Internet Safety
Introduction to Internet Safety
Introduction

We all know we need to stay safe while using the Internet, but we may not know just how to do that. In the past, Internet safety was mostly about protecting your computer from viruses. But today, the Internet's vast reach, constantly changing technologies, and growing social nature have made users more vulnerable to identity theft, privacy violations, and even harassment.
This lesson will introduce you to the types of threats you may encounter while online. It will teach you basic strategies like how to Google yourself and create strong passwords, in addition to encouraging you to adopt a safer mindset toward using the Internet.
Adopting a safer mindset
When it comes to the Internet, people generally believe they are safer than they actually are. Why? Well, often the impersonal nature of technology can give us a false sense of security. After all, no one can physically attack us through a computer screen.
We tend to have an it-won't-happen-to-me attitude. We may even believe that our computer programs and the powers that be are automatically taking care of all that Internet security stuff for us. Sometimes we just avoid it all together because, to be frank, we just don't get it. Does this sound like you? Consider the following the questions:

- Have you ever Googled yourself to see what information can be found on you?
- Have you set your computer's security program to make sure you are getting regular updates?
- Do you have an external backup source for your computer?
- Are you enticed by emails or advertisements with special discount offers?
- When shopping online, do you check a website's security status before entering your billing information?
- Have you customized your privacy settings for your social networking accounts like Facebook, MySpace, and Skype?
Do these questions make you nervous? Don't worry, this tutorial is not meant to scold or scare you but instead to make you realize that there are precautions we should all be taking on a regular basis to maintain our personal safety and protect our computer while using the Internet.
Think of the Internet as you would a shopping mall

Generally, a mall is not considered a dangerous place. We go there to shop, run errands, and meet people, but we also take precautions while there. We wouldn't leave our car unlocked in the parking lot or walk around with our wallet hanging out of our purse. We wouldn't tell a sales clerk our Social Security Number or give our address to a stranger we just met.
The same applies when we are on the Internet. We need not fear our every mouse click, but we should take precautions to ensure our safety.
Understanding Internet threats
Before we can learn how to protect ourselves, we need to understand what the threats are on the Internet. Click the buttons in the interactive below to learn common Internet safety terms that pertain to our computers and identity theft.

Pharming
Pharming is a technique used to redirect a legitimate website's traffic to another illegitimate website in order to gain access to a user's personal information.
Mousetrapping
Mousetrapping keeps visitors from leaving a website by locking them into a window, opening multiple windows on the desktop, or relaunching their website in a window that can't be closed.
Hoax
A hoax is an email chain letter that warns of impending viruses and tries to scare users into forwarding and continuing the hoax email.
Browser Hijacking
Browser hijacking occurs when malware or spyware replaces your browser's home page with its own in order to force more hits to a particular website.
Clickjacking
Clickjacking is a technique that tricks users into clicking on a malicious link by adding the link to a transparent layer over what appears to be a legitimate web page.
Users think they are clicking on buttons or links in the legitimate page, when in reality they are clicking on the concealed links in the hidden page and often providing access to confidential information in the process.
Spyware
Spyware is a type of malware that collects information about users without their knowledge, often to track browsing habits and to create pop-up advertisements. Along with invading your privacy, it can sometimes interfere with a computer's functions.
Spyware is sometimes bundled with other software. Before downloading software, it's a good idea to read the reviews to see if it has a good reputation.
Spam
Spam is unsolicited email or junk mail. Sometimes, it comes from legitimate companies, but it can also be used for scams, phishing, and malware.

Malware
Malware is intentionally malicious software or code that is designed to damage your computer or collect information without your knowledge.
Viruses, Trojan horses, worms, spyware and keystroke-logging snoopware are all considered malware. Sometimes adware and freeware can be malicious.
Trojan Horse
A Trojan horse is a type of malware that appears to be benign or desirable and thus tricks the user into allowing the program access to their computer, usually through a download or email attachment.

Phishing
Phishing is mail or instant message scams that are disguised to look like official communications from a legitimate website. They fool users into providing sensitive information like passwords, credit card details, etc.

Virus
A virus is a self-replicating program that is designed to infect a computer by rapidly spreading from one file to another, sometimes causing great harm.
*Worms are similar, except they are usually spread over a network without human help.
For the latest Internet terms and text and chat acronyms, visit NetLingo.com.
Internet safety and privacy
In the past, Internet safety generally referred to threats to computer hardware or identity theft, but now with the Internet becoming more and more social, privacy has become a significant safety concern. Privacy violations can especially affect our mental and physical well-being, thus creating distress or harm from the following:
- Undesired advertisements that can be annoying
- Embarrassing or humiliating photos or videos
- Legal entanglements from libelous posts
- Cyber-harassment or cyber-stalking
- Identity theft
- Offline or real-world crimes
Understanding the lingo
Click the buttons in the interactive below to learn about Internet safety terms that relate to privacy and social networking.

Flame War
A flame war is a heated argument in a social media outlet such as a web forum, mailing list or chat room, in which intentionally insulting comments and personal attacks become a focus of conversation.
Dooced
If someone loses their job because of something they posted on a blog or social networking site, they have been dooced.
Troll
A troll is a person who posts comments just to get a rise out of people and cause a distraction.
Trolls might say something rude, assert incorrect information, or ask questions unrelated to the topic at hand. People who respond to obvious trolling posts are said to be feeding the trolls, which often causes the trolls to return and continue disrupting the discussion.
Avatar
An avatar is a virtual representation of yourself. The term usually refers to a virtual image.
Instead of using your picture on a social networking profile, you might use an avatar to protect your privacy.
![]()
Sockpuppet
A sockpuppet is a fake identify that someone creates and uses to deceive others for some kind of personal gain. On most websites it is possible to have more than one account, so it is easy to create sockpuppets.
For example, John could have a few online identities for the same chat service: John45, Sarah03, and HarmonicasRock12. When he is HarmonicasRock12, he might pretend to be a 30-year-old music enthusiast to find out what music stores you go to. And when he is Sarah03, he might pretend to be a 20-year old college student to find out where you went to college.
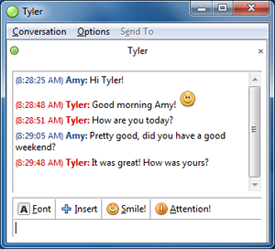
Chats
Chats are live, online conversations. You can chat with people in a chat room or by using an instant messaging service.
Unlike having a conversation with someone out loud, everything you write in your chat session can easily be saved and shared with others. Think before you press send!
Posts
Content that people publish on websites involving social media, such as blogs, newsgroups, and forums are called posts. Twitter calls the posts that users make to Twitter sites tweets.
Posts are available to everyone who has access to the site. You do not always have the option to change or delete your post once it is posted. It is an instantly public representation of you or your online identify. Think before you post!
Meme
Meme is something that has gone viral, or spread rapidly around the internet, such as a catchphrase, hoax, topic, concept or piece of media.
Memes are often cute, funny or curious and make you want to pass them on! If you are forwarding an email, just remember that everyone who gets that email in the future could have access to your email address.
Screen Name
A screen name, sometimes called a user name, is a virtual name that is used to identify users of a website where social media is a component. Your screen name can be your real name or a pseudonym.
On sites where you regularly interact with strangers, it is a good idea to choose a pseudonym. When choosing a descriptive pseudonym such as tennis247 or partyboy18, keep in mind the image it might protray and the response it will solicit.
Flamebait
A comment posted by someone trying to provoke a flame, or an angry response, is called flamebait.
If anyone responds to the comment, they are said to have taken the bait.
Googling yourself
Do you know how much anyone can quickly find out about you and your background just by conducting a simple web search? Most people don't know that personal records such as their address, phone number, and sometimes even pictures can be easily accessible to anyone online. While this information may not be harmful, in some situations you could put yourself at risk by not knowing what is out there. For instance, someone only needs to find out your home phone number, and they can find your address and directions to your house just by doing a simple online search. Google yourself regularly to find out which websites and public databases share information about you.
Make the most out of your search
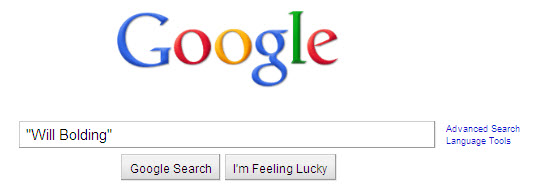
Enter search terms such as your name, email address, home and work address, and phone number in a variety of ways to get the most accurate and complete results. Also, putting quotes around your search terms tells the search engine to find a specific phrase just how you wrote it. This will make your search more efficient.
- First name and last name: "Will Bolding”
- First, middle, and last name: “Will Edward Bolding”
- Last name followed by a comma and then your first name: “Bolding, Will”
- Last name followed by a comma, your first name, and middle name: “Bolding, Will Edward”
- Street address: “2521 Street Address Lane”
- Phone number (using no spaces or hyphens searches all instances of your number): “9195554444”
- Email address: “boldingsoccer@email.com”
Removing your information from websites
You can ask a website to remove your information. Keep in mind that they are not always obligated to comply with your request. If the information posted about you is a direct threat to your safety and you need help negotiating with a website to remove the content, you can contact WiredSafety.org. They will be able to advise you on your specific case.
You can also pay an outside service like Reputation.com to remove your personal information online. For most people, this kind of service is unnecessary, but keep in mind that it is an option.


