Bearded Beggarticks (Biology)
Contents
Bearded Beggarticks
Bearded Beggarticks
Bidens aristosa (Michx.) Britt.
This article was produced by the USDA Forest Service, Forest Health Staff, Newtown Square, PA. WOW 01-21-05. Invasive Plants website.
Common Names
Bearded beggarticks, swamp marigold, tickseed sunflower, longbracted beggar-ticks
Native Origin
A naturalized invasive plant of the United States
Description
An upright annual or shortlived perennial in the aster family (Asteraceae) growing to a height of 1-5 feet and having slender, leafy, branched stems bearing several golden yellow, daisy-like flower heads. Leaves are approximately 6 inches long, opposite, pinnately divided, and segments toothed. Flowers head are 1-2 inches wide blooming August-October. Seed-like fruits are flat, ovoid, usually with 2 barbed spines.
Habitat
Wet meadows, roadside ditches, abandoned fields, low ground, open bottomlands, stream banks, and other damp areas such as ditches.
Distribution
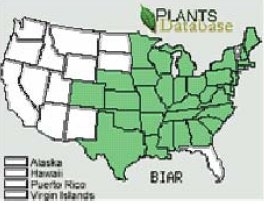 This species is reported from states shaded on Plants Database map.
This species is reported from states shaded on Plants Database map.
Ecological Impacts
The prickly fruit are known as beggars'-ticks with 2-pronged "stickers" that cling to clothing in autumn. This species spreads to displace native plant species.
Control and Management
- Manual - Mow to prevent encroachment.
- Chemical - It can be effectively controlled using any of several readily available general use herbicides such as glyphosate, dicaba, or picloram. Follow label and state requirements.
- Biocontrol.
 Flowers, Bearded beggarticks. Reference
Flowers, Bearded beggarticks. Reference
- http://plants.usda.gov ,
- http://www.enature.com/fieldguide , www.invasive.org ,
- Mid Atlantic Plant Council List, www.forestryimages.org
- www.hear.org/gcw/html/autogend/species/2709.HTM
Editor's Note
- Bearded Beggarticks. U.S. Forest Service.
