Moist Mid-latitude Climates with Mild Winters - C Climate Type
| Topics: |
Contents
Introduction
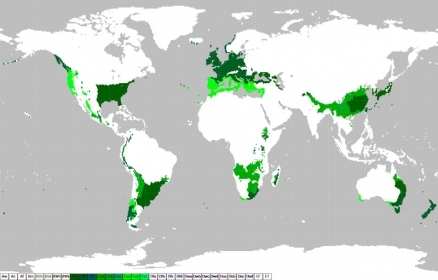
Within the Köppen Climate Classification System, this climate type generally has warm and humid summers with mild winters. Its extent is from 30 to 50° of latitude mainly on the eastern and western borders of most continents. During the winter, the main weather feature is the mid-latitude cyclone. Convective thunderstorms provide precipitation in the summer months.
See link for high reslution Köppen Climate Map to see the spatial distribution of the C climate type.
Several dominant minor types exist:
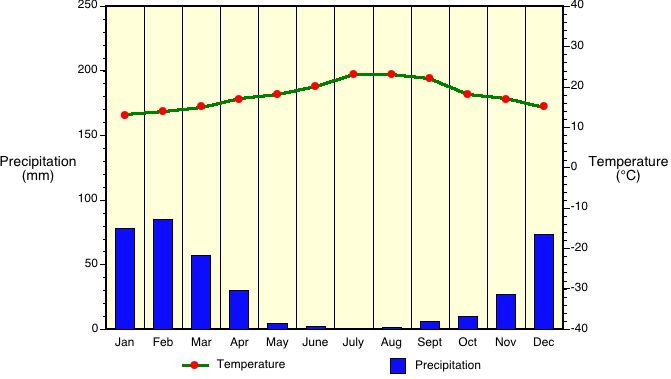
Cfa – Humid Subtropical
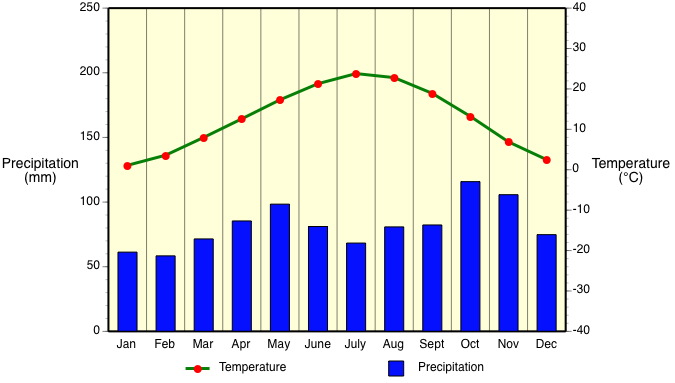
The humid subtropical climate (Cfa) has hot muggy summers and frequent thunderstorms. Winters are mild and precipitation during this season comes from mid-latitude cyclones. This climate type is quite common on the east coasts of continents. A good example of a region of the world with a Cfa climate is the southeastern USA. Average temperature of the warmest month is above 22°C (72°F). Average temperature of the coldest month is below 18°C (64°F) but above -3°C (27°F). Rainfall is equally spread out through the year.
Locations: Southeastern United States, northern Argentina, Uruguay, southern Brazil, southern Japan, and southern China.
Controlling Weather Factors: Mid-latitude cyclones in winter. Summer dominated by frequent thunderstorms because of the presence of Maritime Tropical air masses and intense surface heating.
Climate Characteristics: High humidity occurs in summer months. Summer climate is much like humid tropics. Frost can occasionally occur with the presence of Continental Polar air masses in winter. Precipitation varies from 650 to 2500 mm (26 and 98 in.).
Example:
Cfb/Cfc – Marine
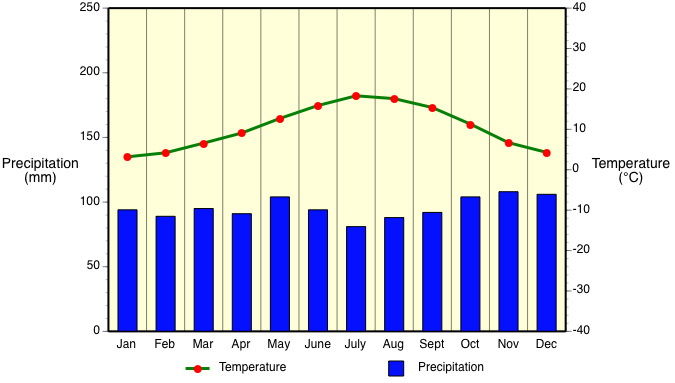
Cfb/Cfc marine climates are often found on the western coasts of continents. They have a humid climate with short dry summers. Heavy precipitation occurs during the mild winters because of the continuous presence of mid-latitude cyclones.
Cfb: Marine - Mild Winter
The average temperature of all months is less than 22°C (72°F). At least four months have an average temperature greater than 10°C (50°F). The average temperature of coldest month is below 18°C (64°F) but above -3°C (27°F). Precipitation is distributed evenly throughout year.
Cfc: Marine - Cool Winter
The average temperature of all months is less than 22°C (72°F). Only one to three months have an average temperature greater than 10°C (50°F). The average temperature of coldest month is below 18°C (64°F) but above -3°C (27°F). Precipitation is distributed equally throughout year.
Locations: Coastal Oregon, Washington, west coast of Canada and southern west coast of Alaska, central and northwest Europe, southern Chile, southern coast of South Africa, southeast Australia and New Zealand.
Controlling Weather Factors (both Cfb and Cfc): Mid-latitude cyclones influence weather for most of the year. Warm ocean currents keep these climates mild in winter and cool in the summer.
Climate Characteristics (both Cfb and Cfc): These climates have mild winters and cool summers with low annual temperature range. Frontal activity produces heavy cloud cover and high humidity during fall, winter, and spring. Long periods of rain and drizzle from frequent occurrence of mid-latitude cyclones. Frost can sometimes occur during the winter season.
Example:
Cwa/Cwb/Cwc – Dry Winter, Wet Summer
Cwa/Cwb/Cwc dry winter, wet summer climates are generally found in the interiors of continents at the mid-latitudes. They have a humid climate with short dry summers. Heavy precipitation occurs during the summers because of the seasonal presence of unstable humid air masses that encourage the development of thunderstorms. These climates are quite limited in their distribution.
Locations (Cwa/Cwb/Cwc): Interior of central Mexico, northwestern Argentina, parts of Bolivia, Nepal, northern India, northern Bangladesh, northern Myanmar, parts of China, Angola, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and eastern South Africa.
Controlling Weather Factors (Cwa/Cwb/Cwc): Climate is influenced by hot and unstable humid air masses that dominate generally in late spring, summer, and early fall. Relatively dry winter season is often due to the presence dry continental polar air masses.
Climate Characteristics (Cwa/Cwb/Cwc): High humidity occurs in summer months. Summer climate can be very similar to the humid tropics. Winters tend to be dry and cool.
Example:
Csa/Csb – Mediterranean
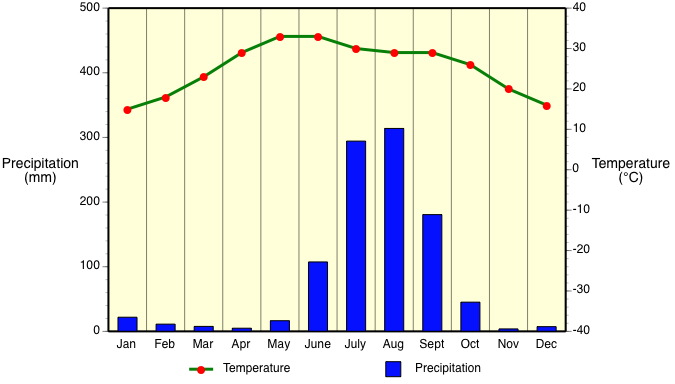
Mediterranean climates (Csa/Csb) receive rain primarily during winter season from the mid-latitude cyclone. Extreme summer aridity is caused by the sinking air of the subtropical highs and may exist for up to 5 months. Locations in North America are from Portland, Oregon to all of California.
Csa: Interior Mediterranean
Warm mid-latitude climate with distinctly dry hot summer caused by continental high-pressure influence. Average temperature of the coldest month is less than 18°C (64°F) but above -3°C (27°F). Wettest winter month has about 3 times more precipitation when compared to the driest summer month. Precipitation in driest summer month is less than 40 mm (1.6 in.). Warmest month has average temperature above 22°C (72°F) and at least 4 months have average temperatures above 10°C (50°F).
Csb: Coastal Mediterranean
Cool mid-latitude climate with distinctly dry cool summer caused by maritime high-pressure influence. Average temperature of the coldest month is less than 18°C (64°F) but above -3°C (27°F). Wettest winter month has about 3 times more precipitation when compared to the driest summer month. Precipitation in driest summer month is less than 40 mm (1.6 in.). No month with an average temperature above 22°C (72°F) and at least 4 months have average temperatures above 10°C (50°F).
Locations (both Csa and Csb): Interior and coastal areas of California, interior and coastal areas of Chile, area around the Mediterranean Sea, Iranian highlands, southwest tip of South Africa, and southern and southwestern regions of Australia.
Controlling Weather Factors (both Csa and Csb): Climate is influenced by subtropical highs in fall, summer, and spring and mid-latitude cyclones in winter.
Climate Characteristics (both Csa and Csb): Climate switches from mild, wet winters to hot, arid summers. This climate has a high percentage of sunshine. Diurnal range between maximum and minimum daily temperatures is quite large. Has some danger of frost during winter season. Coastal locations can often experience low clouds and fog.
Example:
Online Köppen Maps
References
- Aguado, E. and James E. Burt. 2010. Understanding Weather and Climate. Fifth Edition. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey.
- Ahrens, C. D. 2006. Meteorology Today. An Introduction to Weather, Climate, and the Environment. Eighth Edition. Thompson, Brooks/Cole. USA.
- Lutgens, F.K. and E.J. Tarbuck. 2004. The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology. NinthEdition. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey.
- Lydolph, P.E. 1985. The Climate of the Earth. Rowman and Allanheld Publishers, Totowa, New Jersey.
- Oliver, J.E. and J.J. Hidore. 2002. Climatology: An Atmospheric Science. Second Edition. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey.
- Peel, Murray C. 2011. Updated Köppen-Geiger Climate Map of the World. http://people.eng.unimelb.edu.au/mpeel/koppen.html