation, and urban development in the floodplains are some of the threats that endanger the Fraser. Concern over these problems has led to initiatives such as the Fraser River Action Plan, a federal government program designed to achieve sustainable economic growth and improve fish and wildlife habitat.
History

The river's upper section was first explored by Sir Alexander Mackenzie in 1793. In 1807, Simon Fraser of the North West Company established Fort George (now Prince George) at the junction with the Nechako River and set out to trace the course of the Fraser (which he and others had mistakenly believed to be the Columbia River). The Fraser River was extensively used as a fur trade route and the fur industry is still important in the Prince George area. Fort Langley (now Vancouver) was established at the mouth of the river in 1827.