Energy profile of Arizona, United States
Contents
Quick Facts
- Arizona’s Palo Verde nuclear power plant is the highest capacity nuclear plant in the United States.
- Arizona power plants export large amounts of electricity to neighboring States, particularly to markets in Southern California.
- Arizona’s large desert areas offer the highest solar power potential in the country.
- Substantial coal production takes place in the Black Mesa Basin in northeast Arizona.
Overview (Energy profile of Arizona, United States)
Resources and Consumption
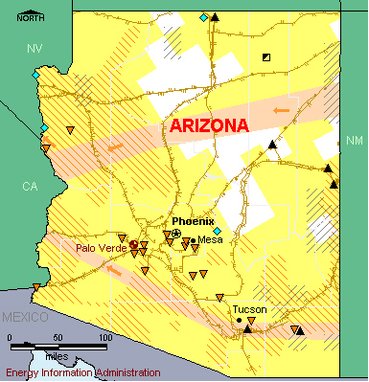 Map of Arizona's energy infrastructure. (Source: EIA)
Map of Arizona's energy infrastructure. (Source: EIA) Arizona has substantial coal deposits but few other fossil fuel resources. The coal deposits are concentrated in the Black Mesa Basin in the northeast part of the State. Arizona has one nuclear power plant and extensive solar energy potential. Its large desert areas offer the highest solar power potential in the country, and the Colorado River is a tremendous source of hydropower. While Arizona ranks near the middle of the States in total energy consumption, per capita energy consumption is low, and the State economy is not energy intensive. The transportation sector is the leading energy-consuming sector in the State.
Petroleum
Arizona’s annual crude oil production is minimal. Arizona has no refineries and receives its petroleum product supply via two pipelines, one from southern California and the other from El Paso, Texas. In summer 2003, a rupture on the line from El Paso caused an oil spill and shut down the section between Tucson and Phoenix. The accident caused shortages at Phoenix area motor gasoline fueling stations. A new refinery in Yuma County, Arizona, about 100 miles southwest of Phoenix, has been proposed and is expected to be operational by 2010. The refinery would receive crude oil supplies via a pipeline from Mexico and would ease motor gasoline supply constraints throughout the State. An oxygenated motor gasoline blend is used in the Tucson area during the winter and in Maricopa County (Phoenix) year-round.
Natural Gas
Arizona relies on interstate deliveries to meet most of its natural gas demand. Several major natural gas (Natural Gas Act of 1938, United States) pipelines from production areas in Texas and the Rocky Mountains supply Arizona markets as they flow west towards southern California. The electric power sector dominates natural gas consumption in Arizona, consuming roughly three-fourths of State supply. Winters are generally mild and almost two-fifths of Arizona households rely on natural gas as their primary energy (Energy quality) source for home heating.
Coal, Electricity, and Renewables
Arizona's coal production takes place primarily in the Black Mesa Basin and large volumes of coal move in and out of the State via rail. More than one-third of the coal produced in Arizona is delivered to coal-fired generators in Nevada. The remaining two-thirds, along with coal supplies transported primarily from New Mexico, are consumed at power plants in the State.
Coal-fired plants supply roughly two-fifths of Arizona’s demand for electricity. Natural gas-fired plants and nuclear power supply most of the remainder. Arizona’s sole nuclear power plant, the 3-unit Palo Verde plant, provides about one-fourth of the State's total electricity generation. Palo Verde is the Nation's largest nuclear plant and has the second-highest rated capacity of any power plant in the United States. The Glen Canyon and Hoover Dams, both located on the Colorado River in northern Arizona, provide hydroelectric power. Although Arizona leads the Nation in solar power potential, its solar-powered generation facilities are small and the State has not yet developed its solar resource on a large scale. More than one-half of Arizona households rely on electricity as their primary energy source for home heating.
Data
See the Energy Information Administration's Energy profile of Arizona for more information on the state's energy use, including data on Economy, Prices, Reserves & Supply, Distribution and Marketing, Consumption, and Environment.
Related Reports
- State Consumption, Prices and Expenditures (SEDS) tables that display comprehensive State data from as early as 1960 to the present.
- State Electricity Profiles tables that provide time series data from 1990 forward for key electricity indicators by State.
- State Compendium of Nuclear Power Plants State-by-State reports on the nuclear industry.
- Natural Gas Residential Choice Programs written overviews of the status of natural gas industry restructuring in each State, focusing on the residential customer class.
- Status of Electricity Restructuring by State annotated map showing details of the status of electricity restructuring in each State.
- Regional Energy Profiles reports and maps that explore regional variations in U.S. energy consumption.
References
- Notes & Sources: Maps | Data
- State Data Directory
- About State Energy Profiles
| Disclaimer: This article is taken wholly from, or contains information that was originally published by, the Energy Information Administration. Topic editors and authors for the Encyclopedia of Earth may have edited its content or added new information. The use of information from the Energy Information Administration should not be construed as support for or endorsement by that organization for any new information added by EoE personnel, or for any editing of the original content. |