Computer Basics
Web Apps and the Cloud
What is the cloud?
You may have heard people using terms like the cloud, cloud computing, or cloud storage. But what exactly is the cloud? Basically, the cloud is the Internet—more specifically, it's all of the things you can access remotely over the Internet. When something is in the cloud, it means it's stored on servers on the Internet instead of on your computer. It lets you access your calendar, email, files, and more from any computer with an Internet connection.
Watch the video to learn about the cloud.
 The Cloud
The CloudIf you've ever used web-based email, then you've used the cloud—all of the emails in your inbox are stored on servers. However, there are many other services that use the cloud in different ways. Here are just a few examples:
- Dropbox is a cloud storage service that lets you easily store and share files with other people, and it lets you access your files from a mobile device as well.
- Evernote lets you type notes, clip webpages, take photos, and organize all of them from your computer or mobile device.
- Mozy and Carbonite can automatically back up your data in case your computer is lost, stolen, or damaged.
Why use the cloud?
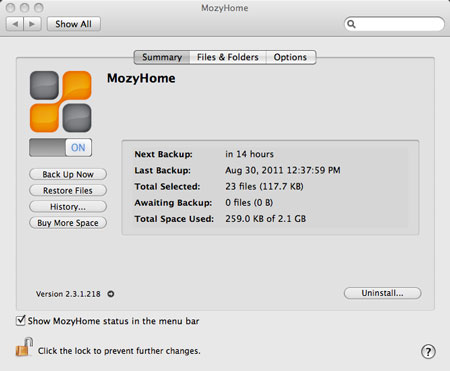 Using Mozy to back up files
Using Mozy to back up filesThere are many reasons to use the cloud, but the main reasons are convenience and reliability. In the past, if you wanted to bring a file with you, you would have to save it to a USB flash drive, external hard drive, or CD-R disc. Saving a file to the cloud ensures that you'll be able to access it with any computer that has an Internet connection, so you don't have any physical media to keep track of. The cloud also makes it much easier to share a file with coworkers or friends, making it possible to collaborate over the Web.
With the cloud, you're much less likely to lose your data because it is stored on servers. However, just like anything online, there is always a risk that someone may try to gain access to your personal data, so it's important to choose a strong password and pay attention to any privacy settings for the service you're using.
What is a web app?
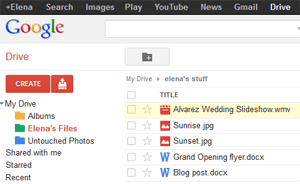 Google Drive
Google DrivePreviously, we talked about how desktop applications allow you to perform tasks on your computer. However, there are also web applications (or web apps), which run in the cloud and do not need to be installed on your computer. These are sometimes called cloud apps.
Examples of web apps
Here are a few examples of web apps:
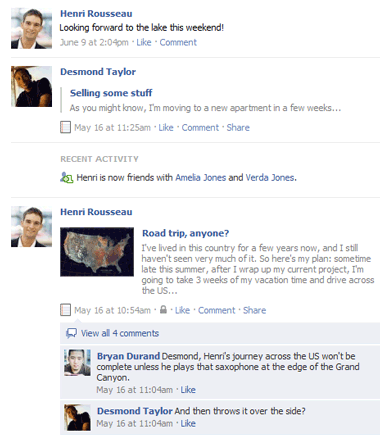 Facebook
Facebook- Online email services: Services like Gmail and Yahoo! Mail run within your browser and can do many of the same things email programs like Microsoft Outlook can do. After you sign up for an online email service, you can begin using it immediately—no installation is required. Instead of being stored on your computer, your emails are stored in the cloud.
- Google Docs: Google Docs is an office suite that runs within your browser. Much like Microsoft Office, you can use it to create documents, spreadsheets, presentations, and more. Your documents are stored in the cloud, which makes it easy to share them with other people.
- Facebook: Facebook lets you create an online profile and interact with your friends. Profiles and conversations are constantly evolving, so Facebook uses web app technologies throughout the site to keep the information up-to-date. There are also games and other web apps you can add to your Facebook profile.
Web apps are becoming more and more integrated with websites, and it may be difficult to distinguish between a web application and a "regular" website. In many cases, you may be using a web application without even knowing it!
How do web apps work?
When you use a web app, you are working from your computer or mobile device, but much of the actual processing is done by a network of servers. These servers can pool all of their processing power in order to handle requests from all over the world. They also use specialized servers to store the data you're working with, as well as the data from all other users. All of this happens very seamlessly, so it looks almost like the application is running on your computer.
For example, if you open a document with Google Docs, your web browser will communicate with the network of servers to display your document. As you edit the document, your browser will work closely with the servers to make sure everything is kept up-to-date.
 Google Docs
Google DocsChallenge!
- Do you already use the cloud for things like web-based email?
- What are some other ways you could use the cloud?
- How is a web app different from a desktop application?



