Environmental Protection Agency, United States
Contents
Introduction
The United States Environmental Protection Agency ("US EPA" or simply "EPA") is an independent agency of the federal government of the United States. One of the major environmental bodies of the national government, the US EPA is tasked with administering and enforcing over a dozen major environmental laws federal government in order to "protect and safeguard human health and the environment." Lisa Jackson, Administrator of the US EPA 2009 - The EPA is lead by an Administrator nominated by the President and confirmed by the U.S. Senate. The Administrator reports directly to the President of the United States. The current EPA Administrator is Lisa Jackson, she was nominated to the position by President Barack Obama (December 15, 2008), confirmed by the U.S. Senate (January 23, 2009) and sworn in on January 26, 2009. The US EPA has approximately 18,000 employees who carry out the work of the agency through offices organized around environmental themes (e.g., water, air, toxics, etc.), geographic regions, or by supporting the agency in a cross cutting fashion (e.g., research and development, adminstration, legal counsel, etc.)The US EPA has a budget of $7.8 Billion in Fiscal Year (FY) 2009. Nearly half of the EPA budget goes to support State level programs through a variety of grants. In addition, the agency received $7.2 Billion in additional "one-time" funding under the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (often referred to as the "Stimulus Bill"). President Obama has requested a budget for FY 2010 of $10.5 billion. (Environmental Protection Agency, United States)
Environmental Laws Administered by the EPA
The EPA administers over a dozen major environmental laws including:
- Clean Air Act
- Clean Water Act
- Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA, also known as Superfund) and Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act (SARA)
- Emergency Planning & Community Right-to-Know Act
- Environmental Research, Development & Demonstration Authorization Act
- Federal Insecticide, Fungicide & Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) and Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA)
- National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA)
- Ocean Dumping Act
- Oil Pollution Act of 1990
- Pollution Prevention Act of 1990
- Safe Drinking Water Act
- Solid Waste Disposal Act and Resource Conservation & Recovery Act (RCRA)
- Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA)
Organization
- Office of the Administrator
Environmental-themed offices
- Air and Radiation
- Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances
- Solid Waste and Emergency Response
- Water
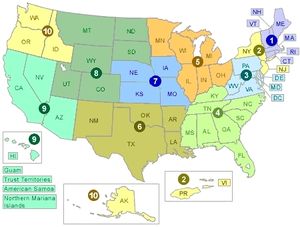
Regional Offices
- Region 1 - Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut
- Region 2 - New York, New Jersey, Puerto Rico, and Virgin Islands
- Region 3 - Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, West Virginia, and Virginia
- Region 4 - Kentucky, Tennessee, North Carolina, South Carolina, Mississippi, Alabama, Georgia, and Florida
- Region 5 - Ohio, Michigan, Wisconsin, Minnesota, Illinois, and Indiana
- Region 6 - New Mexico, Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, and Louisiana
- Region 7 - Nebraska, Iowa, Kansas, and Missouri
- Region 8 - Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Wyoming, Utah, and Colorado
- Region 9 - California, Nevada, Arizona, Hawaii, Guam, Trust Territories, American Samoa, and Northern Mariana Islands
- Region 10 - Washington, Oregon, Idaho and Alaska
Cross-Cutting:
- Administration and Resources Management
- Chief Financial Officer
- Enforcement & Compliance Assurance
- General Counsel
- Inspector General (audits and investigations of Agency programs and operations.)
- Research and Development
- International Affairs
Other Offices
- American Indian Environmental Office
- Science Policy Council
- Environmental Justice (focal point for communities comprised predominately of people of color or low income populations.)
History
See also Origins of the Environmental Protection Agency
The US Environmental Protection Agency was created by Reorganization Plan No. 3 of 1970, part of a major reorganization of the federal government carried out under President Nixon. It occurred at a time of rising public concern about the condition of the environment and its impact on human health which culminated in the first Earth Day celebration on April 22, 1970. The US EPA was formed by consolidating a number of existing programs that were scattered across several agencies. However, EPA quickly expanded in response to new environmental laws which assigned it new responsibilities and powers during the 1970s.
EPA Administrators
|
William Ruckelshaus |
1970-73 |
Office of Research and Development
The Office of Research and Development (ORD) is the principal scientific and research arm of the Environmental Protection Agency. ORD's Strategic Plan, describes its approach to fulfilling a mission to "conduct leading-edge research and foster the sound use of science and technology to fulfill EPA's mission to protect human health and safeguard the natural environment. This mission commits ORD to conduct its research in a way that will have a direct and meaningful impact on EPA's decisions and programs." ORD is organized into three national laboratories and four national centers located in a dozen facilities around the country and in Washington, DC. This includes:
- National Exposure Research Laboratory
- National Health and Environmental Effects Research Laboratory
- National Risk Management Research Laboratory
- National Center for Computational Toxicology
- National Center for Environmental Research
- National Center for Environmental Assessment
- National Homeland Security Research Center
- Office of Science Policy
- Office of the Science Advisor
- Other EPA Research Facilities