Excel 2003
Identifying Basic Parts of the Excel Window
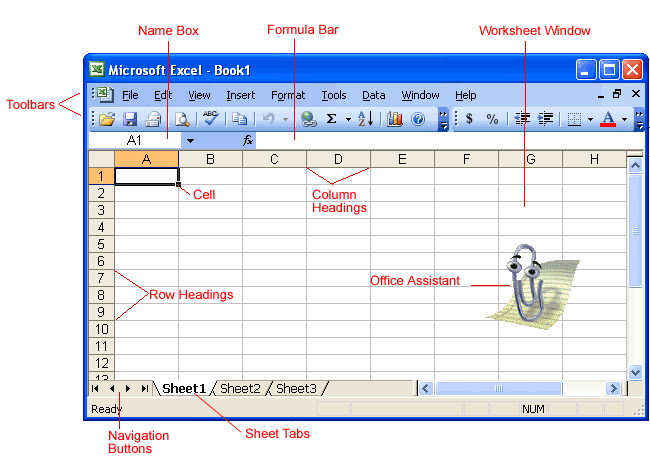
The Excel window
Many items you see on the Excel 2003 screen are standard in almost all other Microsoft software programs, including Word, PowerPoint, and previous versions of Excel. Some elements are specific to this version of Excel.
Workbook
Also called a spreadsheet, the workbook is a unique file created by Excel.
Title bar

The Title bar displays both the name of the application and the name of the spreadsheet.
Menu bar

The Menu bar displays all of the menus that are available for use in Excel 2003. The contents of any menu can be displayed by clicking on the menu name with the left mouse button.
Toolbar
Some commands in the menus have pictures or icons associated with them. These pictures may also appear as shortcuts in the toolbar.
![]()
Column headings

Each Excel spreadsheet contains 256 columns. Each column is named by a letter or combination of letters.
Row headings

Each spreadsheet contains 65,536 rows. Each row is named by a number.
Name Box
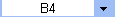
This shows the address of the current selection or active cell.
Formula bar

The Formula bar displays information entered—or being entered as you type—in the current or active cell. The contents of a cell can also be edited in the Formula bar.
Cell
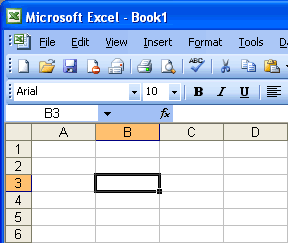
A cell is an intersection of a column and row. Each cell has a unique cell address. In the picture above, the cell address of the selected cell is B3. The heavy border around the selected cell is called the cell pointer.
Navigation buttons and sheet tabs
Navigation buttons allow you to move to another worksheet in an Excel workbook. They are used to display the first, previous, next, or last worksheets in a workbook.
Sheet tabs separate a workbook into specific worksheets. A workbook defaults to three worksheets. Each workbook must contain at least one worksheet.