Equatorial Guinea
Countries and Regions of the World Collection  Equatorial Guinea is a nation of about 668,000 people in western Africa, composed of a mainland portion between Cameroon and Gabon, plus five inhabited islands. It is is one of the smallest countries on the African continent.
Equatorial Guinea is a nation of about 668,000 people in western Africa, composed of a mainland portion between Cameroon and Gabon, plus five inhabited islands. It is is one of the smallest countries on the African continent.
The terraine of Equatorial Guinea is coastal plains which rise to interior hills on the mainland. The islands are volcanic. The insular and continental regions are widely separated.
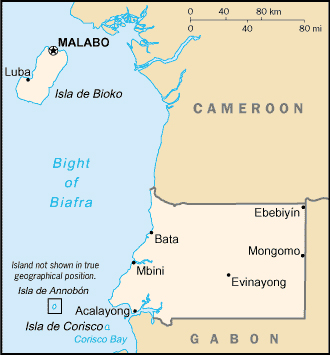 Source: CIA Source: CIA
|
Major environmental issues include:
- tap water is not potable; and,
- deforestation.
Equatorial Guinea is vulnerable to violent windstorms and flash floods.
Equatorial Guinea gained independence in 1968 after 190 years of Spanish rule.
President Teodoro Obian Nguema Mbasogo has ruled the country since 1979 when he seized power in a coup.
Although nominally a constitutional democracy since 1991, the 1996, 2002, and 2009 presidential elections - as well as the 1999, 2004, and 2008 legislative elections - were widely seen as flawed. The president exerts almost total control over the political system and has discouraged political opposition.
Equatorial Guinea has experienced rapid economic growth due to the discovery of large offshore oil reserves, and in the last decade has become Sub-Saharan Africa's third largest oil exporter.
Despite the country's economic windfall from oil production resulting in a massive increase in government revenue in recent years, improvements in the population's living standards have been slow to develop.
Contents
Geography
Location: Western Africa, bordering the Bight of Biafra, between Cameroon and Gabon
Geographic Coordinates: 2 00 N, 10 00 E
Area: 28,051 km2 (28,051 km2 land and 0 km2water)
Land Boundaries: 539 km. Border countries: Cameroon 189 km, Gabon 350 km
Coastline: 296 km
Maritime Claims:
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Natural Hazards: violent windstorms, flash floods
Volcanism: Santa Isabel (elev. 3,007 m), which last erupted in 1923, is the country's only historically active volcano. Santa Isabel, along with two dormant volcanoes, forms Bioko Island in the Gulf of Guinea
Terrain: Coastal plains rise to interior hills; islands are volcanic. The highest point is Pico Basile (3,008 m).
Climate: Tropical; always hot, humid.
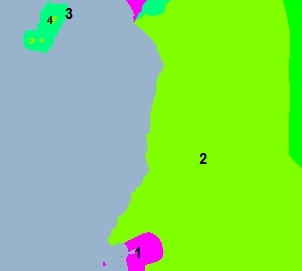
Ecology and Biodiversity
|
Mainland:
Bioko Island
|
Ecoregions of Equatorial Guinea. Source: World |
Government
|
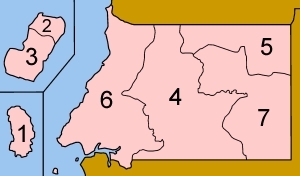
Type: Republic Capital: Malabo. Population: 128,000 (2009) Administrative Divisions: 7 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia);
|
Source: Wikimedia Commons |
Independence Date: 12 October 1968 (from Spain)
Legal System: partly based on Spanish civil law and tribal custom; has not accepted compulsory International Court of Justice jurisdiction
Suffrage: 18 years of age; universal
International Agreement
Equatorial Guinea is party to treaties on: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
People and Society
Population: 668,225 (July 2011 est.)
Age Structure:
0-14 years: 41.5% (male 140,946/female 136,294)
15-64 years: 54.4% (male 179,141/female 184,358)
65 years and over: 4.1% (male 11,880/female 15,606) (2011 est.)
Population Growth Rate: 2.641% (2011 est.)
Birthrate: 35.43 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
Infant Mortality: 77.3 deaths/1,000 live births
Deathrate: 9.03 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
Net Migration Rate: 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
Life Expectancy at Birth: 62.37 years
Total Fertility Rate: 4.91 children born/woman (2011 est.)
Languages: Spanish 67.6% (official), other 32.4% (includes French (official), Fang, Bubi) (1994 census)
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 87%
male: 93.4%
female: 80.5% (2000 est.)
Water
Total Renewable Water Resources: 26 cu km (2001)
Freshwater Withdrawal: 0.11 cu km/yr (83% domestic, 16% industrial, 1% agricultural)
Per Capita Freshwater Withdrawal: 220 cu m/yr (2000)
Access to improved water sources: 43% of population
Access to improved sanitation facilities:
Agriculture
Agricultural Products: coffee, cocoa, rice, yams, cassava (tapioca), bananas, palm oil nuts; livestock; timber
Irrigated Land: NA
Resources
Natural Resources: petroleum, natural gas, timber, gold, bauxite, diamonds, tantalum, sand and gravel, clay
Land Use:
arable land: 4.63%
permanent crops: 3.57%
other: 91.8% (2005)
Energy
| Production | Consumption | Exports | Imports | Reserves | |
| Electricity | 28 million kWh (2007 est.) |
26.04 million kWh (2007 est.) |
0 kWh (2007) |
0 kWh (2007) |
|
| Oil | 346,000 bbl/day (2009 est.) |
1,000 bbl/day (2009 est.) |
362,900 bbl/day (2007 est.) |
1,114 bbl/day (2007 est.) |
1.1 billion bbl (1 January 2010 est.) |
| Natural Gas | 6.67 billion cu m (2008 est.) |
1.5 billion cu m (2008 est.) |
5.17 billion cu m (2008 est.) |
0 cu m (2008 est.) |
36.81 billion cu m (1 January 2010 est.) |
| Source: CIA Factbook | |||||
Economy
The discovery and exploitation of large oil and gas reserves have contributed to dramatic economic growth but fluctuating oil prices have produced huge swings in GDP growth in recent years.
Forestry and farming are also minor components of GDP. Subsistence farming is the dominate form of livelihood.
Although pre-independence Equatorial Guinea counted on cocoa production for hard currency earnings, the neglect of the rural economy under successive regimes has diminished potential for agriculture-led growth (the government has stated its intention to reinvest some oil revenue into agriculture).
A number of aid programs sponsored by the World Bank and the IMF have been cut off since 1993 because of corruption and mismanagement.
The government has been widely criticized for its lack of transparency and misuse of oil revenues. However, in 2010, under Equatorial Guinea's candidacy in the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative, the government published oil revenue figures for the first time.
Undeveloped natural resources include gold, zinc, diamonds, columbite-tantalite, and other base metals.
Growth remained strong in 2008, when oil production peaked, but slowed in 2009-10, as the price of oil and the production level dropped.
Growth returned in 2011 stimulated by higher oil prices and large investments in public infrastructure and hotels.
GDP (purchasing power parity): $26.11 billion (2011 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate): $19.4 billion (2011 est.)
GDP - per capita (PPP): $19,300 (2011 est.)
GDP - composition by sector:
agriculture: 3.4%
industry: 91.7%
services: 4.9% (2011 est.)
Industries: petroleum, natural gas, sawmilling
Exports: petroleum, methanol, timber, cocoa
Export Partners: China 19.9%, US 17%, Spain 15%, France 9.3%, Cote d'Ivoire 6.2%, Italy 4.9% (2009)
Imports: petroleum sector equipment, other equipment
Import Partners: US 18.2%, Spain 12.7%, Cote d'Ivoire 11%, France 8.9%, South Korea 8.5%, China 7.1%, Italy 6.1%, UK 6% (2006)
Economic Aid Recipient: $39 million (2005)
Currency: Communaute Financiere Africaine franc (XAF)
Transportation
Airports: 5 (2007)
Pipelines: condensate 42 km; condensate/gas 5 km; gas 80 km; oil 54 km (2007)
Roadways: total: 2,880 km (2000)
Ports and Terminals: Bata, Malabo