|
Micronutrients
|
Micronutrients
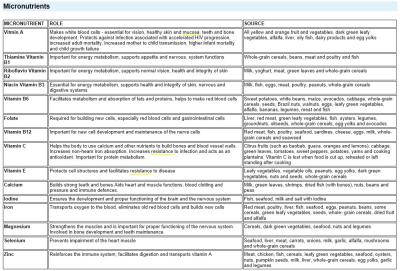
| MICRONUTRIENT | ROLE | SOURCE |
| Vitmin A | Makes white blood cells - essential for vision, healthy skin and mucosa, teeth and bone development. Protects against infection associated with accelerated HIV progression, increased adult mortality, increased mother to child transmission, higher infant mortality and child growth failure | All yellow and orange fruit and vegetables, dark green leafy vegetables, alfalfa, liver, oily fish, dairy products and egg yolks |
| Thiamine Vitamin B1 | Important for energy metabolism, supports appetite and nervous, system functions | Whole-grain cereals, beans, meat and poultry and fish |
| Riboflavin Vitamin B2 | Important for energy metabolism, supports normal vision, health and integrity of skin | Milk, yoghurt, meat, green leaves and whole-grain cereals |
| Niacin Vitamin B3 | Essential for energy metabolism, supports health and integrity of skin, nervous and digestive systems | Milk, fish, eggs, meat, poultry, peanuts, whole-grain cereals |
| Vitamin B6 | Facilitates metabolism and absorption of fats and proteins, helps to make red blood cells | Sweet potatoes, white beans, maize, avocados, cabbage, whole-grain cereals, seeds, Brazil nuts, walnuts, eggs, leafy green vegetables, alfalfa, bananas, legumes, meat and fish |
| Folate | Required for building new cells, especially red blood cells and gastrointestinal cells | Liver, red meat, green leafy vegetables, fish, oysters, legumes, groundnuts, oilseeds, whole-grain cereals, egg yolks and avocados |
| Vitamin B12 | Important for new cell development and maintenance of the nerve cells | Red meat, fish, poultry, seafood, sardines, cheese, eggs, milk, whole-grain cereals and seaweed |
| Vitamin C | Helps the body to use calcium and other nutrients to build bones and blood vessel walls. Increases non-heam iron absorption. Increases resistance to infection and acts as an antioxidant. Important for protein metabolism. | Citrus fruits (such as baobab, guava, oranges and lemons), cabbage, green leaves, tomatoes, sweet peppers, potatoes, yams and cooking plantains. Vitamin C is lost when food is cut up, reheated or left standing after cooking. |
| Vitamin E | Protects cell structures and facilitates resistance to disease | Leafy vegetables, vegetable oils, peanuts, egg yolks, dark green vegetables, nuts and seeds, whole-grain cereals |
| Calcium | Builds strong teeth and bones Aids heart and muscle functions, blood clotting and pressure and immune defences. | Milk, green leaves, shrimps, dried fish (with bones), nuts, beans and peas |
| Iodine | Ensures the development and proper functioning of the brain and the nervous system | Fish, seafood, milk and salt with iodine |
| Iron | Transports oxygen to the blood, eliminates old red blood cells and builds new cells | Red meat, poultry, liver, fish, seafood, eggs, peanuts, beans, some cereals, green leafy vegetables, seeds, whole- grain cereals, dried fruit and alfalfa |
| Magnesium | Strengthens the muscles and is important for proper functioning of the nervous system. Involved in bone development and teeth maintenance | Cereals, dark green vegetables, seafood, nuts and legumes |
| Selenium | Prevents impairment of the heart muscle | Seafood, liver, meat, carrots, onions, milk, garlic, alfalfa, mushrooms and whole-grain cereals |
| Zinc | Reinforces the immune system, facilitates digestion and transports vitamin A | Meat, chicken, fish, cereals, leafy green vegetables, seafood, oysters, nuts, pumpkin seeds, milk, liver, whole-grain cereals, egg yolks, garlic and legumes |
Information Source Links
- Human Vitamins requirement; Report of Joint FAO?WHO expert Consultation 2002 ( Bangkok Thailand)
- Phylis A. Balch, and James F Balch, Prescription fro Nutritional healing, 3rd Edition.
- Lee V, Ahmed F, Wada S, et al. Extent of vitamin A deficiency among rural pregnant women in Bangladesh. PUBLIC HEALTH NUTR. Jun 12 2008;1-6.
- D'Souza RM, D'Souza R. Vitamin A for treating measles in children. COCHRANE DATABASE SYST REV. 2002;(1):CD001479.
 Back
Back