Arrow Bamboo (Biology)
Contents
Arrow Bamboo
Arrow Bamboo
Pseudosasa japonica (Sieb. & Zucc. ex Steud.) Makino ex Nakai
This article was produced by the USDA Forest Service, Forest Health Staff, Newtown Square, PA. WOW 07-09-05. Invasive Plants Website
Common Names
Arrow bamboo, hardy bamboo, slash bamboo, and metake
Native Origin
Japan & Korea and used to manufacture arrow shafts. It was introduced into U.S. from Japan in
1850 as an ornamental.
Description
Arrow bamboo is an evergreen perennial shrub or subshrub within group Monocot, of the Poaceae
family. Erect culms (canes) with a .5 inch diameter grow up to 18 feet in height. Large glossy, dark green leaves grow approximately 1 foot long by 1.5 inches wide. Plants reproduce vegetatively with far-reaching rhizomes.
Habitat
Arrow bamboo prefers moist, well drained soil and will grow in sun or shade. Habitat includes USDA zones 6-10 where people have planted it and peripheral areas where it has spread.
Distribution
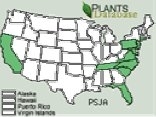 The National Park Service reports this species to be invasive in Maryland, West Virginia and Pennsylvania. It is distributed to the states shaded on the Plant Database map.
The National Park Service reports this species to be invasive in Maryland, West Virginia and Pennsylvania. It is distributed to the states shaded on the Plant Database map.
Ecological Impacts
Arrow bamboo has been widely planted for its ornamental value, and typically it expands, via underground rhizomes, into areas where it is not wanted. Rhizomes can grow 5 feet or more a year. Once established, it can aggressively invade parklands or woodlands adjacent to planted groves.
Control and Management
Do not plant exotic bamboo.
- Manual - Place barriers between plantings, break off or cut new shoots, mow around edges of groves to prevent spread
- Chemical - Use glyphosate herbicide in September of October and repeat applications for re-growth
References
- http://plants.usda.gov, http://pubs.caes.uga.edu,
- www.nps.gov/plants/alien/map/psja1.htm, Nonnative Invasive Plants of
Editor's Note
- Arrow Bamboo. U.S. Forest Service.
