Excel 2010
Cell Basics
Introduction to cells and cell content
Cells are the basic building blocks of a worksheet. Cells can contain a variety of content such as text, formatting attributes, formulas, and functions. To work with cells, you'll need to know how to select them, insert content, and delete cells and cell content.
The cell
Each rectangle in a worksheet is called a cell. A cell is the intersection of a row and a column.
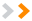
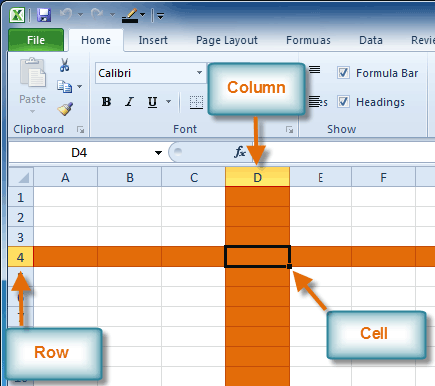 Row 4, Column D
Row 4, Column DEach cell has a name, or a cell address based on which column and row it intersects. The cell address of a selected cell appears in the Name box. Here you can see that C5 is selected.
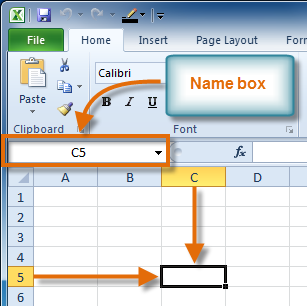 Cell address
Cell addressYou can also select multiple cells at the same time. A group of cells is known as a cell range. Rather than a single cell address, you will refer to a cell range using the cell addresses of the first and last cells in the cell range, separated by a colon. For example, a cell range that included cells A1, A2, A3, A4, and A5 would be written as A1:A5.
If the columns in your spreadsheet are labeled with numbers instead of letters, you'll need to change the default reference style for Excel. Review our Extra on What are Reference Styles? to learn how.
To select a cell:
- Click on a cell to select it. When a cell is selected, you will notice that the borders of the cell appear bold
 and the column heading and row heading of the cell are highlighted.
and the column heading and row heading of the cell are highlighted. - Release your mouse. The cell will stay selected until you click on another cell in the worksheet.
You can also navigate through your worksheet and select a cell by using the arrow keys on your keyboard.
To select multiple cells:
- Click and drag your mouse until all of the adjoining cells you want are highlighted.
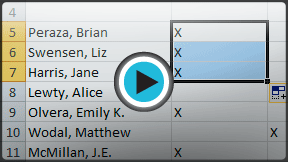
 Selecting multiple cells
Selecting multiple cells - Release your mouse. The cells will stay selected until you click on another cell in the worksheet.