Computer Basics
Understanding Applications
Installing desktop applications
In order to work, an application usually has to be installed on your computer. Typically, installation is as simple as inserting the installation disc and following the instructions on the screen. For software downloaded from the Internet, you can usually double-click it after it is finished downloading and then follow the instructions on the screen. Many applications include a readme file (for example, readme.txt), which includes installation instructions and other information.
Use caution when downloading software, as it can contain viruses or other malware. If you have an antivirus program, you should scan the downloaded software before installing it. For more information, learn about Protecting Your Computer from Internet Threats in our Internet Safety tutorial.
Opening files with applications
Many applications are designed to open one or more types of files (or file formats). For example, Microsoft Word can create and edit Word documents. If you don't have the right kind of application, you won't be able to open a file. For example, if you are taking our Access 2010 tutorial, you will need to have Microsoft Access in order to open the sample database.
There are two main ways to open a file:
- Find the file on your computer, and double-click it. This will open the file using the default program.
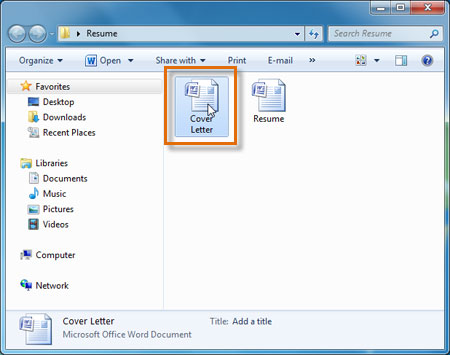 Double-clicking a file to open it
Double-clicking a file to open it - Open the application, then use the application to open the file. Once the application is open, you can go to the File menu at the top of the screen and select Open. This is useful because some files can be opened by several different applications, and this method allows you to choose which application to use.
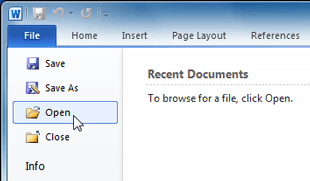 Opening a file within Microsoft Word
Opening a file within Microsoft Word
If you're not sure what a file's format is, you can look at the extension at the end of the file name (for example .docx, .txt, or .jpg). On some computers, the extension may be hidden, and you may need to look at the icon to determine the file format.