Excel 2007
Using Conditional Formatting
Conditional formatting
Watch the video! (5:17 min)
Download the example to work along with the video.
The conditional formatting options
You have many conditional formatting rules, or options, you can apply to cells in your spreadsheet. Each rule will affect selected cells differently. Before you choose a formatting rule, you must identify what questions you are trying to answer. For example, in a sales spreadsheet you might want to identify the salespeople with lower than average sales. To do this, you need to choose a conditional formatting rule that will show you this answer. Not all of the options will provide you with this information.
Some of the conditional formatting options include:
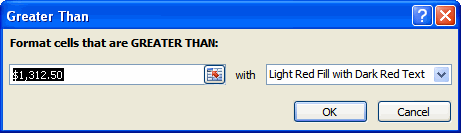
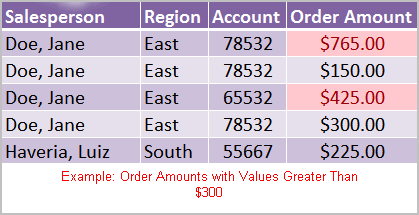
- Highlight cell rules: This rule highlights specific cells based on your option choice. For example, you can choose for Excel to highlight cells that are greater than, less than, or equal to a number, and between two numbers. Also, you can choose for Excel to highlight cells that contain specific text, including a specific date. If you choose this option, a dialog box will appear, and you will have to specify the cells to highlight and the color you would like to highlight the cells.
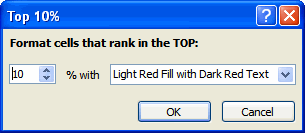
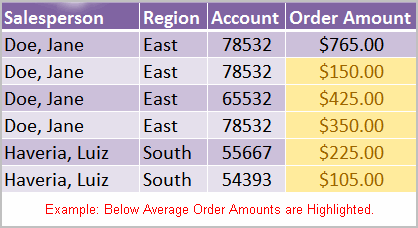
- Top/bottom rules: This conditional formatting option highlights cell values that meet specific criteria, such as top or bottom 10 percent, above average, and below average. If you choose this option, a dialog box will appear, and you will have to specify the cells to highlight and the color you would like to highlight the cells.
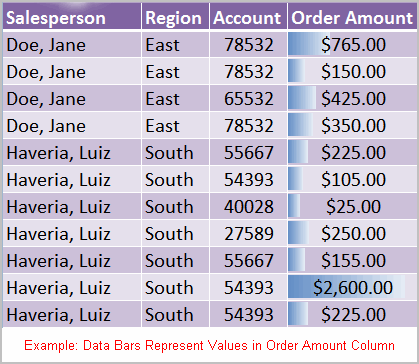
- Data bars: This is an interesting option that formats the selected cells with colored bars. The length of the data bar represents the value in the cell. The longer the bar, the higher the value.
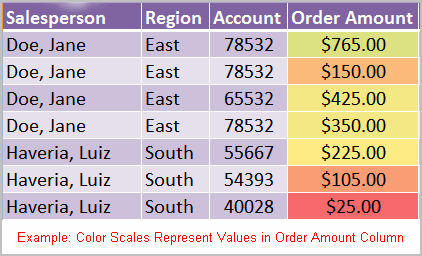
- Color scales: This option applies a two- or three-color gradient to the cells. Different shades and colors represent specific values.