Excel 2000
Using Functions
Introduction
By the end of this lesson, learners should be able to:
- Use functions
Using Functions
Important Term:
- A function is a pre-defined formula that helps perform common mathematical functions.
Each function has a specific order, called syntax. Syntax must be followed for the function to work correctly.
Syntax Order:
- All functions begin with the = sign.
- After the = sign is the function name.
- One or more arguments enclosed in parentheses. If there is more than one argument, they are separated by commas.
An example of a function with one argument:
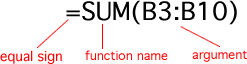
An example of a function with more than one argument:

Excel has hundreds of different functions (pre-defined formulas) to assist you with your calculations. As you know, building individual formulas can be difficult and time consuming. Using Excel's functions can save you a lot of time and headaches.
Excel's Different Functions
There are many different functions in Excel. For
our purposes in Excel 2000, we will discuss some common functions.
Statistical, including:
SUM - summation adds a range of cells together.
AVERAGE - average calculates the average of a range of cells.
COUNT - counts the number of chosen data in a range of cells.
MAX - identifies the largest number in a range of cells.
MIN - identifies the smallest number in a range of cells.
Financial, including:
Interest Rates
Loan Payments
Depreciation Amounts
Date and Time:
Day of Week
Year
Time
Date
![]() You
don't have to memorize the functions, but have an idea of what they will do
for you.
You
don't have to memorize the functions, but have an idea of what they will do
for you.
Accessing Functions
A common function, the Sum function is located on the Standard toolbar.
![]()
To use the Sum Function:
- If necessary, enter the numbers you want to calculate.
- Select the numbers you want to total.
- On the Standard toolbar, click the Sum button.
- Your total appears in the cell below the range you selected.
To Access Other Common Functions:
- Click the cell where you want the result of the function to appear.
- Type =
- On the Formula Bar, click the Edit Formula button.
- Choose a function from the Function Box drop-down list.
- The result of the function appears.
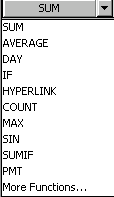
![]() If you didn't see the function you were looking for, there are other functions available through the Paste Function dialog box, explained below.
If you didn't see the function you were looking for, there are other functions available through the Paste Function dialog box, explained below.
Excel will not always tell you if your function contains an error, so it's up to you to check all of your functions. To learn how to do this, read the Double-Check Your Formulas lesson from our Excel Formulas tutorial.
To Access Other Available Functions:
- Click on the cell in which you want to place the end result.
- Type =.
- On the Formula Bar, in the Function Box drop down list, choose More Functions.
- The Paste Function dialog box opens. (Choosing Insert
 Functions or clicking the Paste Function button
Functions or clicking the Paste Function button 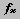 opens the Paste Function dialog box as well.)
opens the Paste Function dialog box as well.) - Notice the Function Categories available, including statistical, financial, and date and time.
- When a function category is selected, the corresponding function names display. Additional information about the function name displays in the lower part of the dialog box.
- Click OK.
If you're comfortable with basic functions, you may want to try a more advanced one like VLOOKUP. You can check out our article on How to Use Excel's VLOOKUP Function for more information. If you want to learn even more about functions, check out our Excel Formulas tutorial.
Challenge!
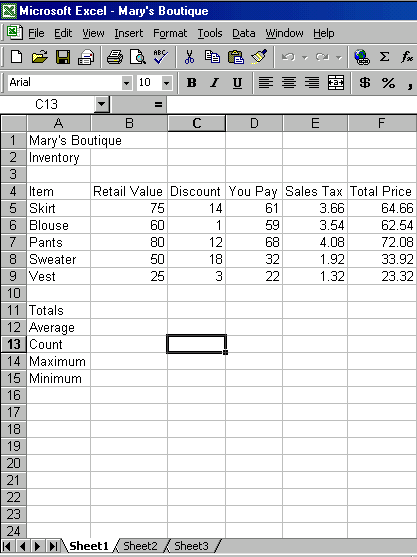
- In Excel, recreate the spreadsheet shown below.
- In cell address B11, enter the sum of the range B5:B9 using the Sum function.
- Copy the formula to the other columns (C11:F11), totaling columns C, D, E, and F.
- In cell address B12, enter the average of the range B5:B9 using the Edit Formula button.
- Copy the function to the other columns (C12:F12), averaging columns C, D, E, and F.
- Use the Paste Function button
 to enter the COUNT in cell B13. Copy the function
to the other columns (C13:F13).
to enter the COUNT in cell B13. Copy the function
to the other columns (C13:F13).