Air Pollution & Air Quality (main)
Air Pollution & Air Quality
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microscopic organisms into the atmosphere; in particular, when concentrations of those substances cause adverse metabolic change to humans or other species. The most common and widespread air pollutants include carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides and particulate matter.
Presently, the greatest occurrences of air pollution are in China, India, Indonesia, South Africa, Brazil, Mexico and Argentina. Each year air pollution is the cause of millions of human deaths, and even larger numbers of respiratory, circulatory, and cancer-related disease occurrences. Also, indoor air pollution is a significant source of human death and disease—mortality and morbidity—through indoor burning of wood and charcoal (especially in developing countries), tobacco smoking, radon trapping and a host of chemical substances found in paints, printing supplies and cleaning products.
An increase of natural background concentrations to concentrations of a few micrograms per cubic meter of such common pollutants as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides and ammonia may produce, for instance, increased growth of forests; however, higher levels of these chemicals produce such adverse effects on forests as decreased growth, greater susceptibility to diseases and pests, and ultimately to forest die-back.
-
 Featured Article
Featured Article  CFC-Ozone Puzzle: LectureSpeakers: F. Sherwood Rowland and Mario J. Molina Series: The John H. Chafee Memorial Lecture on Science and the Environment 1st National... More »
CFC-Ozone Puzzle: LectureSpeakers: F. Sherwood Rowland and Mario J. Molina Series: The John H. Chafee Memorial Lecture on Science and the Environment 1st National... More »
-
 Featured Article
Featured Article  Atmospheric lapse rateThe atmospheric lapse rate ( ) refers to the change of an atmospheric variable with a change of altitude, the variable being temperature unless specified... More »
Atmospheric lapse rateThe atmospheric lapse rate ( ) refers to the change of an atmospheric variable with a change of altitude, the variable being temperature unless specified... More »
-
 Featured Article
Featured Article 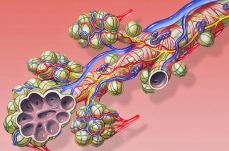 Respiration (Air Pollution & Air Quality)Respiration is the gas exchange effected by living organisms for the purpose of sustaining vital metabolic processes. In the case of most animals, oxygen is taken into the... More »
Respiration (Air Pollution & Air Quality)Respiration is the gas exchange effected by living organisms for the purpose of sustaining vital metabolic processes. In the case of most animals, oxygen is taken into the... More »
-
 Featured Article
Featured Article  Freeway proximity and autism?This study examined the association between autism and proximity of residence to freeways and major roadways during pregnancy and near the time of delivery, as a surrogate for air... More »
Freeway proximity and autism?This study examined the association between autism and proximity of residence to freeways and major roadways during pregnancy and near the time of delivery, as a surrogate for air... More »
-
 Featured Article
Featured Article  Air pollution (Air Pollution & Air Quality)Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microscopic organisms into the atmosphere; in particular, when concentrations of those substances cause... More »
Air pollution (Air Pollution & Air Quality)Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microscopic organisms into the atmosphere; in particular, when concentrations of those substances cause... More »
-
 Featured Article
Featured Article  Dark side of insulationBuilding insulation has become a modish activity in the western world since the 1980s. Considerable benefits can accrue in energy conservation, occupant comfort and reduction of... More »
Dark side of insulationBuilding insulation has become a modish activity in the western world since the 1980s. Considerable benefits can accrue in energy conservation, occupant comfort and reduction of... More »
-
 Featured Article
Featured Article  Heavy metal (Air Pollution & Air Quality)A heavy metal is any one of a number of elements that exhibit metallic properties, which includes transition metals lanthanides actinides as well as the metalloids Arsenic and... More »
Heavy metal (Air Pollution & Air Quality)A heavy metal is any one of a number of elements that exhibit metallic properties, which includes transition metals lanthanides actinides as well as the metalloids Arsenic and... More »
-
 Featured News Article
Featured News Article  Air pollution worsens drought and floodingAir Pollution a Culprit in Worsening Drought and Flooding Increases in aerosols can affect cloud development Increases in air pollution and other particulate matter... More »
Air pollution worsens drought and floodingAir Pollution a Culprit in Worsening Drought and Flooding Increases in aerosols can affect cloud development Increases in air pollution and other particulate matter... More »
-
 Featured Article
Featured Article  Indoor air pollution: sources, health effects...Introduction Indoor air pollution refers to the occurrence of contaminants within a home, workplace (or other inhabited enclosure) arising from such sources as fuel combustion... More »
Indoor air pollution: sources, health effects...Introduction Indoor air pollution refers to the occurrence of contaminants within a home, workplace (or other inhabited enclosure) arising from such sources as fuel combustion... More »
 Agriculture and Greenhouse Gases Last Updated on 2014-11-09 17:57:31 In both industrialized and developing nations, agricultural production of greenhouse gases (GHG) is a significant component of worldwide GHG emissions. There are major contributions to methane production from livestock grazing and rice farming, as well as incomplete combustion of petroleum products in mechanized agricultural equipment. In developing countries agricultural production of greenhouse gases is a much higher percentage of total GHG emissions than for developed countries. For example, rice farming in China and Southeast Asia and livestock grazing in several South American countries contributes proportionately more agricultural GHG than corresponding farming activity in most Western countries. Elimination of overgrazing practises and reduction of dependence of rice farming provide significant opportunities for reducing GHG emissions. There are also large contributions to... More »
Agriculture and Greenhouse Gases Last Updated on 2014-11-09 17:57:31 In both industrialized and developing nations, agricultural production of greenhouse gases (GHG) is a significant component of worldwide GHG emissions. There are major contributions to methane production from livestock grazing and rice farming, as well as incomplete combustion of petroleum products in mechanized agricultural equipment. In developing countries agricultural production of greenhouse gases is a much higher percentage of total GHG emissions than for developed countries. For example, rice farming in China and Southeast Asia and livestock grazing in several South American countries contributes proportionately more agricultural GHG than corresponding farming activity in most Western countries. Elimination of overgrazing practises and reduction of dependence of rice farming provide significant opportunities for reducing GHG emissions. There are also large contributions to... More »  Pollution (Air Pollution & Air Quality) Last Updated on 2014-11-09 17:40:04 Pollution is environmental contamination that results in harm or death to living organisms. Most pollution is in the form of chemical additions to air, water or soil; however, in modern times starting in the mid-twentieth century noise and light have been considered as pollution sources. Most pollution is man-made, with natural fluctuations in atmospheric composition, surface water bodies and soil considered temporal gyrations in the Earth's natural history. The chief driver of pollution is the massive growth in human population, which induces the proximate causes of intensive agriculture and extraordinary industrial output. The United Nations and the Blacksmith Institute[1] are two prominent organisations that tabulate locales of the greatest pollution intensity; while their listings do not correspond precisely, the overlap countries that both entities agree are the worst polluted... More »
Pollution (Air Pollution & Air Quality) Last Updated on 2014-11-09 17:40:04 Pollution is environmental contamination that results in harm or death to living organisms. Most pollution is in the form of chemical additions to air, water or soil; however, in modern times starting in the mid-twentieth century noise and light have been considered as pollution sources. Most pollution is man-made, with natural fluctuations in atmospheric composition, surface water bodies and soil considered temporal gyrations in the Earth's natural history. The chief driver of pollution is the massive growth in human population, which induces the proximate causes of intensive agriculture and extraordinary industrial output. The United Nations and the Blacksmith Institute[1] are two prominent organisations that tabulate locales of the greatest pollution intensity; while their listings do not correspond precisely, the overlap countries that both entities agree are the worst polluted... More »  Fossil fuel (Air Pollution & Air Quality) Last Updated on 2014-10-28 12:02:28 Fossil fuel is any naturally occurring carbon compound found in theEarth's crust that has been produced by anaerobic conditions and high pressures acting on dead organisms. These fossil fuel deposits are typically found at depths beneath the Earth surface or ocean floor of tens of meters to kilometers, and often occur in large agglomerations of gas, liquid or solid matter.Presently, combustion of fossil fuels account for over 86 percent of the world's artificial energy delivered to the human society. These fuels are considered non-renweable in that their natural creation time requires millions of years. The extraction, processing and combustion of fossil fuels causes significant adverse environmental consequences to biodiversity, air quality and water quality, as well as substantial impacts to human health and mortality. These processes also generate large... More »
Fossil fuel (Air Pollution & Air Quality) Last Updated on 2014-10-28 12:02:28 Fossil fuel is any naturally occurring carbon compound found in theEarth's crust that has been produced by anaerobic conditions and high pressures acting on dead organisms. These fossil fuel deposits are typically found at depths beneath the Earth surface or ocean floor of tens of meters to kilometers, and often occur in large agglomerations of gas, liquid or solid matter.Presently, combustion of fossil fuels account for over 86 percent of the world's artificial energy delivered to the human society. These fuels are considered non-renweable in that their natural creation time requires millions of years. The extraction, processing and combustion of fossil fuels causes significant adverse environmental consequences to biodiversity, air quality and water quality, as well as substantial impacts to human health and mortality. These processes also generate large... More »  Meteorology (Air Pollution & Air Quality) Last Updated on 2014-10-26 16:32:04 Meteorology is the scientific study of the atmosphere and physical processes of interaction with the Earth's crust, oceans and outer space. Meteorological phenomena are observable weather events which are investigated by the science of meteorology. The chief parameters comprised by the science of meteorology are: temperature, barometric pressure, humidity, sunlight and the gradients and interactions of each variable, as well as their temporal variability. The majority of Earth's observed weather is located in the troposphere. Different spatial scales are studied to determine how systems on local, regional, and global levels impact meteorological phenomena. Meteorology, climatology, atmospheric physics and atmospheric chemistry are sub-disciplines of the atmospheric sciences. Meteorology and hydrology compose the interdisciplinary field of hydrometeorology. Interactions... More »
Meteorology (Air Pollution & Air Quality) Last Updated on 2014-10-26 16:32:04 Meteorology is the scientific study of the atmosphere and physical processes of interaction with the Earth's crust, oceans and outer space. Meteorological phenomena are observable weather events which are investigated by the science of meteorology. The chief parameters comprised by the science of meteorology are: temperature, barometric pressure, humidity, sunlight and the gradients and interactions of each variable, as well as their temporal variability. The majority of Earth's observed weather is located in the troposphere. Different spatial scales are studied to determine how systems on local, regional, and global levels impact meteorological phenomena. Meteorology, climatology, atmospheric physics and atmospheric chemistry are sub-disciplines of the atmospheric sciences. Meteorology and hydrology compose the interdisciplinary field of hydrometeorology. Interactions... More »  Air quality in megacities Last Updated on 2014-09-18 16:40:27 Ambient air pollution in an increasingly urbanized world directly threatens the health of a large fraction of the world’s population. There is growing recognition that air-borne emissions from major urban and industrial areas influence both air quality and climate change on scales ranging from regional up to continental and global. Deteriorating urban air quality affects the viability of important natural and agricultural ecosystems in regions surrounding highly urbanized areas, and significantly influences regional atmospheric chemistry and global climate change. This challenge is particularly acute in the developing world where the rapid growth of megacities (cities having population equal to or more than 10 million) is producing atmospheric pollution of unprecedented severity and extent. For example, the deterioration of air quality is a problem that is directly experienced... More »
Air quality in megacities Last Updated on 2014-09-18 16:40:27 Ambient air pollution in an increasingly urbanized world directly threatens the health of a large fraction of the world’s population. There is growing recognition that air-borne emissions from major urban and industrial areas influence both air quality and climate change on scales ranging from regional up to continental and global. Deteriorating urban air quality affects the viability of important natural and agricultural ecosystems in regions surrounding highly urbanized areas, and significantly influences regional atmospheric chemistry and global climate change. This challenge is particularly acute in the developing world where the rapid growth of megacities (cities having population equal to or more than 10 million) is producing atmospheric pollution of unprecedented severity and extent. For example, the deterioration of air quality is a problem that is directly experienced... More » 