
|
Early blight
Scientific name:
Alternaria solani
Type:
disease (fungal)
Common names:
Early blight, Alternaria blight, dry blight, leaf spots, seedling blight, damping-off, collar rot, hard-rot of fruits
Host plants: African Nightshade
Eggplant
Okra
Potato
Tomato
|
| General Information on Disease and Damage | Cultural practices | |||
| Biology and Ecology of Early Blight | Biopesticides and physical methods | |||
| Pest and Disease Management | Information Source Links |
General Information on Disease and Damage
Geographical distribution
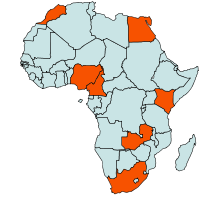 |
| Geographical Distribution of Early blight in Africa (red marked) |
Introduction
Early blight is one of the most common and serious diseases of potato and tomato. It is of particular importance in warm dry areas. Infection first occurs during periods of warm, rainy, humid weather. Increased damage may occur by secretions of toxins by pathogens.Symptoms of Early blight
All above ground parts of the plant can be affected. In seedbeds, pre- and post-emergence damping-off occurs. On young seedlings, collar rot may develop - it is characterized by girdling of the stem at the base of the plant. Affected seedlings are stunted and may wilt and die. When older seedlings are infected, stem lesions (spots) usually are restricted to one side of a stem and become elongated and sunken on stems and leaf petioles.Affected leaves exhibit brown spots with concentric rings. Leaf spotting first appears on the oldest leaves and progresses upward on the plant. Entire plant could be defoliated and killed.
Typical fruit spots occur at the stem-end as a rot that radiates out from the area of attachment between the calyx and the fruit. The spot is usually brown to black, firm, depressed and has distinct concentric rings.
Early blight is sometimes confused with Late blight. Late blight lesions are lighter, smaller and they do not have the circular ridged bands that early blight has.
|
|
Affected plant stages
all growth stages
Affected plant parts
all parts except roots
Symptoms by affected plant parts
Fruits/pods: spots. leaves: spots. Stems: external discoloration.
Biology and Ecology of Early Blight
Spores are formed on infected plant debris at the soil surface or on active lesions over a fairly wide temperature range, especially under alternating wet and dry conditions.
Infection occurs in warm, humid weather with heavy dews or rain. Periods of warm rainy weather, with temperatures between 21-24°C favour outbreaks of early blight.
Seriousness of early blight is dependant on weather conditions and crop variety. Early blight can develop quite rapidly under humid warm conditions and is more severe when plants are stressed by poor nutrition, drought, nematode attack or a heavy fruit load. Tomato plants become more susceptible with age particularly at fruiting. In tomato seedbeds collar rot may appear almost simultaneously on many plants indicating contamination of seeds or soil. Infection of potato tubers occurs through natural openings on the skin or through injuries. Tubers may come in contact with spores during harvest and lesions may continue to develop in storage.
Disease transmission
Early blight can be seed-borne, resulting in damping-off. Infected plant residues in the soil can carry the disease to the following season, particularly if the soil is dry. The spores are formed on the surface of infected tissue and can be spread by the wind and splashes of water. Pest and Disease Management
General illustration of the concept of infonet-biovision
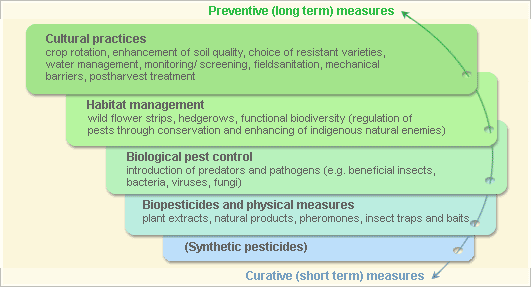
Further below you find concrete preventive and curative methods against Early blight.
Cultural practices
Use clean seed: Make sure that seeds/tubers for sowing and planting are certified and not taken from plants that were previously infected by the early blight. If possible, use potato and tomato varieties that are resistant to the disease.
Use tolerant or resistant varieties: Use plant varieties that are tolerant or resistant to early blight. Examples of tolerant / resistant tomato varieties in Kenya: 'Floradade', 'Hytec 36', 'Julius F1', 'Rio Grande', 'Rossol', 'Summerset F1', 'Zeal F1' and 'Zest F1'.
Destroy crop debris after harvest: Plough under all the crop residues after harvest to physically remove the inoculum (infection) source from the topsoil. Remove also weeds as they may serve as alternate hosts. Burn the infected material and plant debris.
Crop rotation: Fields should not be planted with tomato, Irish potato, or eggplant for at least 2 cropping seasons, since they are hosts to early blight. Also avoid planting new plots of these vegetables alongside old ones. Rotations with small grains, maize or legumes are preferable.
Avoid injury to potato tubers during harvesting and handling: Harvest potato tubers when the soil is not wet and when the vines are dry.
Practise proper plant spacing and staking: Prevent tomato plants from soil contact and prune and stake indeterminate varieties to promote good air circulation. Mulch determinate tomato varieties.
Water management: If possible avoid over-head irrigation. Otherwise, irrigate early in the morning so that the canopy would dry in the evening. In case of Irish potatoes, furrow irrigation should not be used especially after tuber formation.
Soil management: Use plenty of compost or well decomposed animal manures. Maintain soil fertility at optimal levels. Nitrogen and phosphorus deficiency can increase susceptibility to early blight. Also excess nitrogen could induce early blight infection.
Biopesticides and physical methods
Hot water treatment of seeds
Hot water treatment of seeds, where own seeds are used, could help reduce the incidence of seed-borne infection by early blight. It will also take care of other seed-borne problems caused by
pathogens such as Phoma spp., Septoria spp. and bacterial pathogens. Specified temperatures and recommended time for treatment should be strictly followed in order to maintain seed viability. Use a good thermometer or better ask for assistance from qualified personnel from your local extension office.
To make sure that the seed is not damaged it is advisable to test the germination of 100 heat-treated and 100 untreated seeds.
For more information on hot water treatment of seeds click here
Botanical fungicides
Botanicals are derived from plants. Many plant products are said to have fungicidal properties. They are natural products and most of them break down quickly on the leaves or in the soil. However, there is very little information on their effective dose rates, their impact on beneficial organisms or their toxicity to humans. Fermented Marigold extract:
Ingredients: Whole flowering plant, soap and water. Fill-in a drum with 1/2-3/4 full of flowering plants. Leave to stand for 5-10 days. Stir occasionally. Strain before use. Dilute the filtrate with water at a ratio of 1:2. Add 1 teaspoon of soap in every litre of the extract (Stoll, 2000).
Onion bulb extract:
Ingredients: 50 g of bulb onion and 1 litre distilled water. Finely chop the onion. Add to water. Mix well. Strain. Spray thoroughly on the infected plant, preferably early in the morning or late afternoon (Stoll, 2000).
For more information on plant extracts, including standard procedures for the preparation and application of plant extracts click here
Sulphur
Sulphur sprays are permitted as preventive fungicides in organic farming. The commercial product 'Thiovit®' can be used and has been reported by some farmers to have preventive effect on early blight (farmer experience in Kenya), albeit very harmfull to predatory mites.Copper
If the problem of blight is serious, fungicide spraying may be required. Ensure that persons dealing with fungicides are trained on safe use and handling of pesticides.There are many copper compounds that are used as fungicides. Most copper products are either based on copper oxychloride or copper hydroxide and are readily available in the market. Copper is accepted in organic farming provided that the number of applications is strictly followed and a proper soil amendment is observed to prevent copper accumulation in the soil
Note: Excessive use of copper based products can be detrimental to the soil. Constantly shake the sprayer while in the process of application of copper to prevent the solution from clogging. It is advisable to use dry flowable copper products now available in the Kenya pesticide market.
For more information on standard procedures for application of Copper and sulphur click here.
Information Source Links
- CABI. (2004). Crop Protection Compendium, 2004 Edition. © CAB International Publishing. Wallingford, UK. www.cabi.org
- Cornell University. Resource guide for organic insect and disease management. ISBN: 0-9676507-2-0. http://web.pppmb.cals.cornell.edu
- Ellis, B., Bradley, F. (1996). The organic gardener's handbook of natural insect and disease control. Rodale Press. Emmaus, Pennsylvania. ISBN: 0875967531
- HDRA. Henry Doubleday Research Association, UK. Infosheet on Mexican marigold www.organicgardening.org.uk and on Early blight www.gardenorganic.org.uk
- ICIPE (2003). Varela, A.M, Seif, A.A. and Lohr, B. (2003). A Guide to IPM in Tomato Production in Eastern and Southern Africa. pp. 144. ICIPE Science Press, Nairobi, Kenya. ISBN: 92 9064 149 5
- Nega, E., Ulrich, R., Werner, S. und Jahn, M. (2003). Hot water treatment of vegetable seed: an alternative seed treatment method to control seed borne pathogens in organic farming. Journal of Plant Diseases and Protection 110(3):pp. 220-234. orgprints.org
- Ohio State University. Early blight of potato and tomato. Factsheet. ohioline.osu.edul
- Oisat www.oisat.org
- Sridhar, S.; Arumugasamy, S.; Saraswathy, H.; Vijayalakshmi, K. (2002). Organic vegetable gardening. Center for Indian Knowledge Systems. Chennai.
- Stoll, G. (2000). Natural protection in the tropics. Margraf Verlag, Weikersheim. ISBN: 3-8236-1317-0
- TAMU. A guide to the identification of common problems: Tomato disorders. http://aggie-horticulture.tamu.edu
- University of Minnesota Extension. Early blight of potato and tomato. www.extension.umn.edu
- Vijayalakshmi, K.; Subhashini, B. and Koul, S. (1999). Plants in Pest Control: Garlic and onion. Centre for Indian Knowledge Systems, Chennai, India.
 Back
Back


