Energy profile of Cote d'Ivoire
Contents
Introduction Map of Cote d'Ivoire. (Source: EIA (Energy profile of Cote d'Ivoire) )
Côte d’Ivoire relies on oil, natural gas and hydropower to satisfy energy consumption demand. In addition to satisfying domestic demand, Côte d’Ivoire’s oil exports bolster overall economic activity in the country, and represents 28 percent of the country’s total export revenue. According to the World Bank, oil exports have surpassed cocoa exports, which traditionally have been the mainstay of Cote d’Ivoire’s economy. Côte d’Ivoire’s oil production, which is primarily located offshore, should increase slightly in 2007 and 2008.
Oil
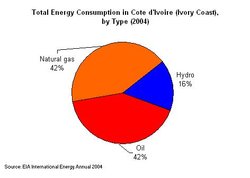 Total energy consumption of Cote d"Ivoire by type, 2004. (Source: EIA, International Energy Annual 2004)
Total energy consumption of Cote d"Ivoire by type, 2004. (Source: EIA, International Energy Annual 2004) Production
Côte d’Ivoire’s oil production increased from 56,000 barrels per day (bbl/d) in 2005 to 89,000 bbl/d in 2006. New fields coming online, as well as field enhancement work allowed for the increasing oil production. Production is forecast to increase slightly over the next 2-year period, with the possibility of reaching 110,000 bbl/d by 2008. According to estimates by Oil and Gas Journal (OGJ), Côte d'Ivoire had 100 million barrels of proven crude oil reserves as of January 2007. The vast majority of reserves are located offshore in shallow marine areas and in deep offshore waters.
Exports
In 2006, Côte d’Ivoire consumed 22,000 bbl/d and exported approximately 67,000 bbl/d of crude oil. According to official trade statistics as reported to the Global Trade Atlas , Western Europe imported over 50 percent of the country’s crude exports, with the majority going to Germany (Energy profile of Germany) (16,000 bbl/d) and France (10,000 bbl/d). The United States (Energy profile of the United States) imported 5,000 bbl/d of crude oil from Côte d’Ivoire in 2006. A ccording to FACTs Global Energy, China (Energy profile of China) imported 3,000 bbl/d. Côte d’Ivoire’s crude export blends are primarily medium and sweet with an API of 33°.
Field Development and Exploration
 Cote d'Ivoire's oil production and consumption, 1986-2006. (Source: EIA, International Energy Annual 2004, Short Term Energy Outlook April 2007)
Cote d'Ivoire's oil production and consumption, 1986-2006. (Source: EIA, International Energy Annual 2004, Short Term Energy Outlook April 2007) In August 2005, Canadian Natural Resources (CNR) brought its Baobab oil field onstream, with initial production averaging 48,000 bbl/d. According to IHS Energy GEPS Reports, Baobab achieved peak production of 52,000 bbl/d during the first quarter of 2006. However, due to sand control problems, Baobab was producing only 25,000 bbl/d during the later half of 2006. The offshore field is located in Block CI-40. CNR is operator of the block with a 57.6 percent interest and is joined with partners Svenska Petroleum Exploration (27.4 percent), and Petroci (15 percent). CNR also operators the Espoir field, which is located in Block CI-26. In 2006, the Espoir field produced an average of 31,000 bbl/d of oil. The field has a life expectancy of 20 to 25 years, with production expected to peak at 35,000 bbl/d of oil. The West Espoir field began producing in mid-2006 and is expected to peak at around 13,000 bbl/d of oil in 2007. CNR holds 58.7 percent interest in Block CI-26 and is joined with partners Tullow Oil (21.3 percent) and Petrosi (20 percent).
Devon Energy Corporation operates the Lion and Panthere fields on Block CI-11, which, according to IHS Energy GEPS Reports, netted the company 3,600 barrels of oil equivalent per day (boe/d) in 2006. Devon's partners on Block CI-11 include Petroci, Pluspetrol of Argentina (Energy profile of Argentina), and International Finance Corporation. In addition to Block CI-11, Devon holds interests (ranging from 35 percent to 80 percent) in several other blocks in Côte d'Ivoire. As of April 2007, Devon was considering selling its Côte d’Ivoire interests.
Refining and Downstream
According to OGJ, Côte d'Ivoire's one refinery, the SIR refinery, has refining capacity of 65,200 bbl/d and is located in Abidjan. An oil pipeline connects the SIR refinery to the Lion and Panther fields. The state currently owns 47.3 percent of SIR, and expects to retain a 10 percent interest if privatization occurs in the future. Burkina Faso owns a 5.39 percent stake in SIR, and Total, Shell, ExxonMobil and Chevron own the remainder. A petroleum products depot, adjacent to SIR, stores petroleum products for domestic use as well as for export. The depot is owned by the Société de Gestion des Stocks Petroliers de Côte d'Ivoire (Gestoci) and supplies products to Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger and Chad (Energy profile of Chad). Gestoci also operates fuel depots in Bouake and Yamoussoukro.
Sector Organization
In 1975, Côte d’Ivoire established the Société Nationale d'Operations Pétrolières de la Côte d'Ivoire (Petroci) to oversee the country’s oil operations. In 1998, the government re-structured Petroci by dividing it into four entities, which include: Petroci Holding (responsible for portfolio management of the oil sector), Petroci Exploration-Production (responsible for upstream hydrocarbon activities), Petroci-Gaz (responsible for the natural gas sector), and Petroci Industries-Services (responsible for all other related services). Foreign companies involved in Côte d’Ivoire’s oil sector include CNR, Dana Petroleum (U.K.), Devon Energy (U.S.), Oil India (Energy profile of India), Pluspetrol (Argentina (Energy profile of Argentina)), Sinopec (China (Energy profile of China)), and Tullow Oil.
Natural Gas
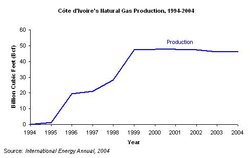 Cote d'Ivoire's natural gas production, 1994-2004. (Source: EIA, International Energy Annual 2004)
Cote d'Ivoire's natural gas production, 1994-2004. (Source: EIA, International Energy Annual 2004) According to 2007 estimates by OGJ, Côte d'Ivoire had one trillion cubic feet (Tcf) of proven natural gas reserves. Although exploration teams first discovered natural gas in Côte d'Ivoire in the 1980s, it was not until the mid-1990s that companies began to develop the resource. In 2004, Côte d'Ivoire produced 46 billion cubic feet (Bcf) of natural gas, all for domestic consumption. Côte d’Ivoire primarily uses its natural gas in the generation of electricity.
Côte d'Ivoire’s largest producing natural gas field is the Foxtrot field in offshore Block CI-27. According to IHS Energy, Foxtrot contains estimated natural gas reserves in place of 950 Bcf, and the field produced around 30 Bcf in 2005. The Block is operated by Foxtrot International (24 percent interest) and partners include Petroci (40 percent), SECI; a member of the Bouygues group of France (24 percent), and Energie de Côte d'Ivoire (Enerci); a joint venture of Gaz de France and EdF Group (12 percent).
CNR operates the Espoir field, which is located offshore in Block CI-26. CNR estimates Espoir's proven natural gas reserves to be 150 billion cubic feet (Bcf). CNR announced that development of the West Espoir field began in mid-2005, with first production online in July 2006. CNR holds 58.7 percent interest in the block and is joined with partners Tullow Oil (21.3 percent) and Petrosi (20 percent).
Electricity
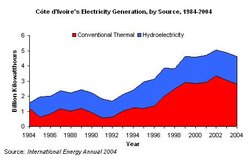 Cote d'Ivoire's electricity generation, by source, 1984-2004. (Source: EIA, International Energy Annual 2004)
Cote d'Ivoire's electricity generation, by source, 1984-2004. (Source: EIA, International Energy Annual 2004) As of January 1, 2004, Côte d'Ivoire had installed electric generation capacity of 919 megawatts (MW). In 2004, Côte d’Ivoire generated 4.6 billion kilowatt-hours (Bkwh) of electricity, while consuming 3.2 Bkwh. The majority of electricity is generated through conventional thermal stations (60 percent), with hydroelectricity comprising the remainder (40 percent). The 288-MW Azito power station, brought online in 1999, is located in Abidjan's suburbs and produces more than a third of the country's power. The phased construction of a third turbine in Azito has been delayed pending a rise in domestic and regional demand for electricity through the West African Power Pool (WAPP). Côte d’Ivoire’s main hydroelectric plants include Ayame I and II, Kossou, Taabo, Buyo and Grah.
Further Reading
- Abidjan Post
- allAfrica News - Côte d'Ivoire
- Columbia University - Côte d'Ivoire information page
- CIA World factbook
- Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- IMF - Côte d'Ivoire Information page
- Library of Congress - Côte d'Ivoire Country Study
- Mbendi - Côte d'Ivoire Profile
- University of Pennsylvania - Côte d'Ivoire Information page
- U.S. State Department Background Notes on Côte d'Ivoire
- U.S. State Department's Consular Information Sheet on Côte d'Ivoire
- U.S. Embassy in Côte d'Ivoire
- Washington Post Côte d'Ivoire page
- World Bank - Côte d'Ivoire Information page
| Disclaimer: This article is taken wholly from, or contains information that was originally published by, the Energy Information Administration. Topic editors and authors for the Encyclopedia of Earth may have edited its content or added new information. The use of information from the Energy Information Administration should not be construed as support for or endorsement by that organization for any new information added by EoE personnel, or for any editing of the original content. |