Windows Basics
Understanding User Accounts
What are user accounts?
A user account allows you to sign in to your computer. By default, your computer already has one user account, which you were required to create when you set up your computer. If you plan to share your computer with others, you can create a separate user account for each person.
Why use separate user accounts?
At this point, you may be wondering, why do I even need to use separate user accounts? Wouldn't it be simpler for everyone just to have use the same account? Well, if you're sharing a computer with multiple people—for example, with your family or at the office—user accounts allow everyone to save their own files, preferences, and settings without affecting other computer users. When you start your computer, you'll be able to choose which account you want to use.

Administrator, Standard, and Managed accounts
Before you create new user accounts, it's important to understand the different types:
- Administrator: Administrator accounts are special accounts that are used for making changes to system settings or managing other people's accounts. They have full access to every setting on the computer. Every computer will have at least one Administrator account, and if you're the owner you should already have a password to this account.
- Standard: Standard accounts are the basic accounts you use for normal everyday tasks. As a Standard user, you can do just about anything you would need to do, such as running software or personalizing your desktop.
- Standard with Family Safety: These are the only accounts that can have parental controls. You can create a Standard account for each child, then go to the Family Safety settings in your Control Panel to set website restrictions, time limits, and more.
Generally, it's safer to be logged in to a Standard account than an Administrator account. If you're logged in as an Administrator, it may actually make it easier for an unauthorized user to make changes to your computer. Therefore, you may want to create a Standard account for yourself, even if you're not sharing the computer with anyone. You'll still be able to make Administrator-level changes; you'll just need to provide your Administrator password when making these changes.
Adding and managing user accounts
The process for adding and managing user accounts is quite different for each version of Windows. To learn more about adding and managing user accounts, check out the appropriate lesson from our different Windows tutorials below:
- Windows 8: Managing User Accounts and Parental Controls
- Windows 7: Managing User Accounts and Parental Controls
- Windows XP: Managing User Accounts
Switching between user accounts
If you have multiple user accounts on your computer, it's easy to switch between users without signing out or closing your current apps. Switching users will lock the current user, so you won't need to worry about someone else accessing your account.
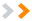
To switch between user accounts (Windows 8):
Click the current user in the upper-right of the Start screen, then select the desired user from the drop-down menu. The user will then need to enter a password to sign in.
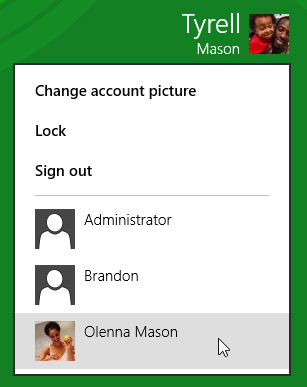
You can switch back by selecting the desired user from the drop-down menu. You'll need to re-enter your password to unlock the account.
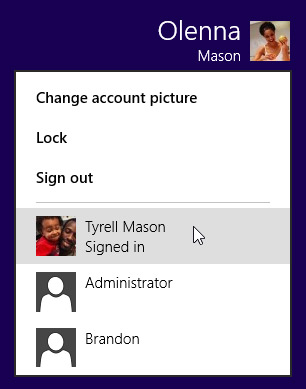
To switch between user accounts on Windows 7:
Click the Start button, click the arrow next to Shut Down, and select Switch user.
If you're finished using the computer, you can also choose to log off. This will allow other users to sign in to the computer with different accounts.