Internet 101
Browser Basics
Introduction
A web browser is the tool you use to access the World Wide Web. In order to get the most out of the Web, it's important to understand the various features of a browser.
In this lesson, we'll talk about navigating the Web with a browser, downloading files, bookmarking your favorite websites, tabbed browsing, and plug-ins.
Browser Basics
To get the most out of your web browser, there are some basic concepts that you need to be familiar with, including navigation, downloading, bookmarking, tabbed browsing, and plug-ins.
Common web browsers
Today, Chrome and Firefox are the most popular web browsers. Other browsers include Internet Explorer, Safari, and Opera. Each one has its own look and feel, but they have the same goal: to display webpages correctly. For most webpages, any well-known browser will work.
- Chrome:
 Chrome
Chrome - Internet Explorer:
 Internet Explorer
Internet Explorer - Firefox:
 Firefox
Firefox
Like most modern programs, browsers use a Graphical User Interface (GUI), which means you can navigate by pointing and clicking with a mouse instead of just typing. Some devices like mobile phones use different types of GUIs, such as touchscreens. However, many of the principles remain the same. In the images below, you can compare a point-and-click interface with a touchscreen interface.
 Point-and-click interface
Point-and-click interface Touchscreen interface
Touchscreen interfaceFor tips that are more specific to your browser, you can check out our tutorials on Internet Explorer, Chrome, and Firefox.
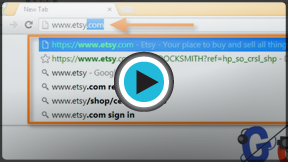
Navigating to a website Watch the video (2:20).
To get the most out of your web browser, there are some basic concepts you need to be familiar with.
Address bar
Browsers have an address bar that shows the web address (also called a URL) of the page you are on. To go to a different page, you can type an address in the address bar and then press Enter (or Return).
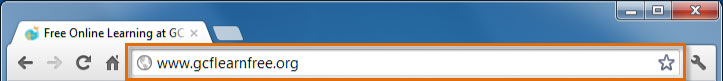 The address bar
The address barLinks
Most of the time, you will get to a different page by clicking on a link. A link can be text or an image, and it's usually formatted to stand out so you know to click on it. Many text links are blue, and they may also be underlined.
For example, this is a link. It will open a webpage in a new window, and you can close it to come back to this page.
A link may lead to another webpage, or it could lead to a document, video, or any other type of file. If you're not sure if something's a link, hover the mouse over it. The pointer should change to a hand symbol.
 Hovering over a link
Hovering over a linkNavigation buttons
Sometimes after you click on a link, you might want to go back to the previous page. You can do this using your browser's Back button. Once you've pressed the Back button, you can press the Forward button to follow the link again.
 The Back and Forward buttons
The Back and Forward buttonsWhen you use the Back and Forward buttons, your browser may use its web cache to display the page. The web cache stores recently viewed webpages so they don't need to be downloaded again. This is good because it speeds up your web browsing, but sometimes you want to see the most up-to-date information on the page. You can use the Refresh button (sometimes called Reload) to tell the browser to load the page again.
 The Refresh button
The Refresh buttonThere are some instances when you don't want to use the navigation buttons. For example, with some online stores you shouldn't refresh the page after purchasing an item because it could cause you to purchase the item twice.
Search bar
Some browsers have a built-in search bar for performing web searches. However, many browsers have combined the address bar and the search bar into a single bar where you can type web addresses or search terms. We'll talk more about web searches in the next lesson.
 The Search Bar in Firefox
The Search Bar in FirefoxSome websites may track your activities online, usually for marketing purposes. It's also possible to encounter malicious sites that could harm your computer. For more tips, check out Staying Safe While Browsing in our Internet Safety tutorial.
Adding bookmarks
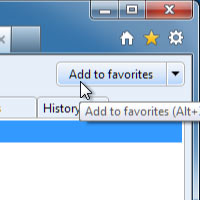
If you've found a page you'd like to go back to later, you can add it to your bookmarks (sometimes called favorites). Bookmarks make it easier to find a page later on. Instead of having to remember the exact web address, you can just scroll through your bookmarks until you see the name of the page.
- In Internet Explorer 9, you can add a bookmark by clicking the star icon and then selecting Add to Favorites. Other browsers are similar, but they may use different wording.
 Adding a bookmark
Adding a bookmarkBrowsing history
Suppose you visited a webpage a few days ago but forgot to bookmark it. You can find the page again by using your history, which is a list of websites you've visited. Usually, pages will stay in the history for a certain number of days. To maintain privacy, you can delete your history at any time.
Viewing your history
- To view your history in Internet Explorer 9, click the star icon, then select the history tab.
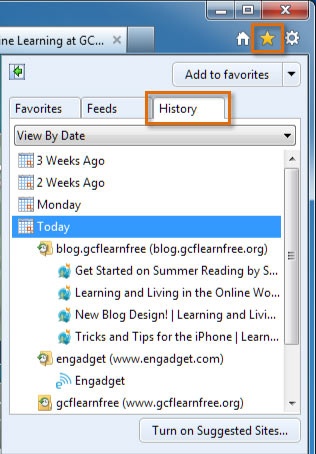 Browsing history
Browsing historyDeleting your history
- In Internet Explorer 9, click the gear icon to open the Tools menu.
- Click Safety, then select Delete browsing history....
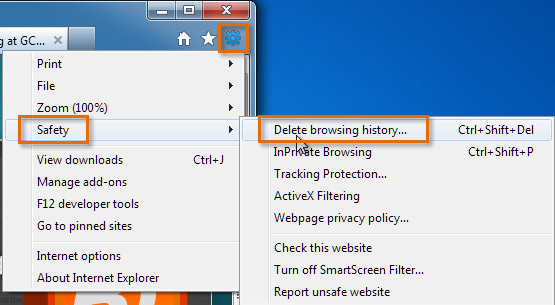 Deleting browsing history
Deleting browsing historyIf you're using a browser other than Internet Explorer, the process of viewing and deleting history will be slightly different.
Tabbed browsing
Many browsers allow you to open a link in a new tab. This allows you to keep the current page open instead of going directly to the new page. For example, if you're reading an article that has a link in it, you can open the link in a new tab so you can finish reading the article. Then you can go to the new tab to view the link.
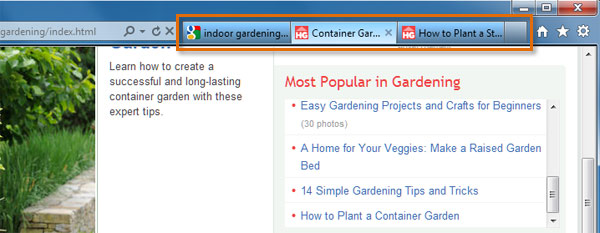 A browser window with three open tabs
A browser window with three open tabsTabs are designed to make browsing more convenient. You can open as many links as you want, and they'll stay in the same browser window instead of cluttering up your screen with multiple windows.
- To open a link in a new tab, right-click the link and click Open in new tab (the wording may vary from browser to browser). To close a tab, click the "X" on the tab.
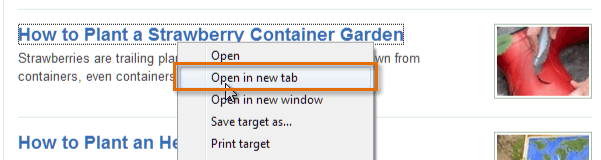 Opening a link in a new tab
Opening a link in a new tabDownloading files
Your browser can display many different types of documents, media, and other files. But there are times when you'll want to access a file outside of your browser. Downloading enables you to do this by putting the file on your computer so you can access it.
For example, suppose you needed to complete and print a form you found online. You could download it to your desktop, then open it with the appropriate program (such as Microsoft Word) to edit it.
How to download a file
If you click on a link to a file, it may download automatically, but sometimes it just opens within your browser instead of downloading. To prevent it from opening in the browser, you can right-click the link and select Save Target As (different browsers may use slightly different wording). You'll be able to choose the folder where the file is saved.
Because the process of downloading a file varies from site to site, it may require some trial and error.
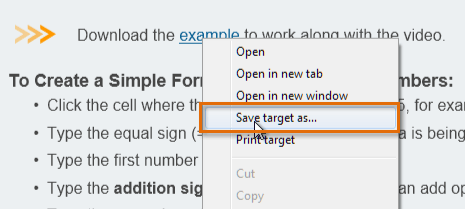 Downloading a file
Downloading a fileFor various reasons, many sites do not allow you to download content. For example, YouTube does not offer a way to download its videos.
To learn more about keeping your computer safe while downloading files from the Internet, check out our Internet Safety tutorial.
Saving images
Sometimes you might want to save an image to your computer. To do this, right-click the image and select Save Picture As.
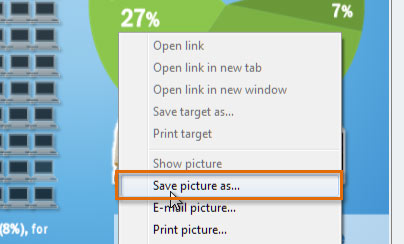 Saving a picture
Saving a pictureSome sites do not allow images to be saved to your computer.
Plug-ins
Plug-ins are programs that are installed in your browser that enable it to play various types of media, such as video. Examples of plug-ins include Quicktime Player and Flash Player. If you don't have the correct plug-in, the site will usually provide a link to download the plug-in.
Once you have the necessary plug-ins, you'll be able to enjoy streaming video from sites such as Hulu, and play games on sites such as Newgrounds.
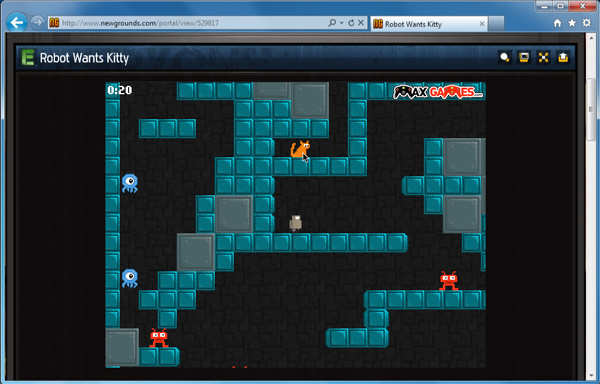 Playing a Flash game in a browser
Playing a Flash game in a browserYour browser may have come with some plug-ins already installed.