Albedo (main)
From The Encyclopedia of Earth
Albedo
-
 Featured Article
Featured Article 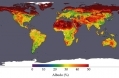 Albedo (Albedo)Introduction Albedo is the fraction of Sun’s radiation reflected from a surface. The term has its origins from the Latin word albus, meaning “white”.... More »
Albedo (Albedo)Introduction Albedo is the fraction of Sun’s radiation reflected from a surface. The term has its origins from the Latin word albus, meaning “white”.... More »
-
 Featured Article
Featured Article 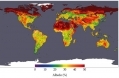 Albedo: Energy Reflected by EarthAlbedo (Latin, white) is the percentage of solar energy reflected by Earth. The albedo of various materials ranges from about 85% for pure, fresh snow to 5% for asphalt parking... More »
Albedo: Energy Reflected by EarthAlbedo (Latin, white) is the percentage of solar energy reflected by Earth. The albedo of various materials ranges from about 85% for pure, fresh snow to 5% for asphalt parking... More »
Recently Updated
 Pacific Coastal Mountain icefields and tundra Last Updated on 2014-05-13 19:12:00 WWF Terrestrial Ecoregions Collection The Pacific Coastal Mountain Icefields and Tundra ecoregion consists of a steep, very rugged range of mountains that stretches from the Kenai Penninsula along the Gulf of Alaska Coast and the Canadian/Alaskan border to the southern end of the Alaska panhandle. In Canada, this ecoregion encompasses the extreme southwestern corner of the Yukon Territory and parts of the coastal mountains in British Columbia south to Portland Inlet. Elevations range from sea level to over 4,500 meters (m), and slopes generally are steeper than seven degrees, ranging to over 20 degrees. The landscape of this ecoregion is dominated by mountains of great height. Most peaks reach between 2,100 m and 3,050 m, but some are over 5000 m (Mount Logan is 5,959 m, and King Peak is 5,175 m). In this high, extreme northern part of the... More »
Pacific Coastal Mountain icefields and tundra Last Updated on 2014-05-13 19:12:00 WWF Terrestrial Ecoregions Collection The Pacific Coastal Mountain Icefields and Tundra ecoregion consists of a steep, very rugged range of mountains that stretches from the Kenai Penninsula along the Gulf of Alaska Coast and the Canadian/Alaskan border to the southern end of the Alaska panhandle. In Canada, this ecoregion encompasses the extreme southwestern corner of the Yukon Territory and parts of the coastal mountains in British Columbia south to Portland Inlet. Elevations range from sea level to over 4,500 meters (m), and slopes generally are steeper than seven degrees, ranging to over 20 degrees. The landscape of this ecoregion is dominated by mountains of great height. Most peaks reach between 2,100 m and 3,050 m, but some are over 5000 m (Mount Logan is 5,959 m, and King Peak is 5,175 m). In this high, extreme northern part of the... More »  Albedo: Energy Reflected by Earth Last Updated on 2010-11-08 00:00:00 Albedo (Latin, white) is the percentage of solar energy reflected by Earth. The albedo of various materials ranges from about 85% for pure, fresh snow to 5% for asphalt parking lots or deep, still water. The global mean is about 29%. Satellite measurements provide a worldwide perspective on albedo. Clearly, deserts and snow-covered regions have a high albedo, whereas forests and agricultural fields have a low albedo. The overall trend seems to be that global albedo is decreasing, most likely due to diminishing snow and ice cover. This change in albedo will increase the amount of solar energy absorbed by the planet. This is an excerpt from the book Global Climate Change: Convergence of Disciplines by Dr. Arnold J. Bloom and taken from UCVerse of the University of California. ©2010 Sinauer Associates and UC Regents More »
Albedo: Energy Reflected by Earth Last Updated on 2010-11-08 00:00:00 Albedo (Latin, white) is the percentage of solar energy reflected by Earth. The albedo of various materials ranges from about 85% for pure, fresh snow to 5% for asphalt parking lots or deep, still water. The global mean is about 29%. Satellite measurements provide a worldwide perspective on albedo. Clearly, deserts and snow-covered regions have a high albedo, whereas forests and agricultural fields have a low albedo. The overall trend seems to be that global albedo is decreasing, most likely due to diminishing snow and ice cover. This change in albedo will increase the amount of solar energy absorbed by the planet. This is an excerpt from the book Global Climate Change: Convergence of Disciplines by Dr. Arnold J. Bloom and taken from UCVerse of the University of California. ©2010 Sinauer Associates and UC Regents More »  Albedo (Albedo) Last Updated on 2010-05-08 03:53:22 Introduction Albedo is the fraction of Sun’s radiation reflected from a surface. The term has its origins from the Latin word albus, meaning “white”. It is quantified as the proportion, or percentage of solar radiation of all wavelengths reflected by a body or surface to the amount incident upon it. An ideal white body has an albedo of 100% and an ideal black body, 0%. Visually we can estimate the albedo of an object’s surface from its tone or color. This method suggests that albedo becomes higher as an object gets lighter in shade. The data in Table 1 verifies this fact. Light toned surfaces like snow do have high albedos. Low albedos are associated with surfaces that appear dark colored to our eyes. Some dark colored surfaces include black-top roads, coniferous forest, and dark soil. Table 1 also indicates that the albedo of water varies with Sun... More »
Albedo (Albedo) Last Updated on 2010-05-08 03:53:22 Introduction Albedo is the fraction of Sun’s radiation reflected from a surface. The term has its origins from the Latin word albus, meaning “white”. It is quantified as the proportion, or percentage of solar radiation of all wavelengths reflected by a body or surface to the amount incident upon it. An ideal white body has an albedo of 100% and an ideal black body, 0%. Visually we can estimate the albedo of an object’s surface from its tone or color. This method suggests that albedo becomes higher as an object gets lighter in shade. The data in Table 1 verifies this fact. Light toned surfaces like snow do have high albedos. Low albedos are associated with surfaces that appear dark colored to our eyes. Some dark colored surfaces include black-top roads, coniferous forest, and dark soil. Table 1 also indicates that the albedo of water varies with Sun... More »