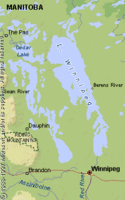
Lake Winnipeg, Manitoba
| Topics: |
Physical Attributes
 (Source: Biodiversity Institute of Ontario)
(Source: Biodiversity Institute of Ontario) - Altitude: 217 m above sea level
- Surface Area: 23,750 sq.km
- Mean Depth: 12 m
- Maximum depth: 36 m
- Volume: 284 cu. km
- Shoreline Length: 1,750 km
- Drainage Basin: 953,250 sq km
General Description
Lake Winnipeg is located on the northern boundaries of the Canadian prairies. Lakes Winnipeg, Winnipegosis and Manitoba represent the substantial residues of the once immense glacial Lake Agassiz. Lake Winnipeg is characterized by a wide northern basin and a narrow southern basin. Its main source of water is the sediment laden Red River, which enters its southern basin. The Nelson River, which carries water from the north basin, is the only outflow from the lake and eventually empties into Hudson Bay. The high turbidity of the lake is due to the resuspension of sediments due to its shallow waters, which are easily mixed by wind and waves. Lake Winnipeg is mostly used by humans for recreational purposes.
Watershed
 Old beach ridges found along the north shore of Lake Winnipeg, near Limestone Bay.(Source: Biodiversity Institute of Ontario)
Old beach ridges found along the north shore of Lake Winnipeg, near Limestone Bay.(Source: Biodiversity Institute of Ontario) The drainage basin of Lake Winnipeg is characterized by wheat fields and grasslands. Woodlands of elm, ash, basswood, maple and aspen are found in the immediate vicinity of the lake. Since the soils of the region are phosphorus rich, lake eutrophication is a natural event. This process, however, is accelerated by sewage treatment effluents as well as agricultural runoff. The City of Winnipeg, located on the inflowing Red River, has particularly contributed to the nutrient loading of the lake.