Excel 2010
Using Conditional Formatting
Introduction
Imagine you have a spreadsheet with thousands of rows of data. It would be extremely difficult to see patterns and trends just from examining the raw data. Excel gives us several tools that will make this task easier. One of these tools is called conditional formatting. With conditional formatting, you can apply formatting to one or more cells based on the value of the cell. You can highlight interesting or unusual cell values, and visualize the data using formatting such as colors, icons, and data bars.
In this lesson, you will learn how to apply, modify, and remove conditional formatting rules.
Conditional formatting
Conditional formatting applies one or more rules to any cells you want. An example of a rule might be "If the value is greater than 5000, color the cell yellow." By applying this rule to the cells in a worksheet, you'll be able to see at a glance which cells are over 5000. There are also rules that can mark the top 10 items, all cells that are below the average, cells that are within a certain date range, and many more.
To create a conditional formatting rule:
- Select the cells you want to add formatting to.
- In the Home tab, click the Conditional Formatting command. A drop-down menu will appear.
- Select Highlight Cells Rules or Top/Bottom Rules. We will choose Highlight Cells Rules for this example. A menu will appear with several rules.
- Select the desired rule (Greater Than, for example).
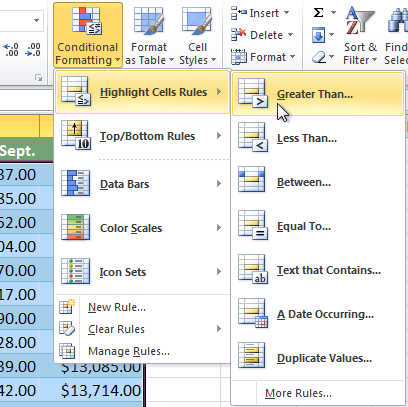 Selecting the Greater Than rule
Selecting the Greater Than rule - From the dialog box, enter a value in the space provided, if applicable. In this example, we want to format cells that are greater than $5000, so we'll enter 5000 as our value. If you want, you can enter a cell reference instead of a number.
- Select a formatting style from the drop-down menu.
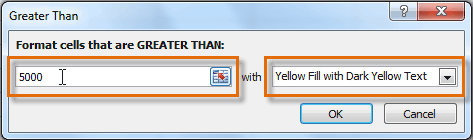 Entering a value and formatting style
Entering a value and formatting style - The formatting will be applied to the selected cells.
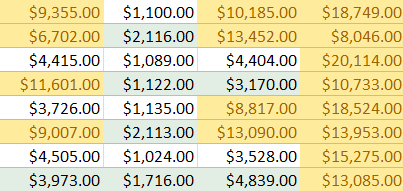 The formatted cells
The formatted cells
If you want, you can apply more than one rule to your cells.
Conditional formatting presets
Excel has a number of presets you can use to quickly apply conditional formatting to your cells. They are grouped into three categories:
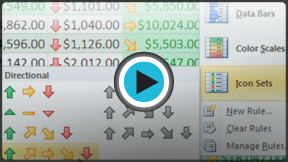
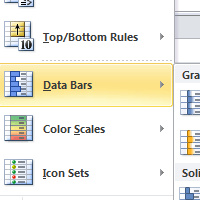
- Data Bars are horizontal bars added to each cell, much like a bar graph.
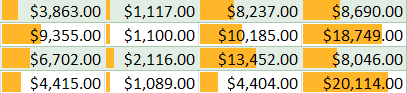 Data Bars
Data Bars - Color Scales change the color of each cell based on its value. Each color scale uses a two- or three-color gradient. For example, in the Green - Yellow - Red color scale, the highest values are green, the average values are yellow, and the lowest values are red.
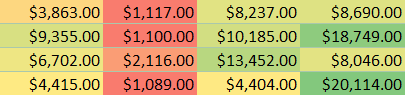 Color Scales
Color Scales - Icon Sets add a specific icon to each cell based on its value.
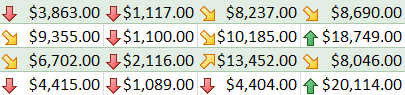 Icon Sets
Icon Sets
To use preset conditional formatting:
- Select the cells you want to add the formatting to.
- In the Home tab, click the Conditional Formatting command. A drop-down menu will appear.
- Select Data Bars, Color Scales, or Icon Sets (Data Bars, for example). Then select the desired preset.
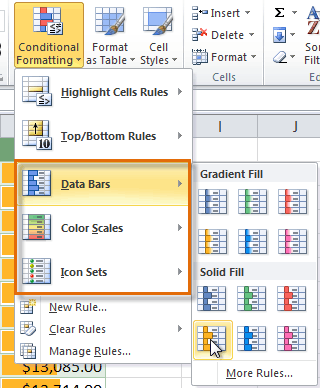 Selecting a formatting preset
Selecting a formatting preset - The conditional formatting will be applied to the selected cells.
 The finished Data Bars
The finished Data Bars
To remove conditional formatting rules:
- Select the cells that have conditional formatting.
- In the Home tab, click the Conditional Formatting command. A drop-down menu will appear.
- Select Clear Rules.
- A menu will appear. You can choose to clear rules from the Selected Cells, Entire Sheet, This Table, or This PivotTable. In this example, we will clear rules from the entire sheet.
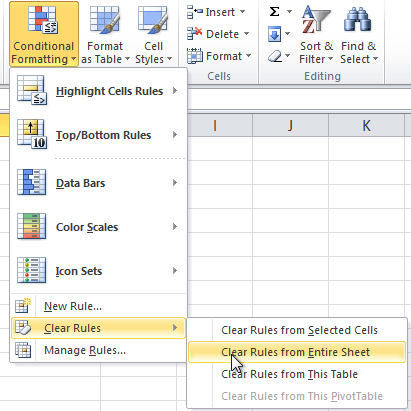 Clearing Rules
Clearing Rules
You can edit or delete individual rules by clicking on the Conditional Formatting command and selecting Manage Rules. This is especially useful if you have applied multiple rules to the cells.
Challenge!
- Open an existing Excel workbook. If you want, you can use this example.
- Apply conditional formatting to a range of cells with numerical values. If you are using the example, apply the formatting to all of the sales data.
- Apply a second conditional formatting rule to the same set of cells.
- Explore the Conditional Formatting Rules Manager dialog box.
- Clear all conditional formatting rules from the worksheet.