Curacao
| Topics: |
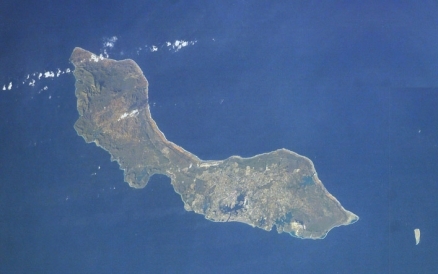
Countries and Regions of the World Collection  Curacao is an island with 142,000 people in the Caribbean Sea, 55 km off the coast of Venezuela. It is a constituent country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Curacao has full autonomy in internal affairs (granted in 2010) while the Dutch Government responsible for defense and foreign affairs
Curacao is an island with 142,000 people in the Caribbean Sea, 55 km off the coast of Venezuela. It is a constituent country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Curacao has full autonomy in internal affairs (granted in 2010) while the Dutch Government responsible for defense and foreign affairs
Curacao is a part of the Windward Islands (southern) group
Its major environmental issues include:
Originally settled by Arawak Indians, Curacao was seized by the Dutch in 1634 along with the neighboring island of Bonaire.
Once the center of the Caribbean slave trade, Curacao was hard hit by the abolition of slavery in 1863. Its prosperity (and that of neighboring Aruba) was restored in the early 20th century with the construction of the Isla Refineria to service the newly discovered Venezuelan oil fields.
In 1954, Curacao and several other Dutch Caribbean possessions were reorganized as the Netherlands Antilles, part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. In referenda in 2005 and 2009, the citizens of Curacao voted to become a self-governing country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The change in status became effective in October of 2010 with the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles.
Contents
Geography
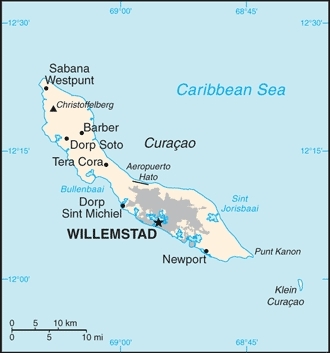
Location: Caribbean, an island in the Caribbean Sea - 55 km off the coast of Venezuela
Geographic Coordinates: 12 10 N, 69 00 W
Area: 444 sq km
Coastline: 364 km
Maritime Claims:
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive fishing zone: 12 nm
Natural Hazards: Curacao is south of the Caribbean hurricane belt and is rarely threatened
Terrain: generally low, hilly terrain. The highest point is Mt. Christoffel (372m).
Climate: tropical marine climate, ameliorated by northeast trade winds, results in mild temperatures; semi-arid with average rainfall of 600 mm/year
Ecology and Biodiversity
|
Caracao has two ecoregions:
See also: Common coral reef fishes of Curacao |
Ecoregions of Curacau (center - Bonair is the island |
Government
Dependency Status: constituent country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands; full autonomy in internal affairs granted in 2010; Dutch Government responsible for defense and foreign affairs
| The Queen Anna floating bridge at Willemstad. |
| Handelskade, Willemstad harbor. Source: Wikimedia Commons. |
Government Type: Parliamentary
Capital: Willemstad
Legal System: based on Dutch civil law system with some English common law influence.
People and Society
Population: 142,180 (est. January 2010)
Age Structure:
0-14 years: 21.1% (males 15,337/females 14,589)
15-64 years: 66.7% (males 42,896/females 51,998)
65 years and over: 12.2% (males 6,972/females 10,388) (2010)
Population Growth Rate: NA
Birthrate: NA
Death Rate: 8 deaths/1,000 population (2009)
Net Migration Rate: 1.27 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2008)
Life Expectancy at Birth:
males: 72.4 years
females: 80.1 years (2009)
Total Fertility Rate: 2.1 children born/woman (2009)
Languages: Papiamentu (a Spanish-Portuguese-Dutch-English dialect) 81.2%, Dutch (official) 8%, Spanish 4%, English 2.9%, other 3.9% (2001 census)
Resources
Natural Resources: calcium phosphates, aloes, sorghum, peanuts, vegetables, tropical fruit
Land Use:
arable land: 10%
permanent crops: 0%
other: 90%
Economy
Tourism, petroleum refining, and offshore finance are the mainstays of this small economy, which is closely tied to the outside world.
Although GDP grew slightly during the past decade, the island enjoys a high per capita income and a well-developed infrastructure compared with other countries in the region.
Curacao has an excellent natural harbor that can accommodate large oil tankers.
The Venezuelan state oil company leases the single refinery on the island from the government. Most of the oil for the refinery is imported from Venezuela and most of the refined products are exported to the US.
Almost all consumer and capital goods are imported, with the US, Brazil, Italy, and Mexico being the major suppliers.
The government is attempting to diversify its industry and trade and has signed an Association Agreement with the European Union to expand business there.
Poor soils and inadequate water supplies hamper the development of agriculture. Budgetary problems complicate reform of the health and pension systems for an aging population.
GDP: (Purchasing Power Parity): $2.838 billion (2008 est.)
GDP: (Official Exchange Rate): $5.08 billion $5.08 billion (2008 est.)
GDP- per capita (PPP): $15,000 (2004 est.)
GDP- composition by sector:
agriculture: 0.7%
industry: 15.5%
services: 83.8% (2010 est.)
Agricultural products: aloe, sorghum, peanuts, vegetables, tropical fruit
Industries: tourism, petroleum refining, petroleum transshipment facilities, light manufacturing
Currency: Netherlands Antillean guilders (ANG)