Internet Safety
Protecting Your Financial Transactions
Security alerts and the SSL certificate
SSL certificate
Secure sites have an SSL certificate. An SSL certificate does two things. First, it acts like a virtual passport or driver's license. It means, "I am who I say I am". Second, it enables encryption. If a site does not have an SSL certificate, the address will begin with http instead of https, and your browser will not show a lock symbol. If it does have an SSL certificate, you can access it by clicking your browser's lock.
What should I look for on an SSL certificate?
The following is an example of an SSL certificate accessed by Firefox. Your browser's SSL certificate may look different from Firefox's, but you should have access to the same information.
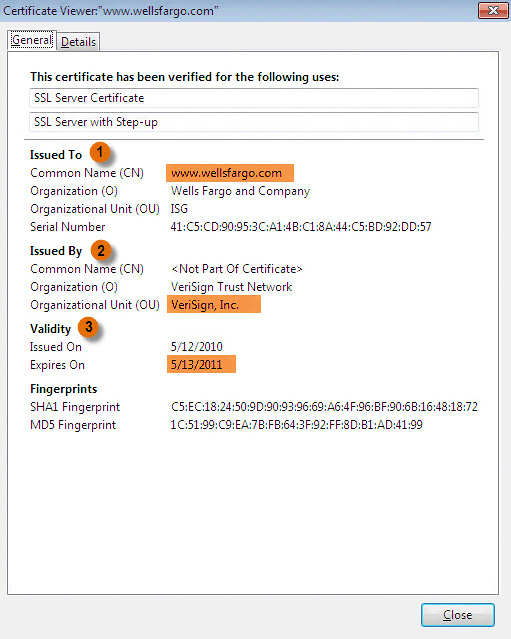 SSL Certificate for Firefox
SSL Certificate for Firefox- Issued To: Check here to make sure the website you are doing business with matches the website on the certificate.
- Issued By: Make sure the certificate authority that issued the SSL certificate to the website is trustworthy. There are many different certificate authorities, and like all companies some are more trustworthy than others. Verifiable SSL certificate authority companies that you are likely to see include VeriSign, RSA Data Security, Thawte, Geotrust, GoDaddy, and Comodo.
- Validity: Make sure the SSL certificate is not expired. If it is expired, your information is not guaranteed to be encrypted.