Excel 2007
Creating Complex Formulas
What is an absolute reference?
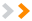
In earlier lessons, we saw how cell references in formulas automatically adjust to new locations when the formula is pasted into different cells. This is called a relative reference.
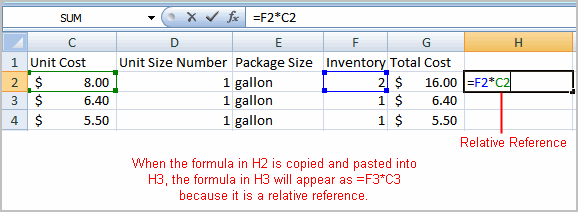
Sometimes when you copy and paste a formula, you don't want one or more cell references to change. An absolute reference solves this problem. Absolute cell references in a formula always refer to the same cell or cell range in a formula. If a formula is copied to a different location, the absolute reference remains the same.
An absolute reference is designated in the formula by the addition of a dollar sign ($). It can precede the column reference or the row reference, or both. Examples of absolute referencing include:

To create an absolute reference:
- Select the cell where you wish to write the formula (in this example, H2).
- Type the equals sign (=) to let Excel know a formula is being defined.
- Click on the first cell to be included in the formula (F2, for example).
- Enter a mathematical operator (use the multiplication symbol for this example).
- Click on the second cell in the formula (C2, for example).
- Add a $ sign before the C and a $ sign before the 2 to create an absolute reference.
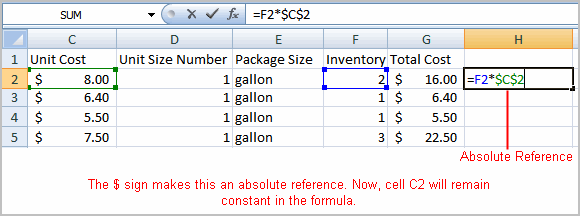
- Copy the formula into H3. The new formula should read =F3*$C$2. The F2 reference changed to F3 because it is a relative reference, but C2 remained constant because you created an absolute reference by inserting the dollar signs.
When writing a formula, you can press the F4 key on your keyboard to switch between relative and absolute cell references. This is an easy way to quickly insert an absolute reference.