Chapter 11
Liquids and Solids
By Boundless
Dipole-dipole interactions are intermolecular attractions that result from two permanent dipoles interacting.
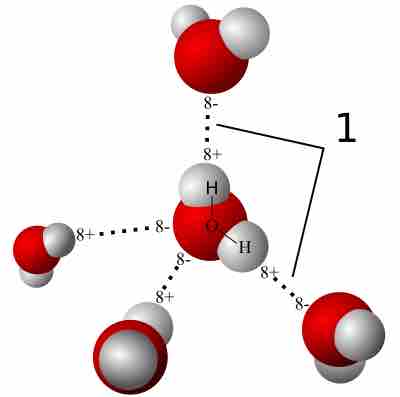
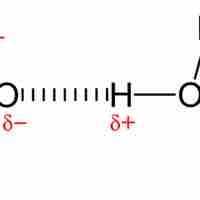
A hydrogen bond is a strong intermolecular force created by the relative positivity of hydrogen atoms.

The ion-dipole force is an intermolecular attraction between an ion and a polar molecule.

Dispersion forces are weak intermolecular forces caused by temporary dipoles.
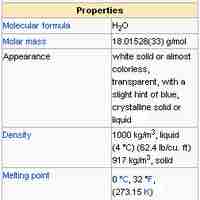
Water (H2O) has many interesting and unique properties.
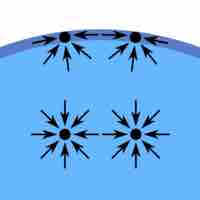
Surface tension is a contractive tendency of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force.
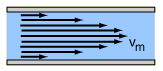
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow.
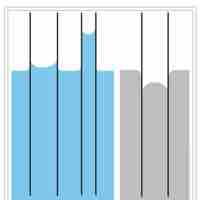
Capillary action is the ability of a liquid to flow in narrow spaces without the assistance of, and in opposition to, external forces.
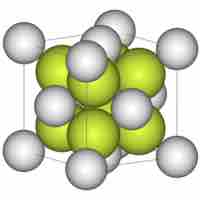
Consider the arrangement of spheres within a lattice to form a view of the structure and complexity of crystalline materials.

Closest packing refers to the most efficient way to arrange atoms in a crystalline unit cells.
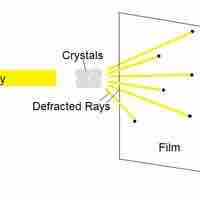
X-ray crystallography is a method of determining the arrangement of atoms within molecules.
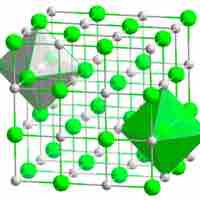
Ions in ionic crystals are bound together by electrostatic attraction.

Atoms in covalent solids are covalently bonded with their neighbors, creating, in effect, one giant molecule.

Molecules held together by van der Waals forces form molecular solids.
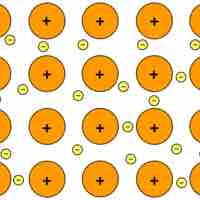
Metallic crystals are held together by metallic bonds, electrostatic interactions between cations and delocalized electrons.
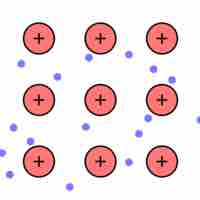
Metallic bonding may be described as the sharing of free electrons among a lattice of positively charged metal ions.
The process of adding substances to a pure semiconductor for the purposes of modulating its electrical properties is known as doping.
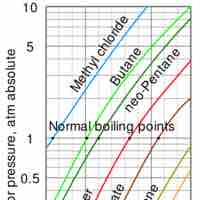
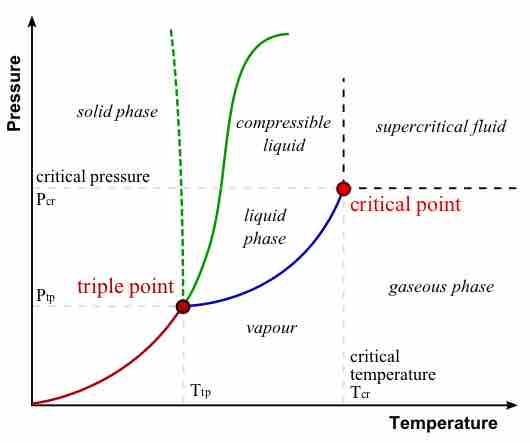
Vaporization of a sample of liquid is a phase transition from the liquid phase to the gas phase.
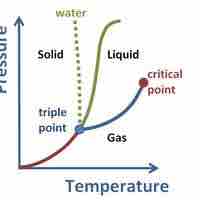
A supercritical fluid is a substance at a temperature and pressure above its critical point, where distinct liquid and gas phases do not exist.

Freezing is a phase transition in which a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered to its freezing point.

Sublimation is the phase transition from the solid to the gaseous phase, without passing through an intermediate liquid phase.
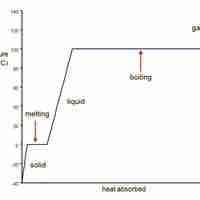
Water transitions from ice to liquid to water vapor as heat is added to it.